Genetics Class-10 Long and Structured Questions Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-3. We Provide Solutions of Long Answer Questions and Structured Questions of Exercise-3 Genetics. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Long and Structured Questions
Ch-3 Genetics Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brothers publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Dr. K.K. Aggrawal |
| Chapter-3 | Genetics |
| Topics | Solutions of Long Answer and Structured Questions |
| Edition | For 2022-2023 Academic Session |
D. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Ch-3 Genetics Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions
(Page-40)
Questions 1: Draw a suitable cross to show Mendel’s first law.
Answer :
Through careful study of patterns of inheritance, Mendel recognized that a single trait could exist in different versions, or alleles, even within an individual plant or animal. For example, he found two allelic forms of a gene for seed color: one allele gave green seeds, and the other gave yellow seeds. Mendel also observed that although different alleles could influence a single trait, they remained indivisible and could be inherited separately. This is the basis of Mendel’s First Law, also called The Law of Equal Segregation, which states: during gamete formation, the two alleles at a gene locus segregate from each other; each gamete has an equal probability of containing either allele.
Questions 2: State Mendel’s law of independent assortment.
Answer : Mendel’s law of independent assortment states that the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene
Questions 3: Explain the following terms
(a) Mutation.
(b) Monohybrid cross
(c) Homologous Chromosome
(d) Phenotype
Answer :
(a) A Mutation occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. A Mutagen is an agent of substance that can bring about a permanent alteration to the physical composition of a DNA gene such that the genetic message is changed
(b) A monohybrid cross is a cross between two organisms with different variations at one genetic locus of interest. The character(s) being studied in a monohybrid cross are governed by two or multiple variations for a single location of a gene
(c) Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism’s mother; the other is inherited from the organism’s father
(d) The term “phenotype” refers to the observable physical properties of an organism; these include the organism’s appearance, development, and behavior. An organism’s phenotype is determined by its genotype, which is the set of genes the organism carries, as well as by environmental influences upon these genes
Questions 4: Give the dihybrid ratio. Name and state the law which explains the same.
Answer :
Dihybrid ratio: 9:3:3:1
The law of independent assortment explains it.
Law of independent assortment: In a dihybrid cross, the distribution of the members of one pair into the gametes is independent of the distribution of the other pair.
Questions 5: State Mendal’s law of segregation.
Answer : According to the law of segregation, only one of the two gene copies present in an organism is distributed to each gamete (egg or sperm cell) that it makes, and the allocation of the gene copies is random.
Questions 6: State Mendel’s Law of Dominance.
Answer : Mendel’s law of dominance states that: “When parents with pure, contrasting traits are crossed together, only one form of trait appears in the next generation.The hybrid offsprings will exhibit only the dominant trait in the phenotype.” Law of dominance is known as the first law of inheritance
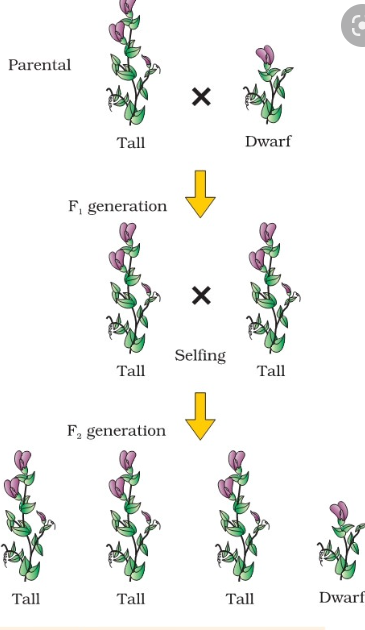
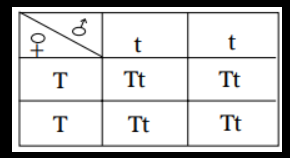
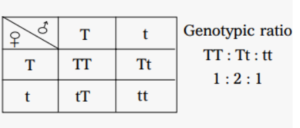
Questions 7: A pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure dwarf plant (tt).
(a) Draw Punnett squares to show:
(1) F1 generation
(2) F2 generation.
(b) Give the phenotype of the F1 generation.
(c) Give the phenotypic and genotypic ratio of the F1 and F2 generation.
Answer :
(a)
(1) F1 generation
(2) F2 generation.
(b) All hybrid tall
(c) Phenotype 3:1 and genotype 1:2:1
Questions 8: Explain any one X-linked disease found in humans.
Answer : X-linked inheritance means that disease is inherited due to the gene located on the X chromosome, like colour blindness and haemophilia
E. STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
Ch-3 Genetics Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions
(Page-41)
Question 1: A family consisting of two parents and their five children. The given pedigree chart shows the inheritance of the trait of colour blinds In them.
Answer the given questions based on It :
(i) Who s the heterozygous for the traits?
(ii) How many daughters and sons are colourblind in the family?
(iii) On which chromosome is the gene for it located?
Answer :
(i) ……………..
(ii) one son and one daughter
(iii) on x chromosome
Question 2: A homozygous tall plant (TT) bearing red coloured (RR) lowers is crossed with a homorygous dwarf plant (tt) bearing white flowers (rr):
(a) Give the genotype and phenotype of the F1 generation.
(b) Give the possible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained from the F1 hybrid.
(c) Give the dihybrid ratio and the phenotype of the off springs of F2 generation when two plants of the F1 generation above are crossed.
Answer :
(a) Genotype of F1 generation plants: TtRr
Phenotype of F1 generation plants: Tall and red-coloured flowers
(b)
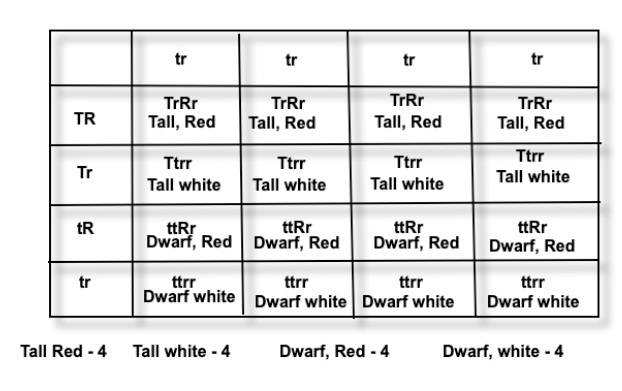
Phenotypes of offspring obtained in the F2 generation:
- Tall plants with red flowers
- Tall plants with white flowers
- Dwarf plants with red flowers
- Dwarf plant with white flowers
(c) The phenotypic ratio obtained in the F2 generation is 9:3:3:1.
Question 3: In a homozygous plant, round seeds (R) are dominant over wrinkled seeds (r):
(i) Draw a Punnett square to show the gametes and offspring when both the plants have heterozygous round seed (Rr).
(ii) Mention the Phenotype and Genotype ratios of the offspring in F2 generation.
(iii) Name the sex chromosomes in human males and females
(iv) Briefly explain the term Mutation
(v) What is the number of chromosomes in the gametes of human beings.
Answer :
(i)
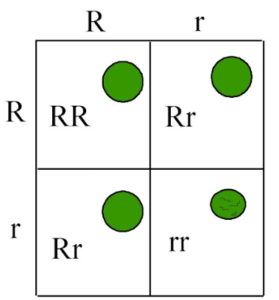
(ii) Genotypic ratio – 1:2:1
1. Homozygous round
2. Heterozygous round
3. Homozygous wrinkled Phenotypic ratio = 3:1
(iii) Human male sex hormone = Testosterone
Human female sex hormone = Oesterogen Progesterone.
(iv) Mutation : The sudden change in one or more genes which changes the hereditary materials of a cell which in turn changes the character of an organism.
(v) 23.
Question 4: A homozygous tall plant () bearing red coloured (R) flowers is crossed with a homozygous dwarf (t) plant bearing white (r) flowers :
(i) Give the genotype and phenotype of the plants of F1 generation.
(ii) Mention the p0ssible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained from the F1 hybrid plant.
(iii) State the Mendel’s law of independent Assortment.
(iv) Mention the phenotypes of the offspring obtained in F2 generation.
(v) What is the phenotypic ratio obtained in F2 generation?
Answer :
(i) Genotype of F1 generation : Tt Rr
Phenotype of F1 generation : All heterozygous tall and red.
(ii)
Red and Tall :TR
Tall and White Tr
Dwarf and Red tR
White and Dwarf tr
(iii) Mendel’s law of independent Assortment: “In a dihybrid cross, one pair of character is independent of the other pair during gamete formation.”
(iv) Tall & Red
Tall & White
Dwarf & Red
Dwarf & white
(v) 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Question 5: In a homozygous pea plant, axial flowers (A) are dominant over terminal flowers (a).
(i) What is the phenotype and genotype of the F1 generation if a plant bearing pure axial flowers is crossed with a plant bearin8 pure terminal flowers?
(ii) Draw a Punnett square board to show the gametes and offsprings when both the parent plants are heterozygous for axial flowers ?
(iii) What is the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of the above cross shown in (ii) ?
(v) State Mendel’s Law of Dominance.
(v) Name two genetic disorders commonly seen in human males.
Answer :
(i) The phenotype of F | generation is all plants grow into axial flowers. The genotype of Fi generation is all plants are Aa.
(ii)
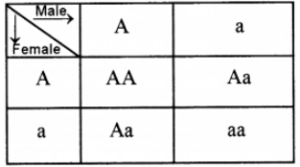
(iii) Phenotypic ratio : 3: 1
Genotypic ratio : 1:2:1
(iv) In heterozygous condition, out of the two alleles, one expresses itself morphologically and the other remains unexpressed. The allele which expresses itself phenotypically is called dominant and the other which remains unexpressed is called recessive.
(v) Colorblindness and Hemophilia.
— : End of Genetics Long and structured Questions Solutions :–
Return to :- ICSE Biology for Class 10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
thanks