Genetics Class 10 Concise Structured Type Answer ICSE Biology Selina Solutions Ch-3. In this article you will get the solutions of Structured Type Questions as council latest syllabus. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.

Genetics Class 10 Concise Structured Type Answer ICSE Biology Selina Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10 |
| Book | Selina Concise |
| Chapter-3 | Genetics: Some Basic Fundamentals |
| Topics | Solutions of Structured Type Questions |
| Session | 2025-26 |
Structured Type Questions on Genetics
Class 10 Concise ICSE Biology Selina Solutions Ch-3 Genetics: Some Basic Fundamentals
Que-1: In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring, when both parents are ‘Bb’ or have heterozygous black fur.
Sol:
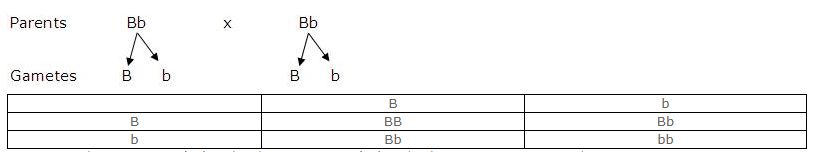
Genotype – 1(Homozygous Black Fur) :2 (Heterozygous Black Fur):1 (Homozygous Brown Fur)
Phenotype – 3 (Black Fur) :1(Brown Fur)
Que-2: Two pairs (A & B) of rabbits were crossed as given below:

(a) Can you tell which coat colour (black or white) is dominant?
(b) Is the coat colour sex-linked?
Sol:
(a) Black
(b) No
Que-3: Make a Punnett square for finding out the proportion of different genotypes in the progeny of a genetic cross between
(a) A pure tall (TT) pea plant with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant.
(b) Red flower variety of pea (RR) with white flower variety of pea (rr).
Sol:

Genotype – 1(Homozygous red) :2 (Heterozygous red):1 (Homozygous white)
Phenotype – 3 (Red) :1(White)
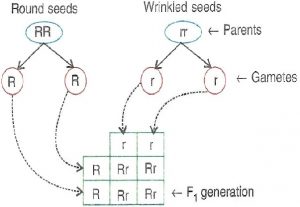
Que-4: Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having round seeds (RR) with a homozygous pea plant having wrinkled seeds (rr). He got different results. On the basis of it, answer the following questions:
(a) Which character of seed is studied in the experiment?
(b) Which of the above two traits is dominant ?
(c) Write the phenotype and genotype of F1 offspring.
(d) Mention and state the Mendel’s law shown in the above cross.
(e) Make a Punnett square for F2 generation when two plants of F1 offspring are crossed with each other.
(f) Write the phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny.
(g) What will be the genotypic ratio of F2 offsprings ?
(h) What are the two traits of seed colour ? Also mention which is dominant and recessive ?
(i) Write the scientific name of garden pea.
(j) Write two main features of pea plant due to which Mendel had selected it for his hybridisation studies.
Sol:
(a) Shape of seed
(b) Round seed shape is dominant.
(c) Phenotype — Round seed
Genotype — Rr
(d) The Law of Dominance states that when two contrasting traits are present together, only one will be expressed, while the other remains hidden or suppressed.
(e)
| Gamete | R | r |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
(f) Phenotypic ratio — 3:1
(g) Genotypic ratio — 1:2:1
(h) The two traits of seed colour are:
- Yellow (dominant)
- Green (recessive)
(i)Pisum sativum
(j) Mendel chose pea plants for two key reasons:
- They exhibited a variety of alternative forms for each character.
- Pea plants have a short life span, allowing multiple generations to be studied in a relatively short period.
Que-5: A homozygous plant having round (R) and yellow (Y) seed is crossed with another homozygous plant having wrinkled (r) and green (y) seeds. Answer the following questions :
(a) Give the genotype of the F1 generation.
(b) Mention the phenotype of the F1 offsprings.
(c) Give the possible combinations of gametes that can be obtained from F1 hybrids.
(d) Give the dihybrid phenotypic ratio and the phenotype of the offsprings of the F2 generation when two plants of F1 generation are crossed.
(e) Name and state the law which explains the dihybrid phenotypic ratio.
Sol:
(a) Genotype : RrYy
(b) All Round and yellow seeds
(c) RY, Ry, rY, ry
(d) 9:3:3:1
(e) The Law of Independent Assortment states that the way alleles for one trait are distributed into gametes occurs independently of how alleles for another trait are distributed.
–: End Genetics Class 10 Concise Structured Type Answer ICSE Biology Selina Solutions :-
Return to:- Concise Selina ICSE Biology Class-10 Solutions
Thanks
Please Share with your friends


