ML Aggarwal Construction of Quadrilaterals Exe-14.2 Class 8 ICSE Ch-14 Maths Solutions. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exe-14.2 Questions for Construction of Quadrilaterals as council prescribe guideline for upcoming board exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-8.
ML Aggarwal Construction of Quadrilaterals Exe-14.2 Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Avichal Publishig Company (APC) |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 8th |
| Chapter-14 | Construction of Quadrilaterals |
| Writer | ML Aggarwal |
| Book Name | Understanding |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-14.2 Questions |
| Edition | 2023-2024 |
Construction of Quadrilaterals Exe-14.2
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-258
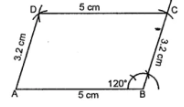
Question 1. Construct a parallelogram ABCD such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 3·2 cm and ∠B 120°.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AB = 5 cm
(ii) At B, Construct angle = 120°
(iii) With B as centre and 3·2 cm as radius cut off ∠B at C.
(iv) With C as centre and AB as radius draw an arc.
(v) With A as centre and 3·2 cm as radius
draw an arc which meets the previous arc at D.
(vi) Join AD and CD.
Then ABCD is required parallelogram
Question 2. Construct a parallelogram ABCD such that AB = 4·8 cm, BC = 4 cm and diagonal BD = 5·4 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Construct a triangle ABD.
(ii) With B as centre and 4 cm as radius draw an arc.
(iii) With Das centre and 4·8 cm as radius,
draw an arc which meets the previous arc at C.
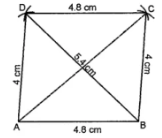
(iv) Join CD, BC and AC
(v) Then ABCD is the required parallelogram.
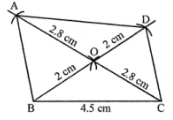
Question 3. Construct a parallelogram ABCD such that BC = 4·5 cm, BD = 4 cm and AC = 5·6 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Construct a ∆ BOC with BC = 4·5 cm,
BO = 1/2 × 4 = 2 cm
and OC = 1/2 AC = 1/2 × 5.6 = 2·8 cm
(∵ Diagonals of ||gm bisect each other)
(ii) Produce OC to A such that OC = OA
(iii) Produce BO to D such that OD = OB.
(iv) Join AD, then ABCD is the required parallelogram.
Question 4. Construct a parallelogram ABCD such that AC = 6 cm, BD = 4·6 cm and angle between them is 45°.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AO = 1/2 AC = 3 cm and produce AO to C
such that OC = OA.
(ii) At O, construct ∠COP = 45°.
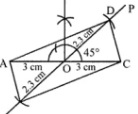
(iii) From OP, cut OD = 1/2 BD = 1/2 × 4·6 cm = 2·3 cm.
(iv) Produce OD to OB such that OB = OD.
(v) Join AB, BC, CD and DA, then
ABCD is the required to parallelogram.
Question 5. Construct a rectangle whose adjacent sides are 5·6 cm and 4 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AB = 5·6 cm.
(ii) At B, construct ∠ABP = 90°
(iii) From BP, cut off BC = 4 cm.
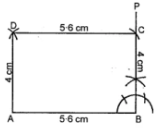
(iv) With C as centre and radius = 5·6 cm draw an arc.
(v) With A as centre and radius = 4 cm,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at D
(vi) Join AD and CD. Then ABCD is the required rectangle
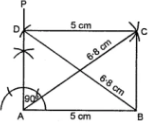
Question 6. Construct a rectangle such that one side is 5 cm and one diagonal is 6·8 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AB = 5 cm.
(ii) At A, construct ∠BAP = 90°.
(iii) With B as centre and radius = 6·8 cm,
draw an arc to meet AP at D.
(iv) With A as centre and radius = 6·8 cm draw an arc.
(v) With D as centre and radius = 5 cm,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at C.
(vi) Join BC and CD. Then ABCD is the required rectangle.
Construction of Quadrilaterals Exe-14.2
ML Aggarwal Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page-259
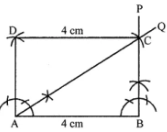
Question 7. Construct a rectangle ABCD such that AB = 4 cm and ∠BAC = 60°.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AB = 4 cm.
(ii) At B, draw ∠ABP = 90°
(iii) At A, construct ∠BAQ = 30°. Let AQ meet BPat D
(iv) With D as centre and radius = 4 cm draw an arc.
(v) With A as centre and radius = BD,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at C.
(vi) Join AC and CD. Then ABCD is the required rectangle.
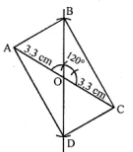
Question 8. Construct a rectangle such that one diagonal is 6-6 cm and angle between two diagonals is 120°.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AO = 1/2 AC = (1/2 × 6·6) cm and produce AO to C
such that OC = OA = 3·3 cm
(ii) At O, construct ∠COB = 120°
(iii) From OB, cut off OB = 1/2 AC = 3·3 cm.
(iv) Produce BO to D such that OB = OD = 3·3 cm.
(v) Join AB, BC, CD and DA.
Then ABCD is the required rectangle.
Question 9. Construct a rhombus whose one side is 5 cm and one angle is 45°
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AB = 5 cm.
(ii) At A, construct ∠BAP = 45°.
(iii) From AP, cut off AD = 5 cm.
(iv) With B as centre and radius = 5 cm, draw an arc.
(v) With D as centre and radius = 5 cm,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at C.
(vi) Join BC and CD. Then ABCD is the required rhombus.
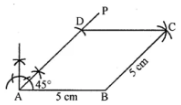
Question 10. Construct a rhombus whose one side is 4·5 cm and one diagonal is 5 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AB = 4·5 cm.
(ii) With A as centre and radius = 4·5 cm, draw an arc.
(iii) With B as centre and radius = 5 cm,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at D.
(iv) With B as centre and radius = 4·5 cm, draw an arc.
(v) With D as centre and radius = 4·5 cm,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at C.
(vi) Join AD, BC and CD. Then ABCD is the required rhombus.
(ML Aggarwal Construction of Quadrilaterals Exe-14.2 Class 8 ICSE )
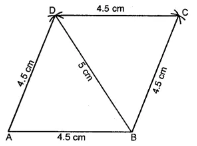
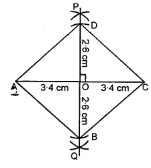
Question 11. Construct a rhombus whose diagonals are 6·8 cm and 5·2 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AC = 6·8 cm.
(ii) Draw 1 bisector PQ of AC to meet it at O.
(iii) From POQ, cut off OB and OD such that
OB = OD = 1/2 BD = 1/2 (5·2) cm = 2·6 cm.
(iv) Join AB, BC, CD and DA. Then ABCD is the required rhombus.
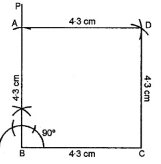
Question 12. Construct a square whose one side is 4·3 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw BC = 4·3 cm.
(ii) At B, construct ∠CBP = 90°
(iii) From BP, cut off BA = 4·3 cm.
(iv) With C as centre and radius = 4·3 cm, draw an arc.
(v) With A as centre and radius = 4·3 cm,
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at D.
(vi) Join AD and CD. Then ABCD is the required square.
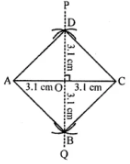
Question 13. Construct a square whose one diagonal is 6·2 cm.
Answer:
Steps of construction :
(i) Draw AC = 6·2 cm.
(ii) Draw ⊥ bisector PQ of AC to meet it at O.
(iii) From POQ, cut off OB = OD = 1/2 AC = 3·1 cm.
(iv) Join AB, BC, CD and DA.
Then ABCD is the required square.
— End of Construction of Quadrilaterals Exe-14.2 Class 8 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to : – ML Aggarwal Maths Solutions for ICSE Class -8
Thanks



👍
Very good
thanks