Genetics Notes for ICSE Class 10 Biology Ch-3 covers the fundamental principles of heredity and inheritance. Key concepts include genes, chromosomes, alleles, and the laws of inheritance. Understanding how traits are passed down from one generation to the next is crucial for grasping this chapter. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
What is Genetics:
The scientific study of heredity and the mechanisms by which traits are transmitted.
Heredity:
The passing of traits (like eye color, height, etc.) from parents to offspring.
Variations in Population
Variations in a population refer to the differences in traits or characteristics among individuals within that population.
Character and Trait
A trait is defined as a state of character, which is a distinctive variety of a phenotypic characteristic of an organism, whereas a character is an identifiable feature that aids in the identification of the organism
Example of Inheritance
- Character: Flower color; Traits: Red, pink, white.
- Character: Seed shape; Traits: Round, wrinkled.
- Character: Height (in plants); Traits: Tall, dwarf.
- Character: Eye color; Traits: Blue, brown, green.
- Character: Hair color; Traits: Brown, blonde, black.
- Character: Blood type; Traits: A, B, AB, O.
- Character: Petal shape; Traits: Rounded, pointed.
- Character: Seed texture; Traits: Smooth, rough.
- Character: Seed color; Traits: Yellow, green.
- Character: Leaf shape; Traits: Elliptical, lanceolate
Chromosomes-The Carrier of Heredity
Chromosomes are called carriers of heredity because they contain genes, which are the units of inheritance that determine an organism’s traits. These genes are composed of DNA, the genetic material responsible for carrying information from one generation to the next
Homologous Chromosomes
pairs of chromosomes within the same cell that share similar characteristics like length, centromere location, and gene sequence, but are not identical One chromosome of each pair is inherited from the mother, and the other from the father. They contain the same genes in the same order.
Autosomes
Autosomes are all chromosomes in an organism except for the sex chromosomes. In humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes, numbered 1 to 22. Autosomes carry genes responsible for various traits and functions, excluding sex determination. In a diploid cell, autosomes exist as homologous pairs, meaning they have the same structure and genes.
Sex Chromosomes
Sex chromosomes are chromosomes that determine an individual’s sex.
Examples: In humans, the sex chromosomes are X and Y. Sex chromosomes carry genes that influence the development of sexual characteristics and determine whether an individual is male (XY) or female (XX). In humans, females typically have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
Sex Determination- Son or Daughter
In humans, the sex of a child is determined by the sperm cell carrying either an X or Y chromosome, which combines with the egg cell’s X chromosome. If the sperm carries an X chromosome, the child will be female (XX), and if the sperm carries a Y chromosome, the child will be male (XY).
Genes: Alleles
Every genes has two alternative forms called Alleles
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
In a pair of contrasting alleles, one allele (the dominant allele) masks the expression of the other allele (the recessive allele).
Genotype, Phenotype:
There are three situation for any pair of genes. RR, Rr, rr
Phenotype refers to the observable physical traits of an individual, whereas genotype refers to a person’s genetic makeup.
Genotype
Homozygous Dominant: Similar pair RR
Heterozygous: Dis similar Pair Rr
from Parent to Children Tongue Rolling Example

Both father and mother are tongue rollers (hollow symbols represent the usual expressed character). . Of the three children born, two can roll (hollow symbols) and one cannot (solid symbol). The recessive trait (rr) of non-rolling in one of the children could have come from nowhere else but the parents
The tongue rolling ability occurs due to the influence of a dominant allele of the gene. A person who has either one or two copies of the dominant allele will be able to twist their tongue. In the case that a person is born with two recessive alleles, they cannot twist their tongue
Sex Linked Inheritance
Sex-linked inheritance refers to the transmission of traits determined by genes located on the sex chromosomes (X and Y). These traits are inherited in patterns that differ between males and females due to the differences in their sex chromosome complements (XX in females, XY in males
X Linked Inheritance
X-linked inheritance refers to the passing down of genes located on the X chromosome. This means that a gene or trait is inherited from parents to children through their X chromosome. Since males have one X chromosome and females have two, X-linked traits are expressed differently in males and female
Males are more likely to be affected by X-linked recessive conditions:
Males have only one X chromosome, so if they inherit a recessive gene on it, they will express the trait
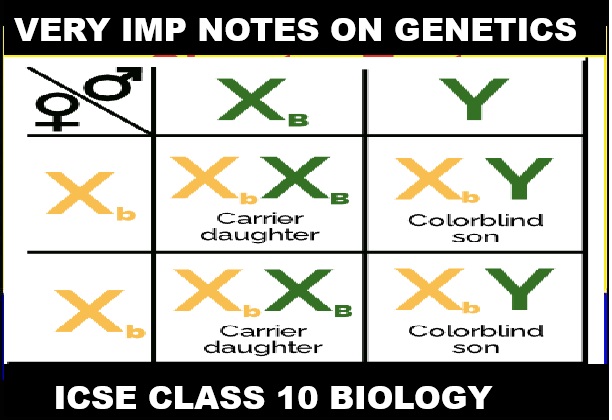
Color Blindness, Hemophilia
The gene for color blindness is recessive, meaning that an individual needs two copies of the gene (one from each X chromosome) to express the trait.
Males are more affected:
Males have only one X chromosome (XY), so if they inherit the gene for color blindness on their single X chromosome, they will have the condition.
Females can be carriers:
Females have two X chromosomes (XX). If they inherit the gene for color blindness on one X chromosome, they will be a carrier, meaning they have one normal gene and one gene for color blindness. Female carriers can pass the gene to their children:
A female carrier has a 50% chance of passing the gene for color blindness to her sons (who will then have the condition) and a 50% chance of passing the gene to her daughters (who may become carriers themselves
–: End of Genetics Notes for ICSE Class 10 Biology Ch-3 principles of heredity and inheritance. :–
Please share with your friends if helpful
Return to :
Thanks


