Laws of Motion Exe-3D Newton’s Third Law Short Answer Type for Class-9 ICSE Concise Physics. There is the solutions of short Answer type Questions of your latest textbook which is applicable in 2025-26 academic session. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Laws of Motion Exe-3D Newton’s Third Law Short Answer
(ICSE Class – 9 Physics Concise Selina Publishers)
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 9th |
| Subject | Physics |
| Writer / Publication | Concise selina Publishers |
| Chapter-3 | Laws of Motion |
| Exe – 3D | Newton’s Third Law |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-3(D) Short Answer Type |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Exe-3D Newton’s Third Law Short Answer Type
Ch-3 Laws of Motion Physics Class-9 ICSE Concise
Page 81
Que-1: State the Usefulness of Newton’s third law of motion.
Ans: Newton’s third law explains how a force acts on an object.
Que-2: State and explain the law of action and reaction. by giving two examples.
Ans: Law of action and reaction: In an interaction of two bodies A and B, the magnitude of action, i.e. the force FAB applied by the body B on the body A, is equal in magnitude to the reaction, i.e., the force FBA applied by the body A on the body B, but they are in directions opposite to each other.
Examples of Law of action and reaction
(i) When a book is placed on a table, it does not move downwards. It implies that the resultant force on the book is zero, which is possible only if the table exerts an upward force of reaction on the book, equal to the weight of the book.
(ii) While moving on the ground, we exert a force by our feet to push the ground backwards; the ground exerts a force of the same magnitude on our feet forward, which makes it easier for us to move.
Explanation of Law of action and reaction
In the above stated example, there are two objects and two forces. the first example, the weight of the book acts downwards (action) and the force of the table acts upwards (reaction).
while In the second example, our feet exerts a force on the ground (action) and the ground exerts an equal and opposite force (reaction) on our feet.
Que-3: Explain the motion of a rocket with the help of Newton’s third law.
Ans: When a rocket moves in space, it pushes gases outside, i.e. the rocket applies force on the gases in the backward direction. As a reaction, the gases put equal amount of force on the rocket in the opposite direction and the rocket moves in the forward direction.

Que-4: When a shot is fired from a gun, the gun is recoiled. Explain.
Ans: When a man fires a bullet from a gun, a force F is exerted on the bullet (action), and the gun experiences an equal and opposite recoil (reaction) and hence gets recoiled

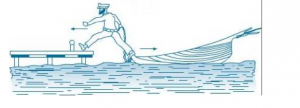
Que-5: When you step ashore from a stationary boat, it tends to leave the shore. Explain.
Ans: When a man exerts a force (action) on the boat by stepping into it, its force of reaction makes him step out of the boat, and the boat tends to leave the shore due to the force exerted by the man (i.e. action).
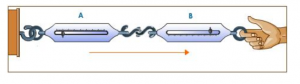
Que-6: When two spring balances joined at their free ends are pulled apart, both show the same reading. Explain.
Ans: Couple two spring balances A and B as shown in the figure. When we pull the balance B, both the balances show the same reading indicating that both the action and reaction forces are equal and opposite. In this case, the pull of either of the two spring balances can be regarded as action and that of the other balance as the reaction
(Laws of Motion Exe-3D Short Class-9 ICSE)
Que-7: To move a boat ahead in water, the boatman has to push the water backwards by his oar. Explain.
Ans: To move a boat, the boatman pushes (action) the water backwards with his oar. In this response, the water exerts an equal and opposite force (reaction) in the forward direction on the boat due to which the boat moves ahead.
Que-8: A person pushing a wall hard is liable to fall backwards. Give reason.
Ans: A person pushing a wall hard (action) by his palm, experiences a force (reaction) exerted by the wall on his palm in the opposite direction; thus, he is liable to fall backwards.
Que-9: A light ball falling on ground, after striking the ground rises upwards. Explain the reason.
Ans: When a falling ball strikes the ground, it exerts a force on the ground. The ground exerts a force back at the ball in the opposite direction. This is the reason the ball rises upwards.
— : End of Laws of Motion Exe-3D Newton’s Third Law Short Answer Type Solutions :–
Return to Concise Selina Physics ICSE Class-9 Solutions
Thanks
Please share with your friends


