Gas Laws Dalal Simplified Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-7. Study of Gas Laws by Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers Answer. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -7 Study of Gas Laws with Additional Questions , Previous Year Questions and Unit Test-7 of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers New Simplified Chemistry . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Study of Gas Laws Dalal Simplified Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-7
–: Select Topics :–
Previous Year Question for Study of Gas Laws
Question 1.(1988)
“When stating the volume of a gas the pressure and temperature should also be given”. Why ?
Answer:
Volume of a gas under goes significant change if its pressure or temperature is slightly changed.
Question 1.(1989)
Define or state : Boyle’s Law
Answer:
Boyle’s Law : “Temperature remaining constant the volume of a given mass of dry gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.”
Question 2.(1989)
Express Kelvin Zero in °C
Answer:
Kelvin zero or absolute zero = — 273°C.
Question 1.(1992)
A fixed volume of a gas occupies 760cm3 at 27° C and 70cm of Hg. What will be its vol. at s.t.p. [637 cm3]
Answer:
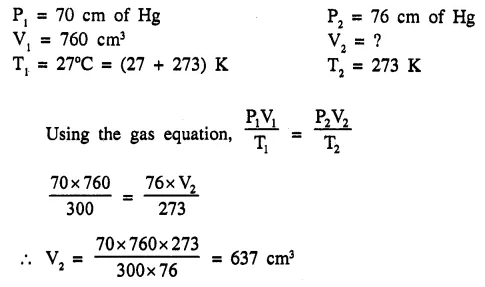
Question 1.(1993)
State : Boyle’s Law
Answer:
Boyle’s Law : “Temperature remaining constant the volume of a given mass of dry gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.”
Question 1.(1995)
At 0°C and 760 mm Hg pressure, a gas occupies a volume of 10Q cm3. The Kelvin temperature (Absolute temperature) of the gas is increased by one-fifth while the pressure is increased one and a half times. Calculate the final volume of the gas. [80 cc.]
Answer:
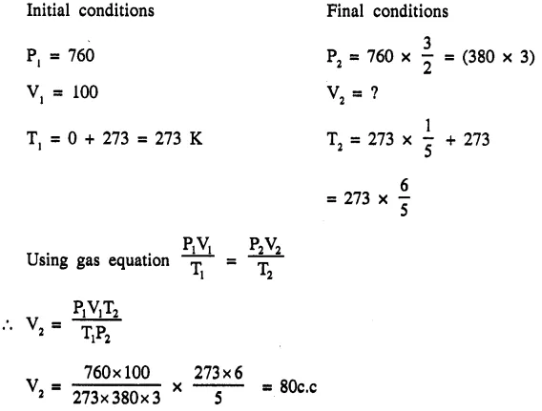
Question 1.(1996)
The pressure on one mole of gas at s.t.p. is doubled and the temperature is raised to 546 K. What is the final volume of the gas ? [one mole of a gas occupies a volume of 22.4 litres at stp.] [22.4 ltrs.]
Answer:
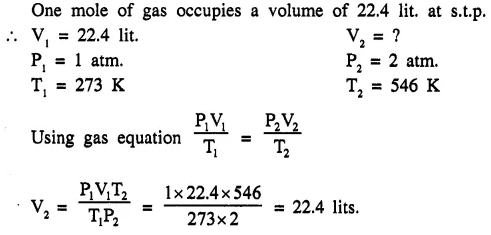
Question 1.(1997)
Is it possible to change the temperature and pressure of a fixed mass of gas without changing its volume. Explain your answer.
Answer:
No, it is not possible as change of any one of the parameters (pressure or temperature) has significant effect on volume.
Additional Questions Study of Gas Laws by Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School New Simplified Chemistry Allied Publishers
Question 1.
What volume will a gas occupy at 740 mm pressure which at 1480 nun occupies 500 cc ? [Temperature being constant] [1000 cc]
Answer:
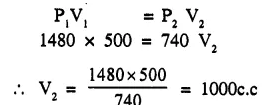
Question 2.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 27°C is 100 cc. To what temperature should it be heated at the same pressure so that it will occupy a volume of 150 cc ?[177°C]
Answer:

Question 3.
A fixed mass of a gas has a volume of 750 cc at—23°C and 800 mm pressure. Calculate the pressure for which its volume will be 720 cc. The temperature being —3°C. [900mm]
Answer:
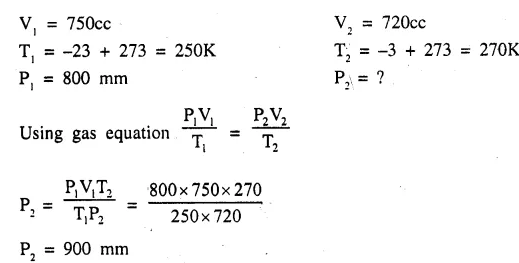
Question 4.
What temperature would be necessary to double the volume of a gas initially at s.t.p. if the pressure is decreased by 50% ? [0°C]
Answer
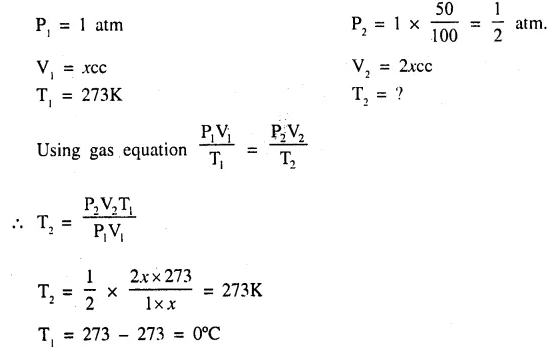
Question 5.
A gas cylinder having a capacity of 20 litres contains a gas at 100 atmos. How many flasks of 200 cm3 capacity can be filled from it at 1 atmos. pressure if the temperature remains constant ? [10,000]
Answer:

Question 6.
A certain mass of gas occupied 850 ml at a pressure of 760 mm of Hg. On increasing the pressure it was found that the volume of the gas was 75% of its initial value. Assuming constant temperature, find the final pressure of the gas? [1013.33 mm of Hg]
Answer:
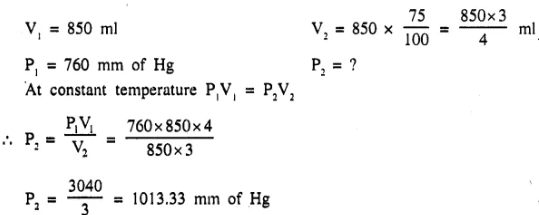
Question 7.
It is required to reduce the volume of a gas by 20% by compressing it at a constant pressure. To do so, the gas has to be cooled. If the gas attains a final temperature of 157°C, find the initial temperature of the gas ? [264.5°C]
Answer:
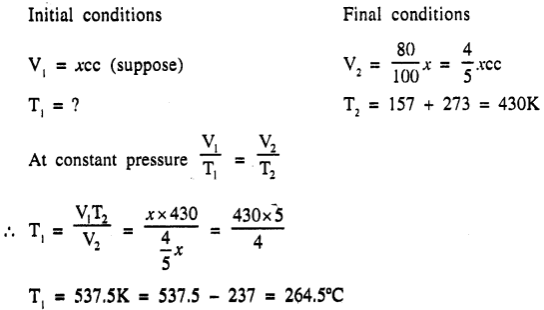
Question 8.
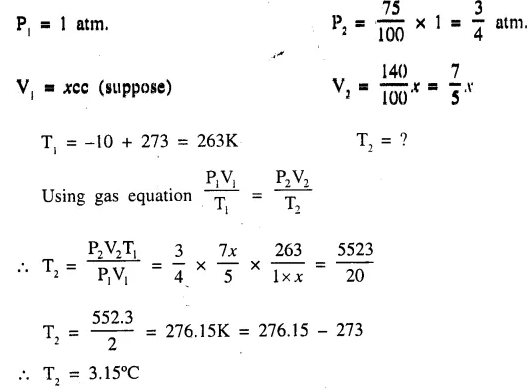
At a given temperature the pressure of a gas reduces to 75% of its initial value and the volume increases by 40% of its initial value. Find this temperature if the initial temperature was —10°C. [3.15°C]
Answer:
Unit Test Paper 7 Study Of Gas Laws Dalal Simplified Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions
Q.1. Name or state the following :
Question 1.
The law which states that pressure remaining constant the volume of a given mass of dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute [Kelvin] temperature.
Answer:
Charle’s Law.
Question 2.
The law which studies the relationship betweeir pressure of a gas and the volume occupied by it at constant temperature.
Answer:
Boyle’s Law.
Question 3.
An equation used in chemical calculations which gives a simultaneous effect of changes of temperature and pressure on the volume of a given mass of dry gas
Answer:
Gas equation.
Question 4.
The standard pressure of a gas in cm. of mercury corresponding to one atmospheric pressure.
Answer:
76 cm.
Question 5.
The absolute temperature value corresponding to 35°C.
Answer:
35 + 273 = 308K
Q.2. Give reasons for the following :(Gas Laws Dalal Simplified )
Question 1.
Gases unlike solids and liquids exert pressure in all directions.
Answer:
Impact of gas molecules with high velocity causes pressure to be exerted on the walls.
Question 2.
Gases have lower densities compared to solids or liquids.
Answer:
Gases have low densities as the inter-molecular distance between the molecules of gases is very large.
Question 3.
Temperature remaining constant the product of the vol. & the press, of a given mass of dry gas is a constant.
Answer:
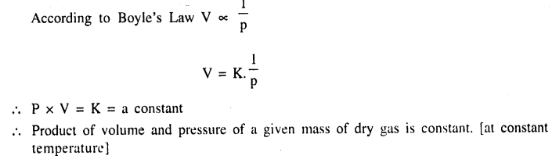
Question 4.
All temperatures on the Kelvin scale are in positive figures.
Answer:
All temperatures on the Kelvin scale are in positive figures.
The temperature -273°C = OK [Absolute zero or zero Kelvin]
Hence it may be negative or positive on Celsius scale, it is always positive on Kelvin as 0°C = 0 + 273 = 273K
30°C = 30 + 273 = 303 K
– 70°C = – 70+ 273;= 203 K
– 273°C = – 273 + 273 = 0K
Question 5.
Volumes of gases are converted into s.t.p. conditions and then compared.
Answer:
Volumes of gases are converted into s.t.p. conditions and then compared as
volumes of gases change with temperature and pressure – hence a standard value of temperature and pressure is chosen to which gas volumes are referred.
Q.3. Calculate the following : (Gas Laws Dalal Simplified )
Question 1.
Calculate the temperature to which a gas must be heated, so that the volume triples without any change in pressure. The gas is originally at 57”C and having a volume 150 cc.
Answer:
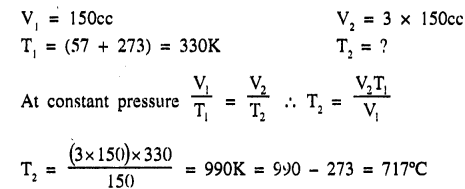
Question 2.
A gas ‘X’ at -33°C is heated to 127° C at constant pressure. Calculate the percentage increase in the volume of the gas.
Answer:
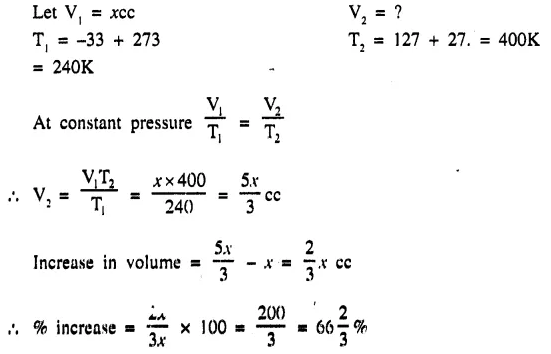
Question 3.
Calculate the volume of a gas ‘A’ at s.t.p., if at 37°C and 775 mm of mercury pressure, it occupies a volume of 9 1/2 litres.
Answer:
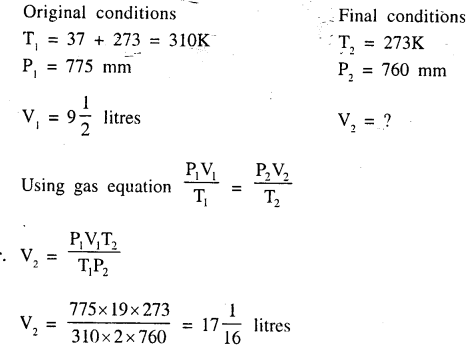
Question 4.
Calculate the temperature at which a gas ‘A’ at 20°C having a volume, of 500 cc. will occupy a volume of 250 cc.
Answer:
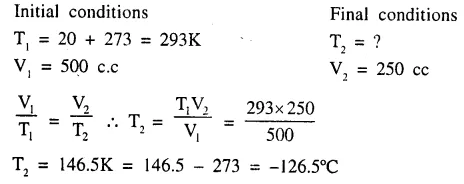
Question 5.
A gas ‘X’ is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mm. pressure. If the volume of the gas collected is 50 cc., calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [at 17°C the vapour pressure is 14 mm.]
Answer:
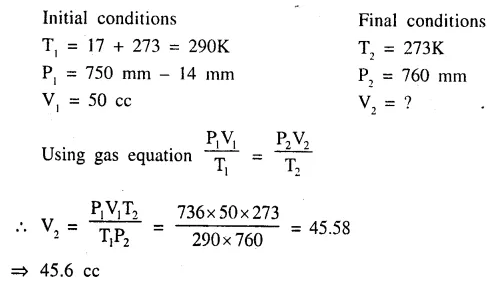
Q.5. Calculate the following : (Gas Laws Dalal Simplified )
Question 1.
The temp, at which 500 cc. of a gas ‘X’ at temp. 293K occupies half it’s original volume [pressure constant].
Answer:

Question 2.
The volume at s.t.p. occupied by a gas “Y” originally occupying 760 cc. at 300K and 70 cm. press, of Hg.
Answer:
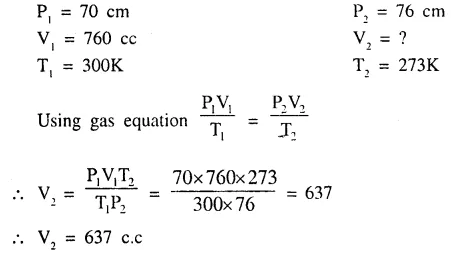
Question 3.
The volume at s.t.p. occupied by a gas ‘Z’ originally occupying 1.57 dm3 at 310.5K and 75 cm. press. of Hg.
Answer:
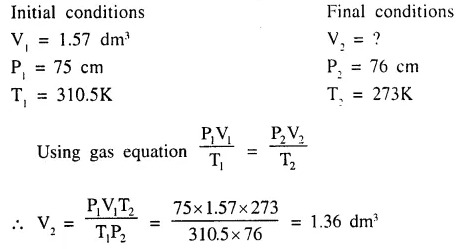
Question 4.
The volume at s.t.p. occupied by a gas ‘Q’ originally occupying 153.7 cm3 at 287K and 750 mm. pressure [vapour pressure of gas ‘Q’ at 287K is 12 mm of Hg.]
Answer:
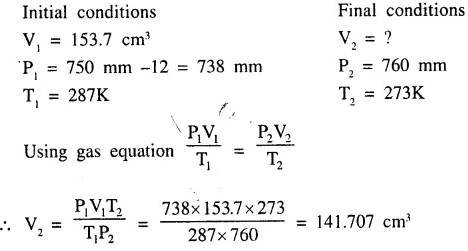
Question 5.
The temperature to which a gas ‘P’ has to be heated to triple it’s volume, if the gas originally occupied 150 cm3 at 330K [pressure remaining constant].
Answer:
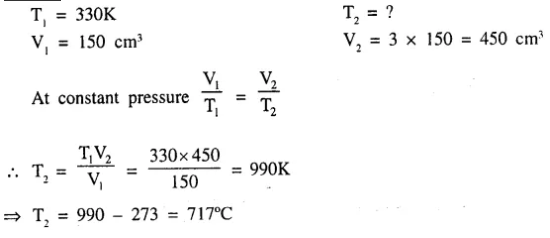
Q.6. Fill in the blanks with the correct word, from the words in bracket : (Gas Laws Dalal Simplified )
Question 1.
If the temperature of a fixed mass of a gas is kept constant and the pressure is increased, the volume correspondingly ____ [increases / decreases]
Answer:
If the temperature of a fixed mass of a gas is kept constant and the pressure is increased, the volume correspondingly decreases.
Question 2.
If the pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is kept constant and the temperature is increased, the volume correspondingly ____ [increases / decreases]
Answer:
If the pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is kept constant and the temperature is increased, the volume correspondingly increases.
Question 3.
1 dm3 of a gas is equal to ____ [1 litre / 100ml. / 100 cc.]
Answer:
1 dm3 of a gas is equal to 1 litre.
Question 4.
All the temperature on the kelvin scale are in ____ figures [negative positive]
Answer:
All the temperature on the kelvin scale are in positive figures.
Question 5.
At -273°C the volume of a gas is theoretically ____ [272 cc. / 0 cc. / 274 cc.]
Answer:
At -273°C the volume of a gas is theoretically 0 cc.
.– : End of Gas Laws Dalal Simplified Solutions :–
Return to New Simplified Dalal ICSE Chemistry Class-9 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends



East or west
Icse help is the best
thanks you very much