Genetics Srijan Publications Long Answer Type question Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-3 . We Provide Solutions of MCQs, and Long Answers type Questions of Exercise-3 Genetics Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Ch-3. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
Genetics Srijan Publications Long Answer Type question Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-3
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-3 | Genetics |
| Topics | Solutions of MCQs and Long Answers Questions |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
C .Long Answer Type Questions
Ch-3 Genetics Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-38)
Questions 1. Describe Mendel’s procedure of conducting a monohybrid cross in a pea plant.
Answer :
A monohybrid cross is the hybrid of two individuals with homozygous genotypes which result in the opposite phenotype for a certain genetic trait.”
“The cross between two monohybrid traits (TT and tt) is called a Monohybrid Cross.”
Monohybrid cross is responsible for the inheritance of one gene
monohybrid cross:- Mendel began with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting traits, i.e., one tall and another dwarf. The cross-pollination of tall and dwarf plants resulted in tall plants. All the hybrid plants were tall. He called this as a first hybrid generation (F1) and offspring were called Filial1 or F1 progeny.
He conducted an experiment with all seven contrasting pairs and observed that the entire F1 progeny showed one pattern in their behaviour, i.e., they resembled one of the parents. Another parent character was completely absent.
Questions 2.
(a) A pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure dwarf Plant (tt). Draw punnett squares to show
(i) F1 generation (ii) F2 generation
Ans:-
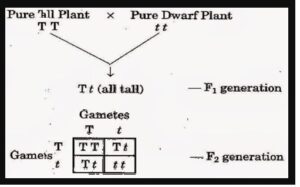
(b) Give the phenotype of the F2 generation.
Ans- 3:1
(c) Give the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F1 and F2 generations.
Ans :
phenotypic ratios of the F1—All same allele
genotypic ratios of the F1— 3:1
phenotypic ratios of the F2—3:1
genotypic ratios of the F2— 1:2:1
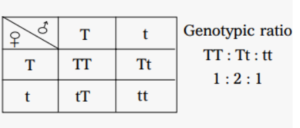
Questions 3. (a) Give the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring produced during following crosses. Represent the results in the form of Punnett Square.
(i) Tt x Tt
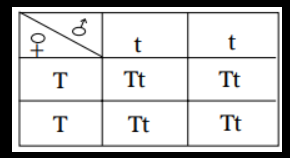
(ii) Tt x tt
(iii) Aa Bb x Aa Bb
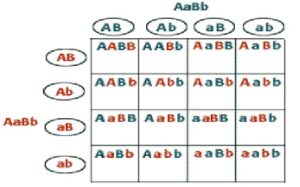
(iv) YY rr x yy RR
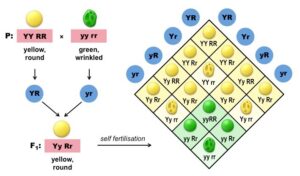
Questions 4.
(a) A cross is made between heterozygous black and homozygous brown mice. Give the genotype and phenotype of offspring that may be produced from this cross Given that black colour is dominant over brown colour.
Ans:- Hence, phenotypic ratio is black : brown i.e. of the progeny would have black mice.
(b) A homozygous tall plant (T) bearing red (R) flowers is crossed with a homozygous dwarf plant (t) bearing white flowers (r):
(i) Give the genotype and phenotype of the F1 gametes that can be obtained from the F1 hybrids.
Ans :- generation — TtRr Selfing TtRr x TtRr
(ii) Give the dihybrid ratio and the phenotype of the offspring of the F2 generation when two plants of the F1 generation above are crossed.
Ans :- generation phenotypic ratio= 9 tall plant, red flower:3 tall plant, white flower:3 dwarf plant, red flower:1 dwarf plant, white flower
(c) In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Predict a genotype and phenotype of the offspring when both parents are Bb’ (having heterozygous black fur).
Ans :-
At the end of the process the genotypic ratio is 1 (BB) : 2(Bb) : 1(bb).
The phenotypic ratio will be 3 (Black fur) : 1 (brown fur)
Questions 5. In a homozygous pea plant, axial flowers (A) are dominant over terminal flowers (a).
(a) What is the phenotype and genotype of the F1 generation if a plant bearing pure axial flowers is crossed with a plant bearing pure terminal flowers?
(b) Draw a Punnett square board to show the gametes and offspring when both the parent plants are heterozygous for axial flowers.
(c) What is the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of the above cross shown in (b) ?
(d) State Mendel’s Law of Dominance.
(e) Name two genetic disorders commonly seen in human males.
Answer :
(a) Phenotype of F1 generation plants: Axial flowers Genotype of F1 generation plants: Aa
(b) Punnett square board to represent gametes and offspring when both parent plants are heterozygous for axial flowers (Aa).
| A | a | |
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | aA | aa |
(c) Phenotypic ratio for the above cross – 3 : 1 (3 pea plants with axial flowers : 1 pea plant with terminal flowers)
Genotypic ratio for the above cross – 1 : 2 : 1 (1 homozygous plant with axial flowers : 2 heterozygous plants with axial flowers : 1 homozygous plant with terminal flowers)
(d) Mendel’s Law of Dominance: Of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one can express itself, while the other remains suppressed. The one which is expressed is the dominant and the one which is not expressed is the recessive.
(e) Genetic disorders commonly seen in human males:
- Haemophilia
- Colour blindness
Questions 6. A pea plant which is homozygous for Green pods which are inflated [GGII] is crossed with a homozygous plant for yellow pods which are constricted [ggii).
Answer the following questions:
(i) Give the phenotype and genotype of the F1 generation. Which type of pollination has occurred to produce F1 generation?
(ii) Write the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation.
(iii) Write the possible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained if two Fi hybrid plants are crossed.
(iv) State Mendel’s law of Segregation of Gametes.
(v) What is the scientific name of the plant which Mendel used for his experiments on inheritance?
Answer :
(i)
- Phenotype of F1 generation: Pea plants with green and inflated pods.
- A genotype of F1 generation: GgIi
- Artificial cross-pollination has occurred to produce the F1 generation
(ii) The phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3: 1
(iii) The possible combination of gametes that can be obtained if two F1 hybrid plants are crossed are as follows: GI, Gi, gI, gi
(iv) The two members of a pair of factors separate during the formation of gametes. This is Mendel’s law of ‘Segregation of Gametes’.
(v) Pisum sativum
Questions 7. In Mendel’s experiments, tall pea plants (T) are dominant over dwarf pea plants (t).
(a) What is the phenotype and genotype of the F1 generation if a homozygous tall plant is crossed with a homozygous dwarf plant?
(b) Draw a Punnett square board to show the gametes and offspring when both the parents are heterozygous for tallness
(c) What is the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of the above cross in (b)?
(d) State Mendel’s Law of Dominance
(e) What is a Dihybrid Cross
Answer :
(a) Phenotype of F1 generation is all are tall plants.
Genotype of F1 generation is all plants are Tf.
(b) Punett square is as follows :

(c) Phenotypic ratio = 3:1
Genotypic ratio = 1:2:1
(d) In a heterozygous condition, out of the two contrasting alleles, one expresses itself morphologically and other remains unexpressed. The factor which expresses itself phenotypically is called dominant and the other which remains unexpressed is called recessive.
(e) A cross between two individuals having two pairs of contrasting traits producing a generation in which all individuals are heterozygous for both the characters.
D. Multiple Choice Type Questions
Ch-3 Genetics Srijan Publications ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-38)
Choose the correct answer.
1. An organism with two unlike genes for a trait is called
(a) Homozygous
(b) Heterozygous
(c) Wild variety
(d) Dominant variety
Answer :(b) Heterozygous
2. A Mendelian cross between tall pea plants having violet flowers and a short pea plant bearing white flowers produced a progeny of tall plants having violet flowers. What will be genotype of tall, violet parent?
(a) TT WW
(b) Tt WW
(c) TT ww
(d) Tt Ww
Answer :(b) Tt WW
3. The outward expression of a gene
(a) Genotype
(b) Phenotype
(c) Variation
(d) Chromosomes
Answer :(b) Phenotype
4. Mendel conducted his famous breeding experiments by working on
(a) Drosophila
(b) Pisum sativum
(c) Escherichia coli
(d) All of these
Answer :(b) Pisum sativum
5. In which generation does the segregation of allelic phenotype take place?
(a) Fo
(b) F2
(c) F1
(d) F3
Answer :(c) F1
6. In human beings, sex of baby is determined at the time of
(a) Intercourse
(b) Gamete formation
(c) Parturition
(d) Fertilization
Answer :(d) Fertilization
7. Gametes contain
(a) Diploid set of chromosomes
(b) Haploid set of chromosomes
(c) Sex chromosomes only
(d) Autosomes only
Answer :(b) Haploid set of chromosomes
8. Term gene was coined by
(a) Mende
(b) Johannsen
(c) Morgan
(d) Bateson
Answer :(b) Johannsen
— : End of Ch-3 Genetics Srijan Publication Long Answer Type question ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions :–
Return to :- Srijan Publication ICSE Biology for Class 10 Solutions
Thanks