ML Aggarwal Constructions Exe-16.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exe-16.2 Questions for Constructions as council prescribe guideline for upcoming board exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
ML Aggarwal Constructions Exe-16.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 10th |
| Chapter-16 | Constructions |
| Writer / Book | Understanding |
| Topics | Solutions of Exe-16.2 |
| Academic Session | 2024-2025 |
Constructions Exe-16.2
ML Aggarwal Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions
(Page 386)
Question 1. Draw an equilateral triangle of side 4 cm. Draw its circumcircle.
Answer 1 Steps of Construction :
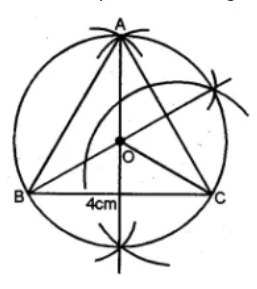
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm
(ii) With centers B and C, draw two arcs of radius 4 cm
which intersect each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC. ∆ ABC is an equilateral triangle.
(iv) Draw the right bisector of BC and AC intersecting each other at O.
(v) Join OA, OB and OC.
(vi) With centre O, and radius equal to OB or OC or OA,
draw a circle which will pass through A, B and C.
This is the required circumcircle of ∆ ABC.
Question 2. Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct:
(i) a triangle ABC given AB = 4cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ABC = 90°.
(ii) a circle which passes through the points A, B and C and mark its centre as O. (2008)
Answer 2 Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 4cm
(ii) At B, draw a ray BX making an angle of 90° and cut off BC = 6 cm.
(iii) Join AC.
(iv) Draw the perpendicular bisectors of sides AB and AC intersecting each other at O.
(v) With centre O, and radius equal to OB or OA or OC,
draw a circle which passes through A, B and C.
This is the required circle.
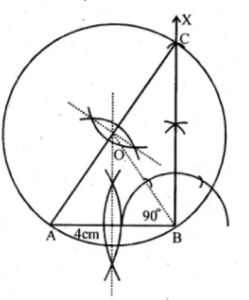
Question 3. Construct a triangle with sides 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm. Draw its circumcircle and measure its radius.
Answer 3 Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm.
(ii) With centre B and radius 3 cm and with centre C and radius 5 cm draw two arcs which intersect each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC.
(iv) Draw the perpendicular bisector of sides BC and AC which intersect each other at O.
(v) Join OB.
(vi) With centre O and radius OB, draw a circle which will pass through A, B and C.
(vii) On measuring the radius OB = 2.5cm
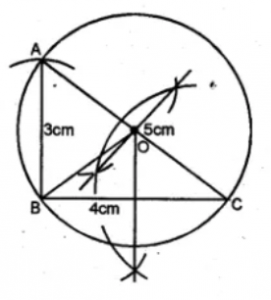
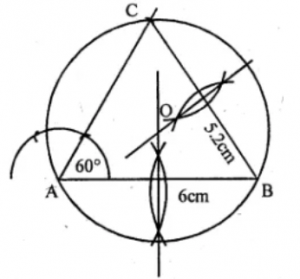
Question 4. Using ruler and compasses only :
(i) Construe a triangle ABC with the following data: Base AB = 6 cm, AC = 5.2 cm and ∠CAB = 60°.
(ii) In the same diagram, draw a circle which passes through the points A, B and C. and mark its centre O.
Answer 4 Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 6 cm.
(ii) At A, draw a ray making an angle of 60°.
(iii) With centre B and radius 5-2 cm. draw an arc which intersects the ray at C.
(iv) Join BC
(v) Draw the perpendicular bisector of AB and BC intersecting each other at O.
(vi) With O as a centre and OA as a radius draw a circle which touches the ∆ABC at A, B and C.
Question 5. Using ruler and compasses only, draw an equilateral triangle of side 5 cm and draw its inscribed circle. Measure the radius of the circle.
Answer 5 Steps of Construction :
(i). Draw a line segment BC = 5 cm
(ii) With centre B and C and radius 5 cm,
draw two arcs intersecting each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC.
(iv) Draw the angle bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersecting each other at I.
(v) From I, draw a perpendicular ID on BC.
(vi) With centre I and radius ID, draw a circle
which touches the sides of the triangle internally.
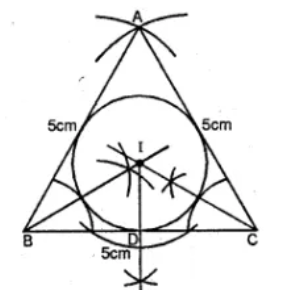
This is the required in circle.
Measure the radius ID which is 1.5 cm (approx.)
ML Aggarwal Constructions Exe-16.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions
(Page 387)
Question 6.
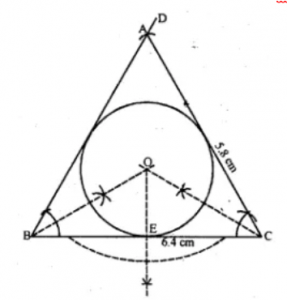
(i) Conduct a triangle ABC with BC = 6.4 cm, CA = 5.8 cm and ∠ ABC = 60°. Draw its incircle. Measure and record the radius of the incircle.
(ii) Construct a ∆ABC with BC = 6.5 cm, AB = 5.5 cm, AC = 5 cm. Construct the incircle of the triangle. Measure and record the radius of the incircle. (2014)
Answer 6 (i)
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 6.4 cm
(ii) Construct ∠ DBC = 60° at B.
(iii) With C as centre and radius CA = 5.8 cm. Draw an arc cutting BD at A.
(iv) Join AC. Then ABC is the required triangle.
(v) Draw the angle bisectors of ∠B and ∠C which intersect each other at O.
(vi) Draw OE ⊥ BC, intersecting BC in E.
(vii) With O as centre and OE as radius draw the required incircle.
Measure the radius OE which is = 1.5cm
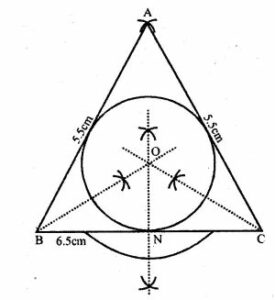
Answer 6 (i) Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line BC = 6.5 cm.
2. With centre B and C draw arcs AB = 5.5 cm and AC = 5 cm
3. Join AB and AC, ABC is the required triangle.
4. Draw the angle bisectors of B and C. Let these bisectors meet at O.
5. Taking O as centre. Draw a incircle which touches all the sides of the ∆ABC.
6. From O draw a perpendicular to side BC which cut at N.
Question 7.Using ruler and compasses only, construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 4 cm, ∠ACB = 45° and the perpendicular from A on BC is 2.5 cm. Draw the circumcircle of triangle ABC and measure its radius.
Answer 7 Constructions
Steps of Construction
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm.
(ii) At B, draw a perpendicular and cut off BE = 2.5 cm.
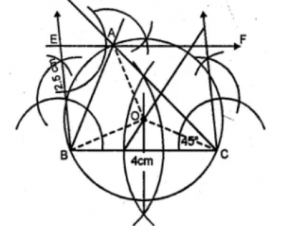
(iii) From E, draw a line EF parallel to BC.
(iv) From C, draw a ray making an angle of 45° which intersects EF at A.
(v) Join AB.
(vi) Draw the perpendicular bisectors of
sides BC and AC intersecting each other at O.
(vii) Join OB, OC and OA.
(viii) With centre 0 and radius OB or OC or OA draw a circle
which will pass through A, B and C.
This circle is the circumcircle of ∆ABC. On measuring its radius OB = 2 cm.
Question 8. Using ruler and compass only, construct a ∆ABC such that BC = 5 cm and AB = 6.5 cm and ∠ABC = 120°.
(ii) Construct a circum-circle of ∆ABC.
(iii) Construct a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, such that D is equidistant from AB and BC.
Answer 8
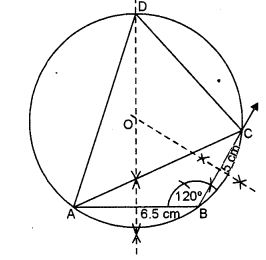
Steps of Construction :
- Draw a line segment AB = 6.5 cm.
- At B, construct an angle of 120° and cut off BC = 5 cm.
- Join AC, to have ∆ABC.
- Draw the perpendicular bisectors of line segments AB and BC.
- Let they intersect each other in 0.
- With 0 as centre and radius OA or OB or OC, draw the circumcircle of ∆ABC.
- Produce perpendicular bisector of line segment AB and let it intersect the circumcircle of ∆ABC at D.
- Join AD and CD.
Thus, quad. ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
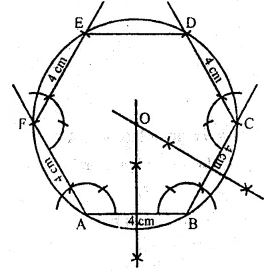
Question 9. Construct a regular hexagon of side 4 cm. Construct a circle circumscribing the hexagon.
Answer 9 Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm.
(ii) At A and B draw rays making on angle of 120° each and cut off AF = BC = 4cm.
(iii) At F and C, draw rays making angle of 120° each and cut off EF = CD = 4cm.
(iv) Join ED.
ABCDEF is the required hexagon.
(v) Draw perpendicular bisectors of sides AB and BC intersecting each other at O.
(vi) With centre O and radius equal OA or OB draw a circle
which passes through the vertices of the hexagon.
This is the required circumcircle of hexagon ABCDEF.
Question 10. Draw a regular hexagon of side 4 cm and construct its in circle.
Answer 10 Steps of constructions :
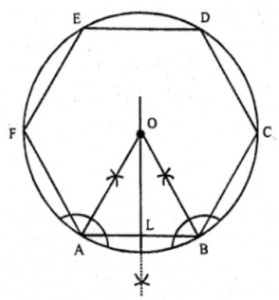
(i) Draw a regular hexagon ABCDEF of side 4 cm.
(ii) Draw the angle bisectors of ∠A and ∠B
which intersect each other at O.
(iii) Draw OL ⊥ AB.
(iv) With centre O and radius OB, draw a circle
which touches the sides of the hexagon
— : End of ML Aggarwal Constructions Exe-16.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to :- ML Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-10
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends