ICSE Chemistry 2021 Specimen Paper for Class-10 Solved on further reduced Syllabus. Specimen Sample model Paper of Chemistry for ICSE Class-10 is helpful for student appearing in 2021 exam of council. This paper content is based on further reduced syllabus as latest council guideline for 2021 exam. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Physics.
ICSE Chemistry 2021 Specimen Sample model Paper for Class-10 Solved
- Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separates
- you will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.This time is to be spent in reading the Question Paper.
- The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
- Attempt all the questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
SECTION I (40 Marks)
ICSE Chemistry 2021 Specimen Paper for Class-10 Solved on further reduced Syllabus
Attempt all questions from this Section
Question-1
(a) Fill in the blanks from the choices given in brackets: [5]
(i) The energy required to remove an electron from a neutral isolated gaseous atom and convert it into a positively charged gaseous ion is called ………. (electron affinity, ionisation potential, electronegativity)
(ii) The compound that does not have a lone pair of electrons is (water, ammonia, carbon tetrachloride)
(iii) When a metallic oxide is dissolved in water, the solution formed has a high concentration of ions. (H+, H3O+, OH–)
(iv) Potassium sulphite on reacting with hydrochloric acid releases ………….. gas. (Cl2, SO2, H2S)
(v) The compound formed when ethene reacts with Hydrogen is ………………………… (CH4, C2H6, C3H8)
(b) Give one word or a phrase for the following statements: [5]
(i) The energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous isolated atom to form a negatively charged ion.
(ii) Process of formation of ions from molecules which are not in ionic state.
(iii) The tendency of an element to form chains of identical atoms.
(iv) The property by which certain hydrated salts, when left exposed to atmosphere, lose their water of crystallization and crumble into powder.
(v) The process by which sulphide ore is concentrated.
(c) Choose the correct answer from the options given below: [5]
(i) An element with the atomic number 19 will most likely combine chemically with the element whose atomic number is:
(A) 17 (B) 11 (C) 18 (D) 20
(ii) The ratio between the number of molecules in 2g of hydrogen and 32g of oxygen is:
(A) 1 : 2 (B) 1 : 0.01 (C) 1 : 1 (D) 0.01 : 1
[Given that H = 1, O = 16]
(iii) The two main metals in Bronze are:
(A) Copper and zinc (B) Copper and lead
(C) Copper and nickel (D) Copper and tin
(iv) The particles present in strong electrolytes are:
(A) Only molecules (B) Mainly ions
(C) Ions and molecules (D) Only atoms
(v) The aim of the Fountain Experiment is to prove that:
(A) HCl turns blue litmus red
(B) HCl is denser than air
(C) HCl is highly soluble in water
(D) HCl fumes in moist air.
(d) Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following : [5]
(i) Action of concentrated sulphuric acid on carbon.
(ii) Reaction of sodium hydroxide solution with iron (III) chloride solution.
(iii) Action of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
(iv) Reaction of zinc with potassium hydroxide solution.
(v) Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on magnesium sulphite.
(e) State one relevant observation for each of the following : [5]
(i) Lead nitrate solution is treated with sodium hydroxide solution drop wise till it is in excess.
(ii) At the anode, when molten lead bromide is electrolyzed using graphite electrodes.
(iii) Lead nitrate solution is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid and heated.
(iv) Anhydrous calcium chloride is exposed to air for sometime.
(v) Barium chloride solution is slowly added to sodium sulphate
(f) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Iron is rendered passive with fuming nitric acid.
(ii) An aqueous solution of sodium chloride conducts electricity.
(iii) Ionisation potential of the element increases across a period.
(iv) Alkali metals are good reducing agents.
(v) Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quick lime. [5]
(g)
(i) Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: [5]
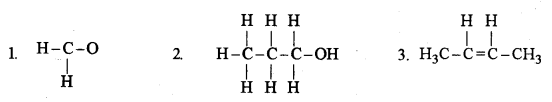
(ii) Write the structural formula of the two isomers of butane.
(h)
(i) Calculate the number of gram atoms in 4.6 grams of sodium (Na = 23). [5]
(ii) Calculate the percentage of water of crystallization CuSO4.5H2O (H = 1,O = 16, S = 32, Cu = 64)
(iii) A compound of X and Y has the empirical formula XY2. Its vapour density is equal to its empirical formula weight. Determine its molecular formula.
SECTION II (40 Marks)
ICSE Chemistry 2021 Specimen Sample model Paper for Class-10 Solved on further reduced Syllabus
Attempt any four questions from this Section
Question 2.
(a) Arrange the following as per the instruction given in the brackets:
(i) He, Ar, Ne (Increasing order of the number of electron shells)
(ii) Na, Li, K (Increasing Ionisation Energy)
(iii) F, Cl, Br (Increasing electronegativity)
(iv) Na, K, Li (Increasing atomic size)
(b) State the type of Bonding in the following molecules: [2]
(i) Water
(ii) Calcium oxide
(c) State your observation in each of the following cases:
(i) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate crystals.
(ii) When excess sodium hydroxide is added to calcium nitrate solution.
(iii) At the cathode when acidified aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolyzed with copper electrodes.
(iv) When calcium hydroxide is heated with ammonium chloride crystals.
(v) When moist starch iodide paper is introduced into chlorine gas. [5]
Question-3
(a) Study the figure given below and answer the questions that follow:

(i) Identify the gas Y.
(ii) What property of gas Y does this experiment demonstrate?
(iii) Name another gas which has the same property and can be demonstrated through this experiment. [3]
(b)
(i) Name the other ion formed when ammonia dissolves in water.
(ii) Give one test that can be used to detect the presence of the ion produced. [2]
(c) Match the following: [5]
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Acid salt | A. Ferrous ammonium Sulphate |
| 2. Double salt | B. Contains only ions |
| 3. Ammonium hydroxide solution | C. Sodium hydrogen sulphate |
| 4. Dilute hydrochloric acid | D. Contains only molecules |
| 5. Carbon tetrachloride | E. Contains ions and molecules |
Question-4
(a)
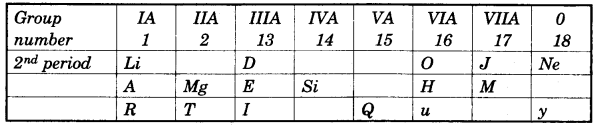
In this table H does not represent hydrogen. Some elements are given in their own symbol and position in the periodic table. While others are shown with a letter.
With reference to the table answer the following questions:
(i) Identify the most electronegative element. [1]
(ii) Identify the most reactive element of group 1. [1]
(iii) Identify the element from period 3 with least atomic size. [1]
(iv) How many valence electrons are present in Q? [1]
(v) Which element from group 2 would have the least ionization energy? [1]
(vi) Identify the noble gas of the fourth period. [1]
(vii) In the compound between A and B what type of bond would be formed and give the molecular formula for the same. [2]
(b) Name the following metals:
(i) A metal present in cryolite other than sodium.
(ii) A metal which is unaffected by dilute or concentrated acids.
(iii) A metal present in period 3, group 1 of the periodic table. [3]
(c) The following questions are based on the preparation of ammonia gas in the laboratory:
(i) Explain why ammonium nitrate is not used in the preparation of ammonia.
(ii) Name the compound normally used as a drying agent during the process.
(iii) How is ammonia gas collected?
(iv) Explain why it is not collected over water. [4]
Question-5
(a)
(i) A compound has the, following percentage composition by mass:
carbon 14.4%, hydrogen 1.2% and chlorine 84.5%. Determine the empirical formula of this compound. Work correct to 1 decimal place. (H = 1; C = 12; Cl = 35.5).
(ii) The relative molecular mass of this compound 168, so what is its molecular formula?
(b) Mr. John wants to electroplate his key chain with nickel to prevent rusting. For this electroplating:
(i) Name the electrolyte
(ii) Name the cathode
(iii) Name the anode
(iv) Give the reaction at the cathode
(v) Give the reaction at the anode.
(c) By the addition of only one solution how would you distinguish between dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid?
Question-6
(a) Give a reason for each of the following: [5]
(i) Ionic compounds have a high melting point.
(ii) Inert gases do not form ions.
(iii) Ionisation potential increases across a period, from left to right.
(iv) Alkali metals are good reducing agents.
(v) Conductivity of dilute hydrochloric acid is greater than that of acetic acid.
(b)
(i) Name the most common ore of the metal aluminum from which the metal is extracted. Write the chemical formula of the ore. [4]
(ii) Name the process by which impure ore of aluminum gets purified by using concentrated solution of an alkali.
(in) Write the equation for the formation of aluminum at the cathode during the electrolysis of alumina.
(c) Three solutions P, Q and R have pH value of 3.5, 5.2 and 12.2 respectively. Which one of these is a :
(i) Weak acid?
(ii) Strong alkali ?
Question-7
(a) Complete the following equations : [3]
(i) S + cone. HNO3 →
(ii) C + cone. H2SO4 →
(iii) Cu + dil.HNO3 →
(b) Answer the following questions based on the extraction of aluminium from alumina by Hall – Heroult’s Process: [4]
(i) What is the function of cryolite used along with alumina as the electrolyte?
(ii) Why is powdered coke sprinkled on top of the electrolyte?
(iii) Name the electrode, from which aluminium is collected.
(c)
(a) Give the chemical formula of: [3]
(i) Bauxite
(ii) Cryolite
(iii) Sodium aluminate
Solutions of ICSE Chemistry 2021 Specimen Sample model Paper for Class-10
( on further reduced Syllabus)
Answer: 1
(a)
(i) ionisation potential
(ii) carbon tetrachloride
(iii) OH–
(iv) SO2
(v) C2H6
(b)
(i) Electron affinity
(ii) Ionisation
(iii) Catenation
(iv) Efflorescence
(v) Froth floatation process.
(c)
(i) (A) 17
(ii) (C) 1 : 1
(iii) (D) Copper and tin
(iv) (B) Mainly ions
(v) (C) HCl is highly soluble in water.
(d)
(i) C + 2H2SO4 → 2H2O + 2SO2↑ + CO2↑
(ii) FeCl3 + 3NaOH → Fe(OH)3 + 3Nacl
(iii) 2Al(OH)3——Al2O3 + 3H2O
(iv) Zn + 2KOH → K2ZnO2 + H2O
(v) MgSO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + SO2↑
(e)
(i)
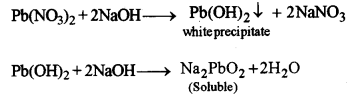
When drop by drop of sodium hydroxide is added, chalky white precipitates appear. These precipitates dissolve in excess of sodium hydroxide forming sodium plumbite.
(ii)
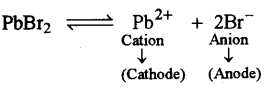
At Anode
2Br– – 2e– → 2Br
Br+Br → Br2↑
At anode reddish vapours of bromine escape in air from lead bromide.
(iii)
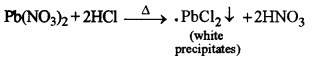
White precipitates of lead chloride are formed which are soluble in hot water and insoluble in cold water.
(iv) Anhydrous calcium chloride absorbs moisture becomes moist and loose its crystalline form showing its deliquescent nature.
(v) BaCl2+Na2SO4 → BaSO4+2NaCl
(f)
(i) Cone. HNO3 being a strong oxidising agent oxidises iron, forming a layer that makes iron non reactive or passive.
(ii) Aqueous solution of sodium chloride contains mobile ions like Na+, Cl–, H+, OH–, H3O+ etc. so they conduct electricity.
(iii) Atomic size decreases and nuclear charges increases as we move from left to right in a period so energy required to remove one electron from the valence shell increases from left to right thus ionisation potential increases.
(iv) Alkali metals readily lose electrons from their valence shell and get oxidised. So they behave as good reducing agents.
(v) Hydrogen chloride is acidic whereas quick lime is basic. So they will react with each other hence quick lime can not be used to dry hydrogen chloride.
(g)
(1) Methanal
(2) Propanol
(3) But-2-ene
(ii)
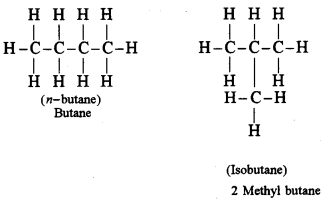
(h)
(i) 23 g of sodium → 1 gram atom
1 g of sodium → 123 gram atom
4.6 g of sodium → = 123×4.610=2100 =0.02gatoms
(ii) Molecular mass of CUSO4.5H2O
= [64 + 32+4 x 16] + 5[18] – [64 + 32+64] + [90]
= 160+90
= 250
% of water of crystallisation =90250×100
= 36%
(iii) E.F. = XY2
E.F.W. = V.D.
M.W. = 2 × V.D.
M.W. = 2 × [E.F.W.]
So molecular formula = (XY2)2 = X2Y4
Answer-2
(a)
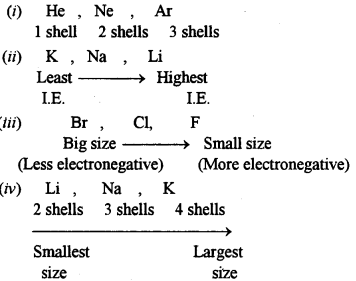
(b)
(i) Covalent bonding
(ii) Ionic bonding
(c)
(i) Brisk effervescence with the release of a colourless odourless gas that extinguish a glowing splint and turns lime water milky i.e., CO2 gas is released.
(ii) A white ppt of Ca(OH)2 is obtained that remains insoluble in excess of NaOH.
(iii) The blue colour of aq.CuSO4 remains unchanged.
(iv) A colourless pungent smelling basic gas i.e., Ammonia is obtained.
(v) Moist starch iodide paper turns blue black.
Answer-3
(a)
(i) Hydrogen chloride gas (HCl).
(ii) Y Gas i.e., HCl gas is highly soluble and acidic in nature.
(iii) Ammonia gas.
(b)
(i) Hydroxyl ion (OH–) other than Ammonium ion.
(ii) Red litmus turns blue/Methyl orange yellow/Phenolphthalein turns
pink.
(c)
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Acid salt | C. Sodium hydrogen sulphate |
| 2. Double salt | A. Ferrous ammonium Sulphate |
| 3. Ammonium hydroxide solution | E. Contains ions and molecules |
| 4. Dilute hydrochloric acid | B. Contains only ions |
| 5. Carbon tetrachloride | D. Contains only molecules |
Answer-4
(a)
(i) J
(ii) R
(iii) M
(iv) 5 electron
(v) T
(vi) y
(vii)
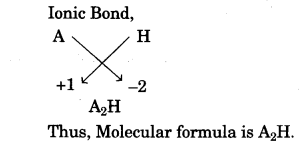
(b)
Aluminium
Gold
Sodium
(c)
(i) Ammonium nitrate is a highly explosive substance and can not be heated.
(ii) Quicklime/CaO.
(iii) By downward displacement of air or upward delivery as it is lighter than air.
(iv) Ammonia is highly soluble in water so it cannot be collected over water.
Answer-5
(a)
| Element | Percentage | At. Mass | Relative No.of atoms | Simplest ratio |
| C | 14.4 | 12 | 14.4/12 = 1.2 | 1.2/1.2 = 1 |
| H | 1.2 | 1 | 1.2/1 = 1.2 | 1.2/1.2 = 1 |
| Cl | 84.5 | 35.5 | 84.5/35.5 = 2.4 | 2.4/1.2 = 2 |
Empirical formula = CHCl2
(ii) Relative molecular mass = 168
Empirical formula mass = 12 + 1 + 71 = 84
𝑛=Relative molecular mass empirical formula mass =16884=2
Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
= (CHCl2)2
= C2H2Cl4.
(b)
(i) Aqueous solution of Nickel Sulphate with few drops of dil. Sulphuric acid.
(ii) The key chain.
(iii) Pure Nickel bar.
(iv) Ni++ + 2e– → Ni
(v) Ni – 2e– → Ni++
(c) Add silver nitrate solution. White ppt of silver chloride obtained with dil. hydrochloric acid. No. ppt obtained with dil. nitric acid.
Answer-6
(a)
(i) Ionic compounds have ions held strongly by electrostatic forces of attraction. These strong forces need more energy to be broken apart. Hence, they have high melting point.
(ii) Inert gases do not form ions because they have completely filled octet. They are extremely stable. Hence, they neither loose, nor gain electrons.
(iii) As we move from left to right along a period, the atomic size decreases due to the increase in nuclear charge thus more energy is required to remove the electron, hence ionisation potential increase.
(iv) Alkali metals have free electrons. They can easily loose electrons to form positive ions. The loss of electron is known as oxidation and the substance/element that lose electrons is said to be reducing agent.
(v) Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid. It splits to give more hydrogen ions as compared to acetic acid. Hence conductivity of dilute hydrochloric acid is more than that of acetic acid.
(b)
(i) Bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O)
(ii) Baeyer’s process
(iii)
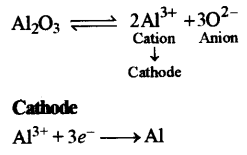
(c)
P=3.5
Q=5.2
R= 12.2
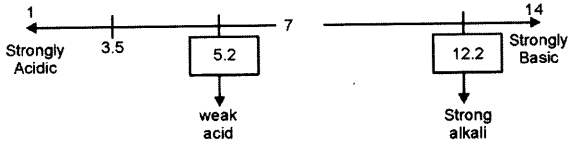
(i) Weak acid = Q
(ii) Strong alkali = R
Answer-7
(a)
(i) S + 6HNO3 → H2 SO4 + 6NO2 + 2H2O
(ii) C + 2H2SO4 → 2H2O + CO2 + 2S02
(iii) 3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3CU(NO3 )2 + 2NO + 4H2O
(b)
(i) Cryolite acts as a solvent and lower the fusion temperature from 2050°C to 950°C.
(ii) A layer of powdered coke is sprinkled over the surface of the electrolyte to reduce the heat loss by radiation and prevent the carbon rod from binning in air.
(iii) Cathode
(c)
(i) Al2O3. 2H2O
(ii) Na3AlF6
(iii) NaAlO2
–: End of ICSE Chemistry 2021 Specimen paper : —
Return to – Specimen paper-2021 for icse class-10
Thanks
Please share with your friends

i wish i had friends to share this with<3
thanks