Hydrogen Chloride Class-10 Goyal Brothers ICSE Solutions Ch-8. Step by Step Solutions of Exercise and Objective Type Questions of Goyal Brothers Prakashan ( A new approach to ICSE ) Chapter-8 Hydrogen Chloride for Class 10 . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Chemistry .
Hydrogen Chloride Class-10 Goyal Brothers ICSE Solutions Ch-8.
-: Select Topics :-
Exercise Page- 146 to147
Hydrogen Chloride Class-10 Goyal Brothers ICSE Solutions Ch-8.
Question 1. How can you obtain hydrogen chloride gas from sodium chloride?
Answer :
We produce Hydrogen Chloride in the laboratory by treating sodium chloride with concentrated sulphuric acid. We, then, heat this mixture up to 420K.
Question 2. Why should the apparatus used for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride be perfectly dry?
Answer :
Hydrogen gas is almost insoluble in water,it can be collected by displacement of water using an inverted apparatus. Hydrogen is highly explosive when mixed with air.
Question 3. With the help of a labelled diagram and balanced chemical equation give lab preparation of hydrogen chloride gas. How will you find that the gas jar is completely filled with hydrogen chloride?
Answer :
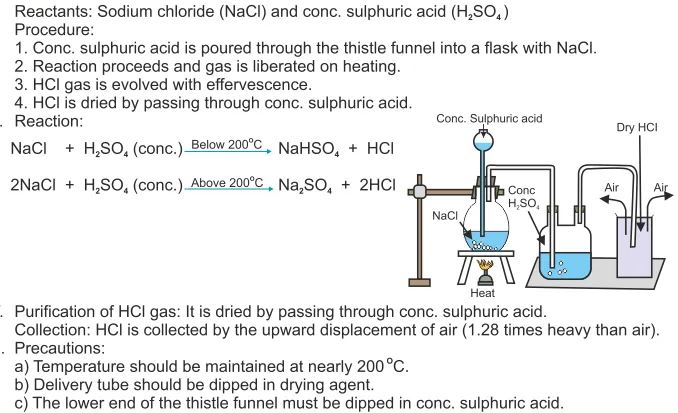
Ammonia has a characteristic sharp, choking smell. It also makes damp red litmus paper turn blue. Ammonia forms a white smoke of ammonium chloride when hydrogen chloride gas, from Concentrated hydrochloric acid, is held near it.
Question 4. How does hydrochloric acid gas (dry) react with (a) Magnesium metal (b) Aqueous silver nitrate solution (c) Lead nitrate solution (d) Ammonium hydroxide solution? Support your answer by fully balanced chemical equations.
Answer :
How does hydrochloric acid gas (dry) react with
(a) Magnesium metal—Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the equation:
Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) –> MgCl 2(aq) + H 2(g)
(b) Aqueous silver nitrate solution—
AgNO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + HNO3 (aq)
(c) Lead nitrate solution–
Pb(NO3)2 + 2 HCl → PbCl2 + 2 HNO3
(d) Ammonium hydroxide solution–
HCl + NH4OH → H2O + NH4Cl
Question 5. Describe an experiment to prove that hydrogen chloride gas is (i) extremely soluble in water (ii) acidic in nature.
Answer :
(i)
experiment to prove that hydrogen chloride gas is extremely soluble in water refer to page number-141
(ii) acidic in nature.
turning blue solution into red in fountain experiment proving that it is acidic in nature
Question 6. How is hydrochloric acid obtained from hydrogen chloride gas? Support your answer by drawing a neat diagram, stating clearly why the arrangement shown in the diagram is most suitable.
Answer :
preparation of hydrochloric acid. In this an inverted funnel is attached to the source of HCl gas. The funnel is placed over a trough filled with water and the end of the funnel should touch the surface of water. HCl gas passes through the funnel and gets dissolved in water
for figure refer page number-143
Question 7. How does dilute hydrochloric acid react with the following? Support your answer by fully balanced chemical equations (i) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (ii) Magnesium carbonate (iii) Copper (II) oxide (iv) Zinc hydroxide (v) Potassium sulphite (vi) Potassium hydrogen sulphite (vii) Iron (II) sulphide (viii) Sodium hydrogen sulphide (ix) Sodium nitrite (x) Sodium thiosulphate.
Answer :
How does dilute hydrochloric acid react with the following?
(i) Sodium hydrogen carbonate-
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + CO2 + H2O
(ii) Magnesium carbonate—
MgCO3 + HCl = MgCl2 + CO2 + H2O
(iii) Copper (II) oxide
CuO(s) + 2HCl(aq) = CuCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
(iv) Zinc hydroxide
Zn(OH)2 + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + 2H2O
(v) Potassium sulphite
K2SO3 + HCL = 2KCL + H2O + SO2.
(vi) Potassium hydrogen sulphite
KHSO4 + HCl–KCl+H2O+SO2
(vii) Iron (II) sulphide–
FeS (s) + 2HCl (aq) → FeCl2 (s) + H2S
(viii) Sodium hydrogen sulphide
NaHSO4 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + SO2
(ix) Sodium nitrite
3NaNO2 + 2HCl  2NaCl + NaNO3 + 2NO + H2O
2NaCl + NaNO3 + 2NO + H2O
(x) Sodium thiosulphate.
Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → S(s) + SO2(g) + 2NaCl(aq) +H2O
Question 8. What is aqua regia? How does it dissolve (1) platinum (ii) gold?
Answer :
Aqua regia is a mixture of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO3) at a ratio of either 3:1 or 4:1. It is a reddish-orange or yellowish-orange fuming liquid. The term is a Latin phrase, meaning “king’s water”. The name reflects the ability of aqua regia to dissolve the noble metals gold, platinum, and palladium.
Question 9. Give four uses of hydrochloric acid.
Answer :
In the manufacture of batteries, photoflash bulbs, and fireworks, hydrochloric acid is also used. It is even used for sugar processing and gelatin production. Like last month’s chlorine compound, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid is another chemical “workhorse” because it is extremely useful in a wide variety of ways
Question 10. Give two chemical tests of hydrochloric acid.
Answer :
Two tests for hydrochloric acid are –
(i) When silver nitrate solution is added to hydrochloric acid, it gives white precipitate of silver chloride. (ii) When lead nitrate solution is added to it, it gives white precipitate of lead chloride.
Question 11. Hydrogen gas is burnt in a gas P when another gas R is formed. Gas. R gives dense white fumes with ammonia liquor. Name the the gases gases P and R. Support your answer by gas chemical equations.
Answer :
P is ammonia
R is HCl
Hydrogen chloride gas gives dense white fumes (of ammonium chloride) with ammonium hydroxide.
(1) P and magnesium (ii) Aqueous solution of R and silver nitrate solution
Answer :
NH3+ HCl (P)——-NH4Cl
AgNO3 +HCl (R) —– HNO3 + AgCl (curdy white ppt)
Objective Type Questions page – 147 to 148
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Class-10 Hydrogen Chloride Goyal Brothers ICSE Solutions Ch-8
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
- ……………
- ………………
- ……………………
- …………….
- ……………
- ………….
- …………
- ………….
- …………..
- ………………
- …………….
- …………………..
- ……………………….
- ……………………….
- ……………..
- …………………….
- ………………………
- ……………………..
II. Fill in the blanks spaces with the choice given in brackets:
- ………..Muriatic acid……………
- ………..Gastric Juice…………..
- ……….explosive………………
- …………Sulphuric acid……………
- …………Sodium Chloride……………
- ………..below………………
- ……….18.5…………
- ………….450……………..
- ……….Con Sulphuric Acid……………
- …………….Ammonium Hydroxide……………..
III. Choose from the following list, as what matches the descriptions given below.
[Hydrogen, carbon dioxide gas, silver chloride, HNO3 ,, chlorine, fountain experiment, lead nitrate, sulphur, sodium sulphate, sodium nitrate]
1. Name of experiment which shows that hydrogen chloride gas is extremely soluble in water.–-fountain experiment
2. A gas liberated when dilute hydrochloric acid is treated with magnesium.–Hydrogen
3. A coloured gas which reacts with hydrogen gas to form hydrogen chloride gas.—chlorine
4. A gas liberated when calcium hydrogen carbonate is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.—carbon dioxide gas
5. A white precipitate formed when sodium chloride solution is treated with silver nitrate solution.–-silver chloride
6. A concentrated acid (1 part) which forms aqua regia, when mixed with three parts of conc. hydrochloric acid.—HNO3
7. An element liberated when sodium thiosulphate solution reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.—-sulphur,
8. A salt of sodium on treating with dilute hydrochloric acid liberates sulphur dioxide gas.—-sodium sulphate
9. A salt of sodium which on heating with conc. hydrochloric acid liberates nitrogen dioxide gas.—sodium nitrate
10. A nitrate of a metal (other than silvery nitrate), which forms white precipitate when treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.—lead nitrate
–: end of Hydrogen Chloride Solutions Goyal Brothers
Return of : Chemistry Class-10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Thanks
Share with your friends

There are not ginen answers of MCQ and Fill in the Blanks so please give the answers of all objectives type question it will be very helpful for us
Do your self if feel difficulty on any chapter whatsapp the image of exercise on 8948221203 we will send or explain answer without any cost.