Geography Part 2 Specimen Paper 2023 ICSE Class 10 Solved. Step by step solutions as council prescribe guideline of model sample question paper. Specimen Question Paper of ICSE 2023 belong to Geography Part 1 and Part 2 . Student can achieve their goal in next upcoming exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10..
Geography Part 2 Specimen Paper 2023 ICSE Class 10 Solved
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 10th (x) |
| Subject | Geography |
| Topic | Specimen Paper Solved |
| Syllabus | Revised Syllabus |
| Session | 2022-23 |
| Section | Part 2 |
| Max mark | 80 |
Warning :- before viewing solution view Question Paper.
Geography Part 2 Specimen Paper 2023 ICSE Class 10 Solved
(Attempt any five questions from this Part.)
Question 4:
(i) (a) Name the type of climate experienced by India.
(b) Mention any two factors responsible for it.
(ii) With the help of a suitable example explain how relief features affect the rainfall of a place.
(iii) Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(a) Annual range of temperature is higher in Delhi than Mumbai.
(b) Mango showers are beneficial local winds.
(c) The North East monsoons bring almost no rain to most parts of India.
(d) Study the climatic data and answer the following questions:
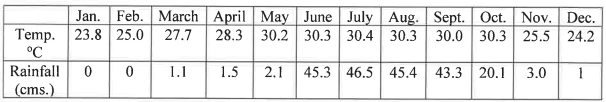
(a) Calculate the annual range of temperature.
(b) What is the total rainfall during the monsoon season?
(c) On which coast is the station located? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
(i) (a) India hosts two climatic subtypes- tropical monsoon climate, tropical wet and dry climate that fall under this group.
(b) (1) Moisture Laiden Monsoon winds of Bay of Bengal Branch of South West Monsoon. (2) Mango Showers
(ii) Climate can be affected by mountains. Mountains receive more rainfall than low lying areas because as air is forced over the higher ground it cools, causing moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall.
(iii)
Question 5:
(i) Differentiate between alluvial and laterite soil.
(ii) Name the following:
(a) This soil is sticky when wet and cracks when dry.
(b) This soil is mainly used for making bricks.
(c) This soil is classified into khadar and bhangar.
(d) When heavy rainfall washes away the topmost layer of the soil.
(iii) Give geographical reasons for the following:
(a) Black soil is a residual soil.
(b) Red soils are generally infertile.
(c) Alluvial soil differs in texture.
(iv) What is Soil Conservation? Mention any two measures taken to conserve soil.
Answer:
(i) Alluvial soil is formed due to the deposition of alluvium from the river whereas laterite soil is formed due to leaching in wet and hot areas. Alluvial soil is light grey in colour whereas laterite soil is reddish. * Alluvial soil isn,t acidic whereas laterite soil is acidic and coarse.
(ii)
(a) Black Soil
(b) Laterite
(c) Alluvial soil.
(d) Soil erosion.
(iii)
(a) Residual soils are formed when soils or rocks weather at the same location due to chemicals, water, and other environmental elements, without being transported.
(b) Red soil is not very fertile soil as it is low in humus and nutrients. Red soil is a soil that expands in warm conditions, moist climate under mixed or deciduous forest.
(c) The alluvial soils vary in texture from clay to sandy loam. Alluvial soils are poor in phosphorus but rich in potash. There are two different types of alluvial soils namely Bhangar and Khadar. The older alluvium is the bhangar and new alluvium is the Khadar.
(iv) Soil conservation is the prevention of loss of the top most layer of the soil from erosion or prevention of reduced fertility caused by over usage, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination. Techniques for improved soil conservation include crop rotation, cover crops, conservation tillage and planted windbreaks, affect both erosion and fertility. When plants die, they decay and become part of the soil. Code 330 defines standard methods recommended by the U.S. Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Question 6 :
(i) Mention any two characteristics of Tropical Evergreen forests.
(ii) Name the forest which is found in the delta of the river Ganga. Name two trees which are found here.
(iii) Give geographical reasons for the following:
(a) Xerophytic plants have long roots.
(b) Forests prevent floods.
(c) Tropical deciduous forests are commercially most exploited.
(iv) Give three reasons why we must conserve our forests.
Answer:
(i) Two characteristics of tropical evergreen forests are that they always appear green as all the trees do not shed their leaves at the same time. Secondly, these forests are dense and the trees are more than 60 m in height.
(ii) Mangrove forests are found in the deltas of rivers Ganga, Mahanadi, Krishna, Godavari, and Kaveri. Some trees found in these forests include sundari, palms, keora, agar, and coconut.
(iii)
(a) Xerophytes such as cacti are capable of withstanding extended periods of dry conditions as they have deep-spreading roots and capacity to store water. Their waxy, thorny leaves prevent loss of moisture. Even their fleshy stems can store water.
(b) Forests can soak up excess rainwater, preventing run-offs and damage from flooding. By releasing water in the dry season, forests can also help provide clean water and mitigate the effects of droughts
(c) The tropical deciduous have been commercially exploited because of the hardwood trees like sal, teak, neem, shisha etc. The timber obtained from the forests is used for making furniture, transport and construction materials.
(iv) Providing clean water for drinking, bathing, and other household needs. Protecting watersheds and reducing or slowing the amount of erosion and chemicals that reach waterways. Providing food and medicine. Serving as a buffer in natural disasters like flood and rainfalls.
Question 7:
(i) Mention two conditions necessary for the construction of wells.
(ii) Define: (a) Surface water (b) Ground Water
(iii) Mention one advantage of canals and two disadvantages of tanks.
(iv) Mention three ways by which you as an individual can reuse and conserve water.
Answer:
(i)
1. Water level should be high. 2. Soil should be loose.
(ii)
(a) Surface water is water located on top of the Earth’s surface, and may also be referred to as blue water. In common usage, it is usually used specifically for terrestrial waterbodies, the vast majority of which is produced by precipitation and runoff from nearby higher areas.
(b) Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth’s surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water.
(iii)
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Water from the rain can also be stored in tanks. | Tanks are difficult to transport to rocky terrain. |
| Tanks can be used to collect more water from rainfall. | Other methods of irrigation have been used in several regions, and the dry beds of tanks have been reclaimed for agriculture. |
(iv)
Question 8:
(i) Mention one advantage and one disadvantage of coal found in India.
(ii) Name two states where copper is found in India. Mention one use of it.
(iii) Mention two advantages of using natural gas over petroleum. Name an area where natural gas is found.
(iv) What are the advantages of using bio gas?
Answer:
(i)
(ii) Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand are the only states involved in production of copper ore in the country. Mostly copper is used in electrical equipment such as wiring and motors.
(iii)
1. Natural gas is the most environmentally friendly
2. More efficient storage and transportation compared to renewable energy.
Almost 70 percent of India’s natural gas reserves are found in Bombay High basin and in Gujarat. rest found in Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu, Maharashtra, Mumbai.
(iv) Biogas is a green energy source in form of electricity and heat for the local grid. Considerable environmental advantages – less emission of the greenhouse gasses methane, CO2 and nitrous oxide. Environmentally friendly recirculation of organic waste from industry and households.
Question 9:
(i) Mention any two problems faced by Indian farmers.
(ii) Differentiate between intensive and extensive farming.
(iii) With reference to rice cultivation answer the following:
(a) Name a state that produces the largest quantity of rice.
(b) Mention any two geographical conditions necessary for its growth.
(c) Which is the best method for its cultivation?
(iv) (a) Mention two reasons why sugarcane cultivation is gaining importance in Peninsular India.
(b) State one problem of sugarcane growers of Uttar Pradesh.
Answer:
(i) West Bengal
(ii)
| Intensive farming | Extensive farming |
|---|---|
| Located in prime location like near to the market | It remotely located |
| Per hectare output is large | Per hectare output is small |
(iii)
(a) West Bengal is the largest rice producing state in India. Almost half of its arable land is under rice cultivation. In the fiscal year 2016, the state produced about 15.75 million tonnes of rice over 5.46 million hectare cultivable area.
(b) Rice crop needs a hot and humid climate. It is best suited to regions which have high humidity, prolonged sunshine and an assured supply of water. The average temperature required throughout the life period of the crop ranges from 21 to 37º C. Maximum temp which the crop can tolerate 400C to 42 0C.
(c) Transplantation is the most commonly used method wherein seeds are first sown in nursery and the seedlings are transplanted to the main field once they show 3-4 leaves. Although this is the best yielding method, it requires heavy labor. Drilling method is exclusive to India.
(iv)
(a)
- The tropical climate of Peninsular India results in a higher yield per unit hectare of land.
- The crushing season is longer in Peninsular India, as it does not get very hot in the summer compared to North India.
(b) he agrarian crisis in UP’s sugarcane belt has been aggravated in the last few years as farmers have witnessed a slump in income, along with rising input costs. The crisis revolves around three major issues — unchanged prices, delayed or staggered payments, and exponential growth in input costs.
Question 10: (Geography Part 2 Specimen Paper 2023 ICSE )
(i) Explain the terms:
(a) Ancillary Industry
(b) Public Sector Industry
(ii) Mention two problems faced by the cotton textile industries.
(iii) From where Tata Steel gets its supply of coal, iron ore and water supply from?
(iv) What is the significance of the Electronics industry for education, entertainment and research?
Answer:
(i) (a) Ancillary industry is an industry which has fixed investment in plant and machines that do not exceed 1 crore rupees. Ancillary industry manufactures parts, components, sub-assemblies, tools, intermediates, machines etc.
(b) The public sector is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises.
(ii) Three major problems faced by the cotton textile industry in India are: i Competition from synthetic fibres which are cheaper and easy to maintain. ii Old and obsolete machinery and technology of production. iii It being an agro based industry is exposed to the vagaries of nature. Any year there is a crop failure.
(iii) Tata Iron and Steel Company is located at Jamshedpur in Jharkhand. Jamshedpur is bordered by the states of Odisha and west Bengal. Iron ore is supplied by the Gurumahisani mines in the Mayurbhanj district of Odisha and from Noamundi mines in Singhbhum district of Jharkhand
(iv)
Question 11 :
(i) What is the Golden Quadrilateral? Mention two economic benefits of it.
(ii) How is a good transport network important for India? (Two points)
(iii) Mention two advantages of railways and one disadvantage of airways.
(iv) (a) Name the terminal stations of East West Corridor.
(b) Who looks after the construction and maintenance of the following?
1. National Highways
2. Border Roads
Answer:
(i) The Golden Quadrilateral, the highway network that links many India’s four key cities – Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai thus connecting the major industrial, agricultural and cultural centres of India- is helping in the economic growth and national integrity of the country.
(ii) Transport System and Economic Development in India.
- A good transport system can broaden the market for goods. It can also make the movement of raw materials, fuel, equipment, etc. to the places of production easy.
- Further, it opens up remote regions as well as resources for production.
(iii) two advantages of railways and one disadvantage of airways
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cheaper infrastructure than rail or road | Air transport accidents are usually fatal |
| Air travel is strategically significant | Huge Initial Investments |
(iv)
1. The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) was constituted by an Act of Parliament, the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988. It is responsible for the development, maintenance and management of National Highways entrusted to it and/or matters connected or incidental thereto.
2. BRO develops and maintains road networks in India’s border areas and friendly neighboring countries. This includes infrastructure operations in 19 states and three union territories (including Andaman and Nicobar Islands) and neighboring countries such as Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Tajikistan and Sri Lanka.
Question 12: (Geography Part 2 Specimen Paper 2023 ICSE )
(i) Give two reasons why we need to manage our waste?
(ii) Mention one advantage of sanitary landfill and one disadvantage of composting.
(iii) Give reasons for the following:
(a) We should avoid using plastics.
(b) Radioactive wastes are hazardous.
(c) Open dumping is not an environment friendly method of managing waste.
(iv) How will you as an individual reduce and reuse waste at home?
Answer:
(i) Waste management is important as it saves the environment from the toxic effects of inorganic and biodegradable element present in waste. Mismanagement of waste can cause water contamination, soil erosion and air contamination. Waste can be recycled if collected and managed efficiently.
(ii) There are many advantages of sanitary landfills. The main advantage is that burying can produce energy and can be obtained by the conversion of landfill gas. The waste products of sanitary landfills can be used as direct fuel for combustion or indirectly they can be processed into another fuel.
(iii)
(iv)
1. Purchase Used or Recycled Materials :
Focus on purchasing items made from recyclable materials such as recycled paper, notebooks and folders. If you are in college and shopping for your textbooks, look to rent or purchase used ones that tend to be cheaper and work just as well as new books. Textbooks are also available to rent online, which would save paper.
2. Eco-friendly Clothing :
Clothes shopping is an important part of back-to-school shopping and kids grow so fast. Think about what clothes you can buy second-hand which is significantly more affordable and eco-friend. When you buy new clothes, consider buying fewer higher quality pieces that your kids can and avoid “fast fashion”—stylish, but low-quality, clothing that is not made to last and can fall apart easily.
3. Buy Items That Will Last:
Buy reusable water bottles, straws and lunch containers reduce trash and use of non-recyclable plastics. Reusable items will also be more cost effective in the long run and reduce the impact on the environment.
4. Support Sustainable Goods :
Choose to purchase from companies that value sustainable practices. Many retailers sell eco-friendly versions of school supplies.
For More Solution See the PDF
–: visit also :–
Return to : ICSE Specimen Paper 2023 Solved
Thanks


Not helpful .Many answers are not visible in this site.
Yeah it’s true 👍