Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE Class-10 Concise Physics Selina Solutions Chapter-10. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exercise-10(A), MCQs-10(A), Exercise-10(B), MCQ-10(B), Exercise-10(C), MCQ-10(C) and Numericals-10(C) Questions of Exercise-10 Electro-Magnetism ICSE Class-10 Concise Class-10 . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Physics |
| Class | 10th |
| Chapter-10 | Electro-Magnetism (Exercise-10C) |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise-10(A), MCQs-10(A), Exercise-10(B), MCQ-10(B), Exercise-10(C), MCQ-10(C) and Num-10(C) |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE Class-10 Concise Physics Selina Solutions Chapter-10.
-: Select Exercise :-
Exercise-10(A), MCQs-10(A), Exercise-10(B), MCQ-10(B),
Exercise-10(C), MCQ-10(C) and Numericals -10(C)
Note:- Read the chapter Electro-Magnetism carefully and then solve All the example given in your text book before starting Solution of Chapter – 10 Electro-Magnetism exercise. Do not forget using keyword in your answer in exam of council.
Selina Physics Solution Electro-Magnetism For ICSE Class 10th Exe-10(C)
Page 258
Question 1
(a) What is the electromagnetic induction?
(b) Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Answer 1
(a) Electromagnetic induction: whenever there is change in number of magnetic field lines associated with conductor, an electromotive force is developed between the ends of the conductor which lasts as long as the change is taking place.
(b) Demonstration of the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction:
In the figure:
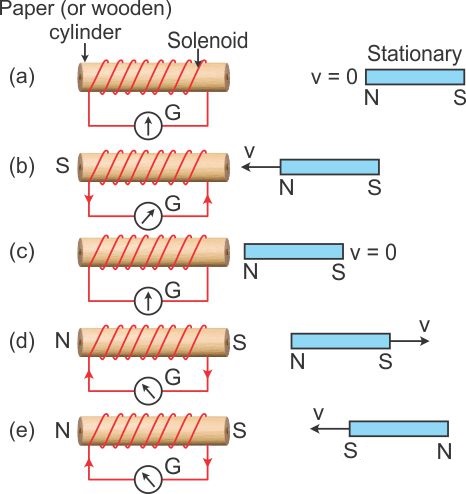
(i)When the magnet is stationary there is no deflection in galvanometer. The pointer read zero. [Fig. (a)]
(ii)when the magnet with north pole facing the solenoid is moved towards the solenoid, the galvanometer shows a deflection towards the right showing that a current flows in the solenoid in the direction as shown in [Fig (b)]
(iii) As the motion of magnet stops, the pointer of the galvanometer comes to the zero position [Fig (c)]. This shows that the current in the solenoid flows as long as the magnet is moving.
(iv)If the magnet is moved away from the solenoid, the current again flows in the solenoid, but now in a direction opposite to that shown in [Fig. (b)] and therefore the pointer of the galvanometer deflects towards left[ Fig. (d)].
(v)If the magnet is moved away rapidly i.e. with more velocity, the extent of deflection in the galvanometer increases although the direction of deflection remains the same. It shows that more current flows now.
(vi)If the polarity of the magnet is reversed and then the magnet is brought towards the solenoid, the current in solenoid flows in the direction opposite to that shown in Fig (b) and so the pointer of galvanometer deflect towards left [Fig. (e)].
Question 2
State Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
Answer 2
Faraday’s formulated two laws of electromagnetic induction:
(i) Whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a coil, an e.m.f. is induced. The induced e.m.f. lasts so long as there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil.
(ii) The magnitude of the e.m.f. induced is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux linked with the coil. If the rate of change of magnetic flux remains uniform, a steady e.m.f. is induced.
Question 3 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
State two factor on which the magnitude of induced e.m.f in a coil depend.
Answer 3
Magnitude of induced e.m.f depend upon:
(i)The change in the magnetic flux.
(ii)The time in which the magnetic flux changes
Question 4
(a)What kind of the energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
(b)Name the phenomenon.
Answer 4
(a) Mechanical energy changes to the electrical energy.
(b) Phenomenon is called electromagnetic induction.
Question 5 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
(a) How would you demonstrate that a momentary current can be obtained by the suitable use of a magnet, a coil of wire and a galvanometer?
(b)What is the source of energy associated with the current obtained in part (a)?
Answer 5
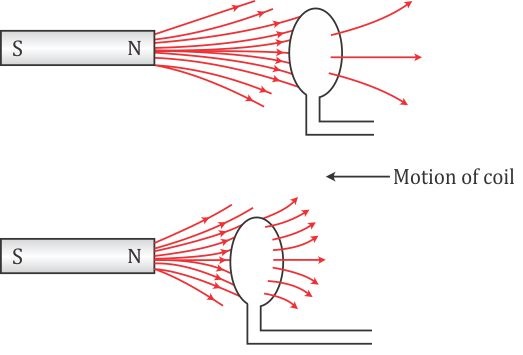
(a)When there is a relative motion between the coil and the magnet, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. If the north pole of the magnet is moved towards the coil, the magnetic flux through the coil increases as shown in above figure. Due to change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil, an e.m.f. is induced in the coil. This e.m.f. causes a current to flow in the coil if the circuit of the coil is closed.
(b)The source of energy associated with the current obtained in part (a) is mechanical energy.
Question 6
(a)Describe briefly one way of producing an induced e.m.f.
(b)State one factor that determines the magnitude of induced e.m.f.
(c)What factor determines the direction of induced e.m.f.?
Answer 6
(a)
Induced current can be produced by following activity:

(i) When the magnet is stationary there is no deflection in galvanometer. The pointer read zero. [Fig (a)]
(ii) and When the magnet with north pole facing the solenoid is moved towards the solenoid, the galvanometer shows a deflection towards the right showing that a current flows in the solenoid in the direction as shown in Fig (b)
(iii) As the motion of magnet stops, the pointer of the galvanometer to the zero position [Fig (c)]. This shows that the current in the solenoid flows as long as the magnet is moving.
(iv) If the magnet is moved away from the solenoid , the current again flows in the solenoid , but now in the direction opposite to that shown in [Fig. (b)] and therefore the pointer of the galvanometer deflects towards left [Fig. (d)].
(v) whenever If the magnet is moved away rapidly i.e. with more velocity, the extent of deflection in the galvanometer increases although the direction of deflection remains the same. It shows that more current flows now.
(vi) the polarity of the magnet is reversed and then the magnet is brought towards the solenoid, the current in solenoid flows in the direction opposite to that shown in Fig (b) and so the pointer of galvanometer deflect towards left [Fig. (e)].
(b)
Magnitude of induced e.m.f depend upon:
(i)The change in the magnetic flux.
(ii)The time in which the magnetic flux changes.
(c) The direction of induced e.m.f depends on whether there is an increase or decrease in the magnetic flux.
Question 7 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
Complete the following sentences:
The current induced in a closed circuit only if there is ________.
Answer 7
The current induced in a closed circuit only if there is relative motion between magnet and coil
Question 8
In which of the following cases e.m.f. is induction?
(i)A current is started in a wire held near a loop of wire.
(ii)The current is switched off in a wire held near a loop of wire.
(iii)A magnet is moved through a loop of wire.
(iv)A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
Answer 8
(i)Yes.
(ii)Yes.
(iii)Yes.
(iv)No.
Question 9
A conductor is moving in a varying magnetic field. Name the law which determines the direction of current induced in the conductor.
Answer 9
Fleming’s right hand rule determines the direction of current induced in the conductor.
Question 10 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
State Fleming’s right hand rule.
Answer 10
Fleming’s right hand rule: Stretch the forefinger, middle finger and the thumb of your right hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic field and the thumb will indicates the direction of motion of conductor, then the middle finger indicates the direction of induced current.
Question 11
What is Lenz’s law?
Answer 11
Lenz’s law: It states that the direction of induced e.m.f. (or induced current) is such that it always tends to oppose the cause which produces it.
Question 12
Why does it more difficult to move a magnet towards a coil when the number of turns in the coil has been increased?
Answer 12
When a coil has a large number of turns, then magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the coil become more and then by Lenz’s law it will oppose more.
Question 13 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
Explain why an induced current must flow in such a direction so as to oppose the change producing it.
Answer 13
So that the mechanical energy spent in producing the change, is transformed into the electrical energy in form of induced current.
Question 14
Explain how does the Lenz’s law to show the conservation of energy in electromagnetic induction.
Answer 14
Lenz’s law implies the law of conservation of energy. It shows that the mechanical energy spent in doing work, against the opposing force experienced by the moving magnet, is transformed into the electrical energy due to which current flows in the solenoid.
Question 15
The diagram in shows a coil of several turns of copper wire near a magnet NS. The coil is moved in the direction of arrow shown in the diagram.

(i) In what direction does the induced current flow in the coil?
(ii) Name the law used to arrive at the conclusion in part (i).
(iii) How would the current in coil be altered if
(a) the coil has twice the number of turns,
(b) the coil was made to move three times fast?
Answer 15
(i) When the coil is moved in the direction of magnet the North pole generates near this end and current starts flowing from A to B.
(ii) Lenz’s law.
(iii) (a)Current is directly proportional to the number of turns, therefore it will also become 2 times
(b) Current becomes thrice.
Page 259
Question 16
The diagram in fig . 10.43 shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
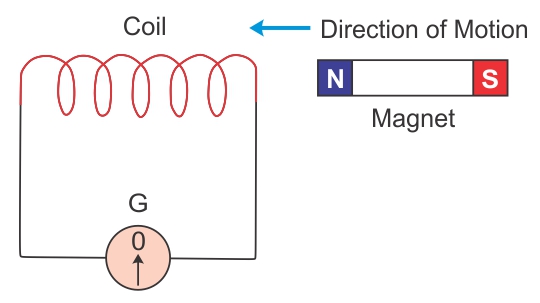
(a)Describe the observation in the galvanometer if (i) the magnet is moved rapidly, (ii) the magnet is kept stationary after it has move into the coil, (iii) the magnet is then rapidly pulled out of the coil.
(b) How would the observation in (i)of a part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Answer 16
(i)The pointer of galvanometer deflects towards left. The deflection lasts so long as the coil moves.
(ii)(a) Deflection becomes twice (b) Deflection becomes thrice.
Question 17
Name and state the principle of a simple a.c. generator. What is its use?
Answer 17
An A.C. generator works on the principle of ‘electromagnetic induction’.
Statement: Whenever a coil is rotated in a magnetic field, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes, and therefore, an EMF is induced between the ends of the coil. Thus, a generator acts like a source of current if an external circuit containing load is connected between the ends of its coil.
Question 18
What determines the frequency of a.c. produced in a generator?
Answer 18
The number of rotations of the coil in one second or the speed of rotation of the coil.
Question 19 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
Complete the sentence:
An a.c. generator changes the ___________ energy to ___________ energy.
Answer 19
Mechanical, Electrical
Question 20
Draw a labelled diagram of a simple a.c generator.
Answer 20
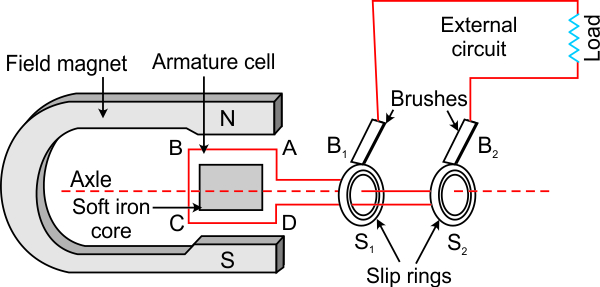
Question 21
In an a.c generator the speed at which the coil rotates is doubled. How would this affect
(a)the frequency of output voltage
(b)the maximum output voltage.
Answer 21
(a)In an a.c generator, if the speed at which the coil rotates is doubled, the frequency is also doubled.
(b) Maximum output voltage is also doubled.
Question 22
State two ways to produce a higher e.m.f. in an a.c generator.
Answer 22
Two ways in an a.c generator to produce a higher e.m.f. are:
(1)By increasing the speed of rotation of the coil.
(2)By increasing the number of turns of coil.
Question 23
What energy conversion does take place in a generator when it is in use?
Answer 23
Mechanical energy changes into the electrical energy.
Question 24
State (i) two dis-similarities, and (ii) two similarity between a D.C. motor and an A.C. generator.
Answer 24
Two dissimilarities between D.C. motor and A.C. generator:
| A.C. Generator | D.C. Motor |
| 1. A generator is a device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. | 1. A D.C. motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy |
| 2. A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. | 2. A D.C. works on the principle of force acting on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. |
Similarity: Both in A.C generator and D.C motor, a coil rotates in a magnetic field between the pole pieces of a powerful electromagnet.
Question 25
State one advantage of using a.c. over the d.c.
Answer 25
The voltage of a.c. can be stepped up by the use of step-up transformer at the power generating station before transmitting it over long distances. It reduces the loss of electrical energy as heat in the transmission line wires. On the other hand, if d.c. is generated at the power generating station, its voltage cannot be increased for transmission, and so due to passage of high current in the transmission line wires, there will be a huge loss of electrical energy as heat in the line wires.
Question 26
For what purpose are the transformers used? On which type of current do transformers work ?
Answer 26
The purpose of the transformer is to step up or step down the a.c. voltage.
A.C. current.
Question 27
State two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coils of a transformer depends.
Answer 27
The magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil of a transformer depends on the following two factors.
a)The ratio of number of turns in the secondary coil to the number of turns in the primary coil.
b)The magnitude emf applied in the primary coil.
Question 28 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
How an e.m.f. in the primary and secondary coils of a transformer related with the number of turns in these coils?
Answer 28
The relation is following:
![]()
S stands for secondary and P stands for primary.
Question 29
Draw a labelled diagram to show the various components of a step up transformer.
Answer 29
Step up transformer:
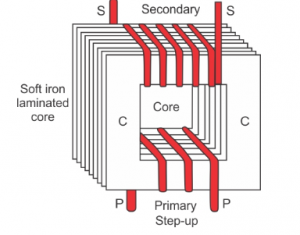
Question 30
Name the device used to transform 12 V a.c. to 200 V a.c. Name the principle on which it works.
Answer 30
The device is step up transformer.
It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Question 31
Draw a labelled diagram of a step-up transformer and explain how does it works. State two characteristics of the primary coil as compared to its secondary coil.
Answer 31
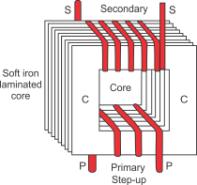
Step-up transformer: The step-up transformer is used to change a low voltage alternating e.m.f. to a high voltage alternating e.m.f. of same frequency.
Working: When the terminals of primary coil are connected to the source of alternating e.m.f., a varying current flows through it which also produces a varying magnetic field in the core of the transformer. Thus, the magnetic field lines linked with the secondary coil vary and induce an e.m.f. in the secondary coil. The induced e.m.f. varies in the same manner as the applied e.m.f. in the primary coil varies, and thus, has the same frequency as that of the applied e.m.f.
The magnitude of e.m.f. induced in the secondary coil depends on the ‘turns ratio’ and the magnitude of the applied e.m.f.
For a transformer,
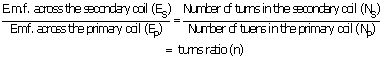
Two characteristics of the primary coil as compared to its secondary coil:
- The number of turns in the primary coil is less than the number of turns in the secondary coil.
- A thicker wire is used in the primary coil as compared to that in the secondary coil.
Question 32 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
Draw a labelled diagram of a device you would use to transform 200 V a.c to 15 V a.c. Name the device and explains how it works. Give its two uses.
Answer 32
The device is step down transformer.

Working: In a step down transformer, the number of turns in secondary coil are less than the number of turns in the primary coil i.e., turns ratio nS/NP<1.
As Es/Ep = NS/NP.
So Es/Eps is less than Ep.
Two uses of step down transformer are:
(i)With electric bells
(ii)At the power sub-stations to step-down the voltage before its distribution to the customers.
Question 33
Name the coil of which the wire is thicker in a (i) step up, (ii) step down transformer. Give reason to your answer.
Answer 33
(i) In case of a step-up transformer, thicker wire is used in the primary coil as compared to that in the secondary coil.
(ii) In a step-down transformer, the wire in the secondary coil is thicker than in the primary coil.
The use of thicker wire reduces its resistance and therefore reduces the loss of energy as heat in the coil. In step up NS > NP therefore ES > EP, but Is < IP i.e., more current flows in the primary coil. The reverse is the case of a step-down transformer. Thus, the thickness of the wire is chosen accordingly.
Question 34
(a)Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labelled A and B.
(b)Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram in part (a).
(c) What is the material of this part named above ?
(d)Is the transformer a step-up or step-down? Give reasons.
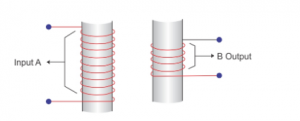
Answer 34
A is the primary coil. B is the secondary coil.
We have drawn laminated core in the diagram.
The material of this part is soft iron.
This transformer a step-down transformer because the number of turns in primary coil is much greater than that in the secondary coil.
Page 260
Question 35 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
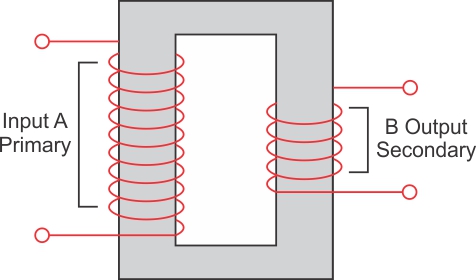
The diagram shows the core of a transformer and its input and output connections.
(a) State the material used for the core and describe its structure.
(b)Complete the diagram of the transformer and connections by labelling all the parts joined by you
(c) Name the transformer: step up or step down?
Answer 35
(a) Soft iron core is used. The core is made up from the thin laminated sheets of soft iron of T and U shape, placed alternately one above the other and insulated from each other by paint or varnish coating over them.
(b)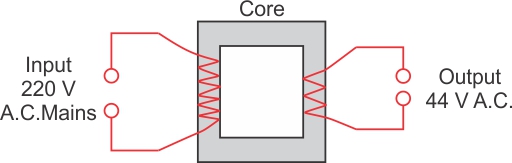
(c) It is a step down transformer.
Question 36
The out put current of a transformer in which the voltage is stepped down are usually higher than the input current. Explain why?
Answer 36
The secondary win dings of a transformer in which the voltage is stepped down are usually made up of thicker than the primary because more current flows in the secondary coil. The use of thicker wire reduces its resistance and therefore the loss of energy as heat in the coil.
Question 37
Why is the iron core of a transformer made is laminated instead of being in one solid piece?
Answer 37
To reduce the energy losses due to eddy currents.
Question 38
Complete the following sentences:
(i)In a step-up transformer, the number of turns in the primary is _______ than the number of turns in the secondary.
(ii)The transformer is used in _______ current circuits.
(iii)In a transformer, the frequency of A.C. voltage ________. (increase / decreases / remains same)
Answer 38
(i)In a step-up transformer, the number of turns in the primary is less than the number of turns in the secondary.
(ii)The transformer is used in alternating current circuits.
(iii)In a transformer, the frequency of A.C. voltage remain same.
Question 39
How do the input and output powers in a transformer compare? State the assumption made?
Answer 39
A transformer is a device by which the amplitude of an alternating e.m.f. can be increased or decreased.
For an ideal transformer , when there is no loss of energy , the output power is equal to input power i.e.,
Power in secondary coil = power in primary coil
![]()
Question 40 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
Name two kinds of energy losses in a transformer. How is it minimized?
Answer 40
The energy loss in a transformer is called ‘copper loss’.
Copper losses: Primary and secondary coils of a transformer are generally made of copper wire. These copper wires have resistance. When current flows through these wires, a part of the energy is lost in the form of heat. This energy lost through the windings of the transformer is known as copper loss.
This loss can be minimized by using thick wires for the windings. Use of thick wire reduces its resistance and therefore reduces the loss of energy as heat in the coil.
- Loss due to eddy current.It can be minimised by using laminated core.
Question 41
Give two points of difference between a step up transformer and a step down transformer.
Answer 41
| Step up transformer | Step down transformer |
| It increases the a.c. voltage and decrease the current. | It decreases the a.c. voltage and increase the current. |
| The wire of primary coil is thicker than that in the secondary coil. | The wire in the secondary coil is thicker than that in the primary coil. |
Question 42
Name the material of core in (a) electric bell, (b) electromagnet, (c) d.c. motor, (d) an a.c. generator and (e) transformer.
Answer 42
Soft iron is used in all.
Question 43
Name the transformer used in the (i) power generating station, (ii) power sub-station.
State the function of each transformer.
Answer 43
(i) Step-up transformer.
In power generating stations the alternating current generated is first stepped up from 11 kV to 132 kV.
(ii) Step-down transformer.
At the power sub-station, voltage is stepped down before its distribution to the consumers.
Transformers are used so as to reduce the loss of energy in the form of heat in the line wires used for transmission.
Selina Physics Solution Electro-Magnetism ICSE Class-10
Exercise – 10 (C) “Multiple Choice Type “
Page 260
Question 1
The direction of induced current is obtained by :
(a) Fleming’s left hand rule
(b) Clock rule
(c) Right hand thumb rule
(d) Fleming’s right hand rule
Answer 1
Fleming’s right hand rule
Statement: According to Fleming’s right hand rule, if we stretch the thumb, middle finger and forefinger of our right hand mutually perpendicular to each other such that the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic field and thumb indicates the direction of motion of conductor, then the middle finger will indicate the direction of induced current.
Question 2 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
In a step-up transformer :
(a) Ns = Np
(b) Ns < Np
(c) Ns > Np
(d) nothing can be said
Answer 2
![]()
Hint: Since a step-up transformer is used to change a low voltage alternating e.m.f. to a high voltage alternating e.m.f. of same frequency, the number of turns in the secondary coil is more than the number of turns in the primary coil, i.e. .
![]()
Selina Physics Solution Electro-Magnetism For ICSE Class 10th
Exercise – 10 (C) , Numericals
Page 260
Question 1
The magnetic flux through a coil having 100 turns decreases from 5 milli weber to zero in 5 second. Calculate the e.m.f. induced in the coil
Answer 1
Given that:
Decrease in the flux = 0.005 – 0 = 0.005 weber,
Number of tuns = 100 turns and
Time = 5 second
e.m.f. induced e = N × Rate of increase of magnetic flux
——————= ![]()
∴ e.m.f. induced e = 0.1 V = 100 mV
Question 2
A primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V a.c supply. What will be the output voltage?
Answer 2
No. of turns in primary coil Np =800
No. of turns in secondary coil Np=8.
Input supply voltage Ep = 220 V.
We know that
![]()
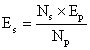 =
= ![]()
Es =2.2 V.
Question 3
A transformer is designed to give a supply of 8 V to ring a house bell from the 240 V a.c mains. The primary coil has 4800 turns. How many turns will be in the secondary coil?
Answer 3
Input ac voltage Ep = 240 V.
Number of turns in primary coil Np = 4800
No. of turns in secondary coil Ns=?
Output voltage Es = 8 V.
We know that
![]()
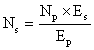 =
= ![]()
Number of turns in secondary coil = 160.
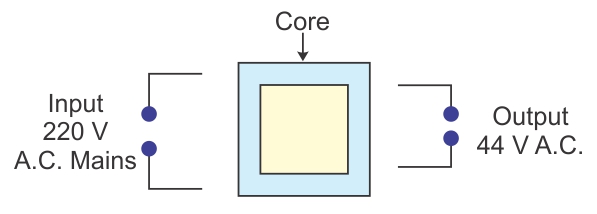
Question 4 (Exe-10C Electro-Magnetism ICSE )
The input and output voltages of a transformer are 220 V and 44V respectively. Find
(a)the turns ratio
(b)the current in input circuit if the output current is 2 A.
Answer 4
(a)We know that
![]()
So turns ratio
![]() =
=![]()
(b)Output current Is= 2A, Es =44V.
Input current Ip =?,Ep =220 V.
We know that =Es Is =EpIp
Ip =![]()
Return to Concise Selina ICSE Physics Class-10
Thanks