ML Aggarwal Rectilinear Figures Exe-13.2 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-13. Step by Step Solutions of Exercise-13.2 Rectilinear Figures of ML Aggarwal for ICSE Class 9th Mathematics Questions. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
ML Aggarwal Rectilinear Figures Exe-13.2 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-13 | Rectilinear Figures |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-13.2 Questions |
| Academic Session | 2024-2025 |
Rectilinear Figures
ML Aggarwal Rectilinear Figures Exe-13.2 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-13
Question 1. Using ruler and compasses only, construct the quadrilateral ABCD in which ∠ BAD = 45°, AD = AB = 6cm, BC = 3.6cm, CD = 5cm. Measure ∠ BCD.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 6cm
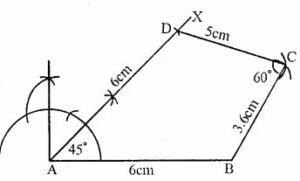
(ii) At A, draw a ray AX making an angle of 45o and cut off AD = 6cm
(iii) With centre B and radius 3.6 cm and with centre D and radius 5 cm, draw two arcs intersecting each other at C.
(iv) Join BC and DC.
ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
On measuring ∠BCD, it is 60o
Question 2. Draw a quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 6cm, BC = 4cm, CD = 4 cm and ∠ ABC = ∠ BCD = 90°
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm
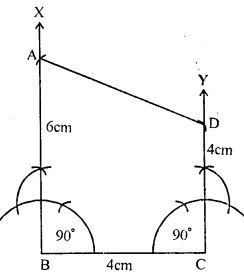
(ii) At B and C draw rays BX and CY making an angle of 90o each
(iii) From BX, cut off BA = 6 cm and from CY, cut off CD = 4cm
(iv) Join AD.
ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 3. Using ruler and compasses only, construct the quadrilateral ABCD given that AB = 5 cm, BC = 2.5 cm, CD = 6 cm, ∠BAD = 90° and the diagonal AC = 5.5 cm.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 5cm
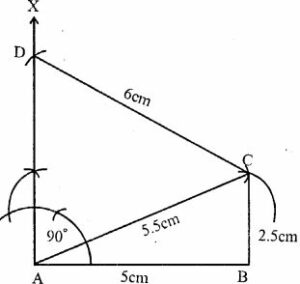
(ii) With centre A and radius 5.5cm and with centre B and radius 2.5cm draw arcs which intersect each other at C.
(iii) Join AC and BC.
(iv) At A, draw a ray AX making an angle of 90o.
(v) With centre C and radius 6cm, draw an arc intersecting AX at D
(vi) Join CD.
ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 4. Construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3.3 cm, BC = 4.9 cm, CD = 5.8 cm, DA = 4 cm and BD = 5.3 cm.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 3.3cm
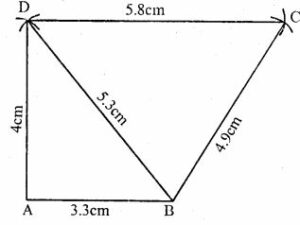
(ii) with centre A and radius 4cm, and with centre B and radius 5.3cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at D.
(iii) Join AD and BD.
(iv) With centre B and radius 4.9 cm and with centre D and radius 5.8cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at C.
(v) Join BC and DC.
ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 5. Construct a trapezium ABCD in which AD || BC, AB = CD = 3 cm, BC = 5.2cm and AD = 4 cm
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 5.2cm
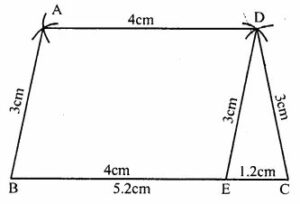
(ii) From BC, cut off BE = AD = 4cm
(iii) With centre E and C, and radius 3 cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at D.
(iv) Join ED and CD.
(v) With centre D and radius 4cm and with centre B and radius 3cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at A.
(vi) Join BA and DA
ABCD is the required trapezium.
Question 6. Construct a trapezium ABCD in which AD || BC, ∠B= 60°, AB = 5 cm. BC = 6.2 cm and CD = 4.8 cm.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 6.2cm
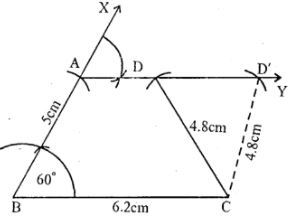
(ii) At B, draw a ray BX making an angle of 60o and cut off AB = 5cm
(iii) From A, draw a line AY parallel to BC.
(iv) With centre C and radius 4.8cm, draw an arc which intersects AY at D and D’.
(v) Join CD and CD’
ABCD and ABCD’ are the required two trapeziums.
Question 7. Using ruler and compasses only, construct a parallelogram ABCD with AB = 5.1 cm, BC = 7 cm and ∠ABC = 75°.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 7cm
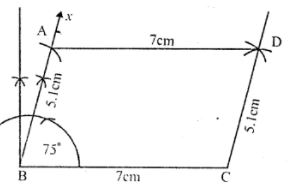
(ii) A to B, draw a ray Bx making an angle of 75o and cut off AB = 5.1cm
(iii) With centre A and radius 7cm with centre C and radius 5.1cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at D.
(iv) Join AD and CD.
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
Question 8. Using ruler and compasses only, construct a parallelogram ABCD in which AB = 4.6 cm, BC = 3.2 cm and AC = 6.1 cm.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 4.6cm
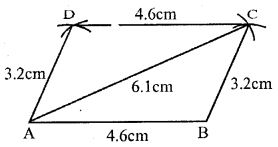
(ii) With centre A and radius 6.1cm and with centre B and radius 3.2cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at C.
(iii) Join AC and BC.
(iv) Again, with centre A and radius 3.2cm and with centre C and radius 4.6cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at C.
(v) Join AD and CD.
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
Question 9. Using ruler and compasses, construct a parallelogram ABCD give that AB = 4 cm, AC = 10 cm, BD = 6 cm. Measure BC.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Construct triangle OAB such that
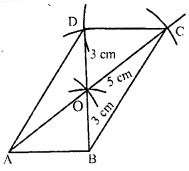
OA = ½ x AC = ½ x 10cm = 5cm
OB = ½ x BD = ½ x 6cm = 3cm
As, diagonals of || gm bisect each other and AB = 4cm
(ii) Produce AO to C such that OA = OC = 5cm
(iii) Produce BO to D such that OB = OD = 3cm
(iv) Join AD, BC and CD
ABCD is the required parallelogram
(v) Measure BC which is equal to 7.2cm
Question 10. Using ruler and compasses only, construct a parallelogram ABCD such that BC = 4 cm, diagonal AC = 8.6 cm and diagonal BD = 4.4 cm. Measure the side AB.
Answer :
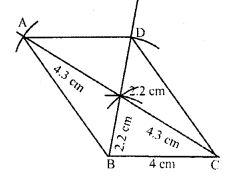
Construction:
(i) Construct triangle OBC such that
OB = ½ x BD = ½ x 4.4cm = 2.2cm
OC = ½ x AC = ½ x 8.6cm = 4.3cm
Since, diagonals of || gm bisect each other and BC = 4cm
(ii) Produce BO to D such that BO = OD = 2.2cm
(iii) Produce CO to A such that CO = OA = 4.3cm
(iv) Join AB, AD and CD
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
(v) Measure the side AB, AB = 5.6cm
Question 11. Use ruler and compasses to construct a parallelogram with diagonals 6 cm and 8 cm in length having given the acute angle between them is 60°. Measure one of the longer sides.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw AC = 6cm
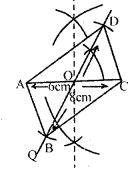
(ii) Find the mid-point O of AC. [Since, diagonals of || gm bisect each other]
(iii) Draw line POQ such that POC = 60o and OB = OD = ½ BD = ½ x 8cm = 4cm
So, from OP cut OD = 4cm and from OQ cut OB = 4cm
(iv) Join AB, BC, CD and DA.
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
(v) Measure the length of side AD = 6.1cm
Question 12. Using ruler and compasses only, draw a parallelogram whose diagonals are 4 cm and 6 cm long and contain an angle of 75°. Measure and write down the length of one of the shorter sides of the parallelogram.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AC = 6cm
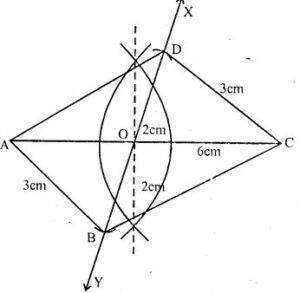
(ii) Bisect AC at O.
(iii) At O, draw a ray XY making an angle of 75o at O.
(iv) From OX and OY, cut off OD = OB = 4/2 = 2cm
(v) Join AB, BC, CD and DA.
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
On measuring one of the shorter sides, we get AB = CD = 3cm
Question 13. Using ruler and compasses only, construct a parallelogram ABCD with AB = 6 cm, altitude = 3.5 cm and side BC = 4 cm. Measure the acute angles of the parallelogram
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw AB = 6cm
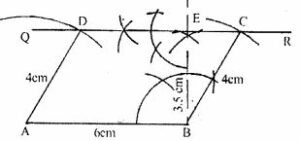
(ii) At B, draw BP ⊥ AB
(iii) From BP, cut BE = 3.5cm = height of || gm
(iv) Through E draw QR parallel to AB
(v) With B as centre and radius BC = 4cm draw an arc which cuts QR at C.
(vi) Since, opposite sides of || gm are equal
So, AD = BC = 4cm
(vii)With A as centre and radius = 4cm draw an arc which cuts QR at D.
ABCD is the required parallelogram.
(viii) To measure the acute angle of parallelogram which is equal to 61o.
Question 14. The perpendicular distances between the pairs of opposite sides of a parallelogram ABCD are 3 cm and 4 cm and one of its angles measures 60°. Using ruler and compasses only, construct ABCD.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a straight-line PQ, take a point A on it.
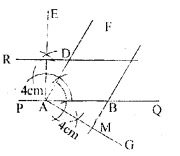
(ii) At A, construct ∠QAF = 60o
(iii) At A, draw AE ⊥ PQ from AE cut off AN = 3cm
(iv) Through N draw a straight line to PQ to meet AF at D.
(v) At D, draw AG ⊥ AD, from AG cut off AM = 4cm
(vi) Through M, draw at straight line parallel to AD to meet AQ in B and ND in C.
ABCD is the required parallelogram
Question 15. Using ruler and compasses, construct a rectangle ABCD with AB = 5cm and AD = 3 cm.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a straight-line AB = 5cm
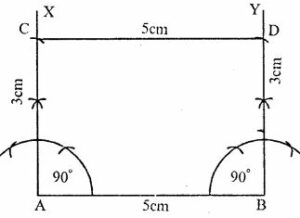
(ii) At A and B construct ∠XAB and ∠YBA = 90o
(iii) From A and B cut off AC and BD = 3cm each
(iv) Join CD.
ABCD is the required rectangle.
Question 16. Using ruler and compasses only, construct a rectangle each of whose diagonals measures 6cm and the diagonals intersect at an angle of 45°.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AC = 6cm
(ii) Bisect AC at O.
(iii) At O, draw a ray XY making an angle of 45o at O.
(iv) From XY, cut off OB = OD = 6/2 = 3cm each
(v) Join AB, BC CD and DA.
ABCD is the required rectangle.
Question 17. Using ruler and compasses only, construct a square having a diagonal of length 5cm. Measure its sides correct to the nearest millimeter.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AC = 5cm
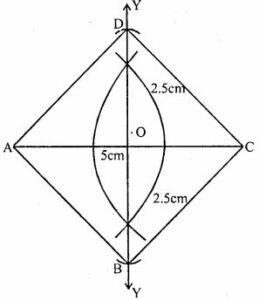
(ii) Draw its percentage bisector XY bisecting it at O
(iii) From XY, cut off
OB = OD = 5/2 = 2.5cm
(iv) Join AB, BC, CD and DA.
ABCD is the required square
On measuring its sides, each = 3.6cm (approximate)
Question 18. Using ruler and compasses only construct A rhombus ABCD given that AB 5cm, AC = 6cm measure ∠BAD.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 5cm
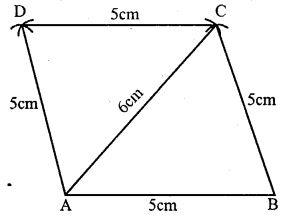
(ii) With centre A and radius 6cm, with centre B and radius 5cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at C.
(iii) Join AC and BC
(iv) With centre A and C and radius 5cm, draw arc intersecting each other 5cm, draw arcs intersecting each other at D
(v) Join AD and CD.
ABCD is a rhombus
On measuring,
∠BAD = 106o.
Question 19. Using ruler and compasses only, construct rhombus ABCD with sides of length 4cm and diagonal AC of length 5 cm. Measure ∠ABC.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AC = 5cm
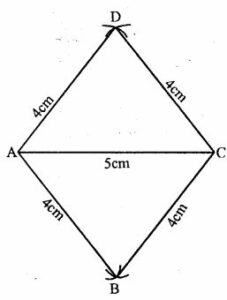
(ii) With centre A and C and radius 4cm, draw arcs intersecting each other above and below AC at D and B.
(iii) Join AB, BC, CD and DA.
ABCD is the required rhombus.
Question 20. Construct a rhombus PQRS whose diagonals PR and QS are 8cip and 6cm respectively.
Answer : Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment PR = 8cm
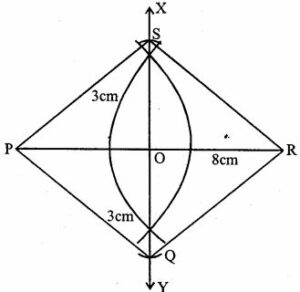
(ii) Draw its perpendicular bisector XY intersecting it at O.
(iii) From XY, cut off OQ = OS = 6/2 = 3cm each
(iv) Join PQ, QR, RS and SP
PQRS is the required rhombus.
Question 21. Construct a rhombus ABCD of side 4.6 cm and ∠BCD = 135°, by using ruler and compasses only.
Answer :
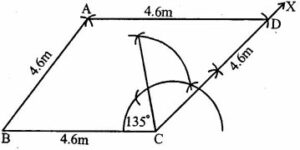
Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 4.6cm
(ii) At C, draw a ray CX making an angle of 135o and cut off CD = 4.6cm
(iii) With centres B and D, and radius 4.6cm draw arcs intersecting each other at A.
(iv) Join BA and DA.
ABCD is the required rhombus.
Question 22. Construct a trapezium in which AB || CD, AB = 4.6 cm, ∠ ABC = 90°, ∠ DAB = 120° and the distance between parallel sides is 2.9 cm.
Answer :
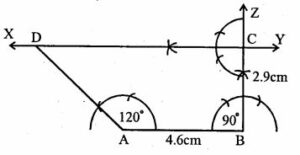
Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 4.6cm
(ii) At B, draw a ray BZ making an angle of 90o and cut off BC = 2.9cm
(iii) At C, draw a parallel line XY to AB.
(iv) At A, draw a ray making an angle of 120o meeting XY at D.
ABCD is the required trapezium.
Question 23. Construct a trapezium ABCD when one of parallel sides AB = 4.8 cm, height = 2.6cm, BC = 3.1 cm and AD = 3.6 cm.
Answer :
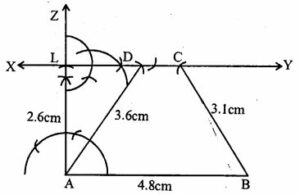
Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 4.8cm
(ii) At A, draw a ray AZ making an angle of 90o cut off AL = 2.6cm
(iii) At L, draw a line XY parallel to AB.
(iv) With centre A and radius 3.6cm and with centre B and radius 3.1cm, draw arcs intersecting XY at D and C respectively.
(v) Join AD and BC
ABCD is the required trapezium.
Question 24. Construct a regular hexagon of side 2.5 cm.
Answer :
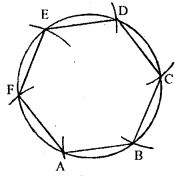
Construction:
(i) With O as centre and radius = 2.5cm, draw a circle
(ii) take any point A on the circumference of circle.
(iii) With A as centre and radius = 2.5cm, draw an arc which cuts the circumference of circle at B.
(iv) With B as centre and radius = 2.5cm, draw an arc which cuts the circumference of circle at C.
(v) With C as centre and radius = 2.5cm, draw an arc which cuts the circumference of circle at D.
(vi) With D as centre and radius = 2.5cm, draw an arc which cuts the circumference of circle at E.
(vii) With E as centre and radius = 2.5cm, draw an arc which cuts the circumference of circle at F.
(viii) Join AB, BC, CD, DE, EF and FA.
(ix) ABCDEF is the required Hexagon.
— : End of ML Aggarwal Rectilinear Figures Exe-13.2 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to :- ML Aggarawal Maths Solutions for ICSE Class-9
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends