Mixtures Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-1 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Unit-2 Mixtures Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-2. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -2 Questions and Answers of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6.
Mixtures Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-2 Unit-2
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 6th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-2 | Elements, Compounds and Mixtures |
| Unit-2 | Mixtures |
| Topic | Solution of exercise questions |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Exercise-1
Mixtures Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-2 Unit-2
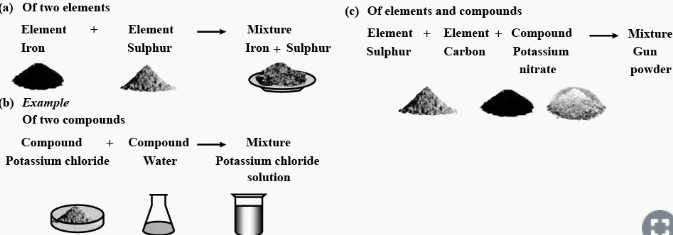
Question: 1. Explain the term mixtures. Give an example of mixtures of –
a] two elements
b] two compounds
c] elements and compounds
Answer: Mixture : A mixture is an impure substance made up of two or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proportion.
Examples:
Question: 2. Differentiate between homogeneous & heterogeneous mixtures with suitable examples.
Answer: The main characteristics of the mixture (Iron + Sulphur) are :
Homogeneous mixtures :
- There constituents are uniformly mixed.
- The properties and composition are the same throughout the mixture.
Examples:
- alcohol and water
- salt and water
- sugar and water
Heterogeneous mixtures :
- Their constituents are not uniformly mixed.
- The properties and composition vary throughout the mixture.
Examples:
- oil and water
- sand and water
- chalk and water
Question: 3. With reference to the mixture of iron and sulphur, state the main characteristics of mixture .
Answer: The main characteristics of the mixture (Iron + Sulphur) are:
- The mixture of iron and sulphur may contain iron and sulphur in varying proportions.
- The original properties of each element are retained in the mixture of iron and sulphur.
- The mixture of the two elements iron and sulphur can be separated by i.e. a physical method, i.e. by using a magnet since iron is attracted to the magnet.
Question: 4. Tabulate a comparative chart – to differentiate between elements, compounds, & mixtures.
Differentiate them with reference to –
a] the term
b] existence
c] properties
d] separation of components
Answer: (a) Term – Elements – Pure substance made up of one kind of atoms only. e.g. Iron [Fe], Sulphur [S]
Compounds – Pure substance made up of two or more different elements, e.g. Iron sulphide [FeS]
Mixtures – Impure substance made up of two or more elements or compounds, e.g. Iron and sulphur mixture.
(b) Existence – Elements-Elements i.e. atoms are present on their own. e.g. Iron and sulphur exist on their own as elements iron and sulphur.
Compounds – Components in a compound present in a definite proportion. e.g. Iron and sulphur are chemically combined in a fixed ratio in iron sulphide.
Mixtures – Components in a mixture present in any proportion. e.g. Iron and sulphur are mixed in any ratio in the mixture of iron and sulphur.
(c) Properties – Elements – Elements have a definite set of properties. Elements classified into metal and non-metals each with its own properties. Compounds – Compounds have a definite set of properties. Elements of a compound do not retain their original properties.
Mixtures – Mixture not have a definite set of properties. Components of a mixture do retain their original properties.
(iv) Separation of compound- Elements – Elements occur on their own or as compounds and can be separated by chemical and physical methods. Example : Iron, copper.
Compounds – Elements in a compound are chemically combined and can be separated by chemical methods only. Example : Iron Sulphide, copper oxide.
Mixtures – Components in a mixture can be separated by physical methods only. Example : Iron + sulphu
Question: 5. State the principle involved in separation of solid-solid mixtures by –
a] sieving
b] magnetic separation
c] sublimation
Answer: (a) Sieving Principle – Based on the difference in the size of the solid particles.
Example – Mixture of rice and soil
(b) Magnetic separation Principle – One component of the mixture is a magnetic substance.
Example – Mixture of iron and sand.
(c) Sublimation Principle – One of the components sublimes on heating.
Question: 6. State the principle involved in separation of solid-liquid mixtures by –
a] sedimentation & decantation
b] filtration
c] evaporation
Answer: (a) Sedimentation and decantation Principle – The solid component is insoluble and heavier than the liquid component. Example – Mixture of sand and water
(b) Filtration-Principle – Separation of insoluble solid component by passing through a porous material like filter paper. Example – Mixture of chalk and water, Mixture of Agcl and Water.
(c) Evaporation – Principle – Separation of the mixture by evaporating the liquid component. The solid should be soluble in the liquid and should not sublime.
Question: 7. Explain the term ‘sieving’. State the structure of a sieve and explain the separation of different sized particles by sieving.
Answer: Sieving – is a method of separation, which is used for separating substances of different sizes that cannot be separated in hand picking.
Principle – Based on the difference in size of the solid particles.
Technique of Separation – The large sized particles are separated from the small or finer particles by passing the mixture through a sieve. The sieve has a wooden frame, with a metal mesh at its base. The mixture is added from the top of the sieve, when the larger particles stay above and the finer particles collect below it on shaking the sieve.
Examples – Separation of rice powder from soil, separation of different sized particles of diamond and of sand.
Question: 8. State what is meant by ‘magnetic separation of two mixtures’. Explain how iron particles can be separated from sulphur particles.
Answer: Magnetism is ideal for separating mixtures of two solids with one part having magnetic properties. Some metals like iron, nickel and cobalt have magnetic properties whiles gold, silver and aluminum do not. Magnetic elements are attracted to a magnet.
Principle- Based on the difference in magnetic and non-magnetic nature of particles.
Technique of Separation – The magnetic particles such as iron are separated from the non-magnetic particles such as sulphur – by utilizing the magnetic properties of iron. The iron gets attracted to the magnet and seperates from the non-magnetic substance.
Question: 9. Give a reason why sublimable & non-sublimable substances can be separated easily, but two sublimable substances cannot.
Answer: While seperating the mixture sublimable and non- sublimable substances, sublimable substance turns directly into vapour on heating whereas non-sublimable solid remains behind. Since, if we try to separate the mixture of two sublimable substances, then both the sublimable substances turns into vapour on heating and vapour on cooling give back the pure same solid.
Question: 10. Explain the technique for separating – insoluble solid particles in a solid-liquid mixture.
Answer: The insoluble solid particles in a solid-liquid mixture can be separated by filtration.
Technique of Separation – A filter paper is made into a cone & placed in a funnel. The solid particles remain behind on the filter paper while the liquid collects below.
Question: 11. Differentiate between the terms – sedimentation & decantation with a suitable experimental technique.
Answer: Sedimentation is defined as the process of settling down of the heavier components present in a mixture. For example: When the mixture of sand in water is allowed to stand undisturbed for some time, it is observed that sand settles at the bottom.
For example: When a mixture of sand and water is allowed to stand, sand settles at the bottom of a container since it is heavier. Water is present in the upper portion of the container. This can be separated from sand settled at the bottom simply by pouring in a different container without using any other separating device. This is known as decantation.
Question: 12. Explain how a solid component is separated – in a soluble solid-liquid mixture.
Answer: A Solid component is separated in a soluble solid-liquid mixture by evaporation.
Principle – Separation of the mixture by evaporating the liquid component. The solid should be soluble in the liquid and should not sublime.
Technique of Separation : The soluble solid can be separated from its liquid component by allowing the liquid component to evaporate either on its own or by heating. During evaporation, the liquid component is lost to the atmosphere & the solid remains behind.
Example : Evaporation of a common salt solution or sea water leaves behind common salt. Common salt remains behind whereas water lost to the atmosphere.
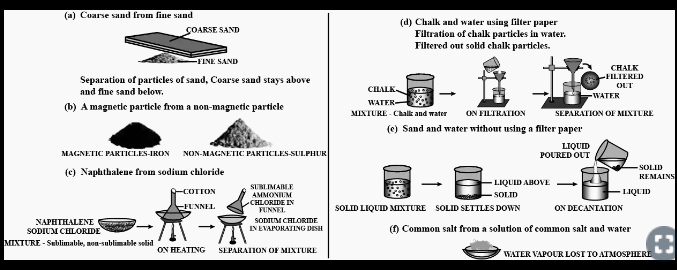
Question: 13. Draw a neat labelled diagram for separation of the following mixtures.
a] Coarse sand from fine sand
b] A magnetic particle from a non-magnetic particle
c] Naphthalene from sodium chloride
d] Chalk & water using a filter paper
e] Sand & water without using a filter paper
f] Common salt from a solution of common salt & water
Answer:
Question: 14. State the technique involved in separating the following:
a] Iodine crystals & potassium chloride
b] Iron & chalk powder
c] Potassium chloride from an aqueous solution of potassium chloride
d] Rice powder from soil particles
e] Iron filings from pieces of copper wire
f] Large diamonds from very small diamonds
Answer: (a) Iodine crystals and potassium chloride: Sublimation (iodine is sublimable)
– : End of Mixtures Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-2 Unit-2 :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-6 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.


