ML Aggarwal Quadratic Equations Ch-Test Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions . We Provide Step by Step Answer of Ch-Test Questions for Quadratic Equations in One Variable as council prescribe guideline for upcoming board exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
ML Aggarwal Solutions of Quadratic Equations in one Variable Chapter-Test Questions for ICSE Class 10 Maths
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-5 | Quadratic Equations |
| Writer / Book | Understanding |
| Topics | Solutions of Ch-Test |
| Academic Session | 2024-2025 |
Quadratic Equations in one Variable Ch-Test
(Class 10 ICSE ML Aggarwal Maths Solutions)
Solve the following equations (1 to 4) by factorization :
Question -1
(i) x² + 6x – 16 = 0
(ii) 3x² + 11x + 10 = 0
Answer -1
(i) x² + 6x – 16 = 0
⇒ x² + 8x – 2x – 16 = 0
⇒ x (x + 8) – 2 (x + 8) = 0
⇒ (x + 8)(x – 2) = 0
Either x + 8 = 0,
then x = –8
or
x – 2 = 0,
then x = 2
Hence x = –8, 2.
(ii) 3x2 + 11x + 10 = 0
⇒ 3x2 + 6x + 5x + 10 = 0
3x(x + 2) + 5(x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(3x + 5) = 0
Either x + 2 = 0,
then x = –2
or
3x + 5 = 0,
then 3x = –5
⇒ x = –5/3
Hence x = –2, –5/3.
Question -2
(i) 2x² + ax – a² = 0
(ii)√3 x² + 10 x +7√3=0
Answer- 2
(i) 2x² + ax – a² = 0
2x² + 2ax – ax – a² = 0
2x2 + ax – a2= 0
2x2 + 2ax – ax – a2 = 0
2x(x + a) –a(x + a) = 0
(x + a)(2x – a) = 0
if x + a = 0,
then x = -a
or
2x – a = 0,
then 2x = a
⇒ x = a/2
Hence x = –a, a/2.

(i) x(x + 1) + (x + 2)(x + 3) = 42
(ii)6/x -2/(x-1)=1/x-2
Answer -3
(i) x(x + 1) + (x + 2)(x + 3) = 42
⇒ 2x2 + 6x + 6 – 42 = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x – 18 = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x – 18 = 0 ..(Dividing by 2)
⇒ x2 + 6x – 3x – 18 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) 3(x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6)(x – 3) = 0
Either x + 6 = 0,
then x = –6
or
x – 3 = 0,
then x = 3
Hence x = –6, 3.
(ii) 6/x -2/(x-1)=1/x-2
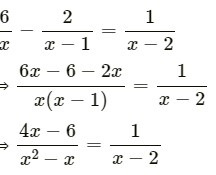
⇒ (4x – 6)(x – 2) = x6 – x
⇒ 4x2 – 8x – 6x + 12 = x2 – x
⇒ 4x2 – 14x + 12 – x2 + x = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 13x + 12 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 9x – 4x + 12 = 0
⇒ 3x(x – 3) -4(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 3)(3x – 4) = 0
Either x – 3 = 0,
then x = 3
or
3x – 4 = 0,
then 3x = 4
⇒ x = 4/3
Hence x = 3, 4/3.
Question -4
(i)√(x+15) =x +3
(ii)√(3x²-2x-1)=2x-2
Answer -4
(i) √(x+15) =x +3
Squaring on both sides
x + 15 = (x + 3)²
⇒ x2 + 6x + 9 – x – 15 = 0
⇒ x2 + 5x – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x – x – 6 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) –1(x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6)(x – 1) = 0
Either x + 6 = 0,
then x = -6
or
x – 1 = 0,
then x = 1
∴ x = –6, 1
Check :
(i) If x = –6 then
L.H.S. = √(x+15)
= √(-6+15)
=√ 9
= 3
R.H.S. = x + 3
= –6 + 3
= –3
∵ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ x = –6 is not a root
(ii)Squaring both sides
3x2 – 2x – 1 = (2x – 2)2
⇒ 3x2 – 2x – 1 = 4x2 – 8x + 4
⇒ 4x2 – 8x + 4 – 3x2 + 2x + 1 = 0
⇒ x2 – 6x + 5 = 0
⇒ x2 – 5x – x + 5 = 0
⇒ x(x – 5) –1(x – 5) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(x – 1) = 0
Either x – 5 = 0,
then x = 5
or
x – 1 = 0,
then x = 1
Check :
(i) If x = 5, then
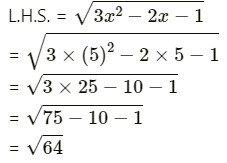
=8
R.H.S. = 2x – 2
= 2 x 5 – 2
= 10 – 2
= 8
∵ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ x = 5 is a root
(ii) If x = 1, then
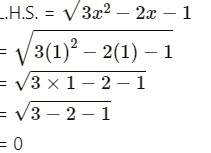
R.H.S. = 2x – 2
= 2 x 1 – 2
= 2 – 2
= 0
∵ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ x = 1 is also its root
Hence x = 5, 1.
Question -5
(i) 2x² – 3x – 1 = 0
(ii) x(3x+1/2)=6
Answer -5
(i) 2x² – 3x – 1 = 0
Here a = 2, b = -3, c = -1
D = b2 – 4ac
= (-3)2 – 4 x 2 x (-1)
= 9 + 8
= 17
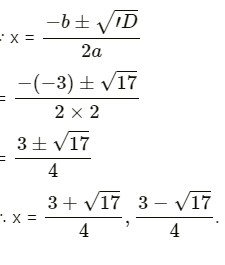
(ii)⇒ 6x2 + x = 12
⇒ 6x2 + x – 12 = 0
Here a = 6, b = 1, c = –12
D = b2 – 4ac
= (1)2 – 4 x 6 x (–12)
= 1 + 288
= 289
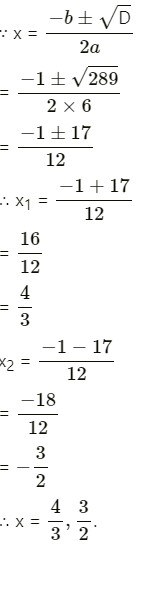
Question- 6
(i)( 2x+5)/(3x+4)=(x+1)/(x+3)
(ii) 2/(x+2)-1/(x+1)=4/(x+4)-3/(x+3)
Answer -6
(i) ( 2x+5)/(3x+4)=(x+1)/(x+3)
(2x + 5)(x + 3) = (x + 1)(3x + 4)
2x2 + 6x + 5x + 15 = 3x2 + 4x + 3x + 4
⇒ 3x2 + 7x + 4 – 2x2 – 11x – 15 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x – 11 = 0
Here a = 1, b = –4, c = –11
D = b2 – 4ac
= (–4)2 – 4 x 1 x (–11)
= 16 + 44
=60
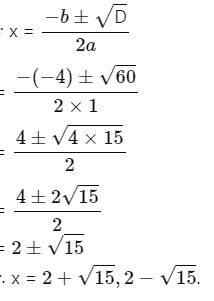
(ii) 2/(x+2)-1/(x+1)=4/(x+4)-3/(x+3)
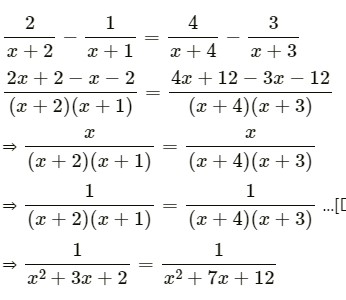
⇒ x2 + 7x + 12 – x2 – 3x – 2 = 0
⇒ 4x + 10
⇒ 2x + 5 = 0
⇒ 2x = –5
⇒ x = -5/2
If x = 0, then
0/(x+2)(x+1)=0/(x+4)(x+3)
which is correct
hence x=0,-5/2
Question -7
(i) (3x-4)/7+7/(3x-4)=5/2
(ii)( 4/x )-3 =5/(2x+3)
Answer -7
(i) (3x-4)/7+7/(3x-4)=5/2
let ( 3x–4)/7 = y, then
y+1/y=5/2
⇒ 2y2 + 2 = 5y
⇒ 2y2 – 5y + 2 = 0
⇒ 2y2 – y – 4y + 2 = 0
⇒ y(2y – 1) –2(2y – 1) = 0
⇒ (2y – 1)(y – 2) = 0
Either 2y – 1 = 0,
then 2y = 1
⇒ y = 1/2
or
y – 2 = 0,
then y = 2
When y = 1/2,
then( 3x-4)/7=1/2
⇒ 6x – 8 = 7
⇒ 6x = 7 + 8
⇒ 6x = 15
⇒ x = 15/6=5/2
y = 2, then
(3x-4)/7=2/1
⇒ 3x – 4 = 14
⇒ 3x = 14 + 4 = 18
⇒ x = 18/3 = 6
∴ x = 6, 5/2.
(ii) ( 4/x )-3 =5/(2x+3)
⇒ (4 – 3x)(2x + 3) = 5x
⇒ 8x + 12 – 6x2 – 9x – 5x = 0
⇒ –6x2 – 6x + 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + x – 2 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2x – x – 2 = 0
⇒ x(x + 2) –1(x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(x – 1) = 0
Either x + 2 = 0,
then x = –2
or
x – 1 = 0,
then x = 1
∴ x = 1, –2.
Question- 8
(i) x² + (4 – 3a)x – 12a = 0
(ii) 10ax² – 6x + 15ax – 9 = 0,a≠0
Answer -8
(i)x² + (4 – 3a)x – 12a = 0
Here a = 1, b = 4 – 3a, c = -12a
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (4 – 3a)2 – 4 x 1 x (–12a)
= 16 – 24a + 9a2 + 48a
= 16 + 24a + 9a2 = (4 + 3a)
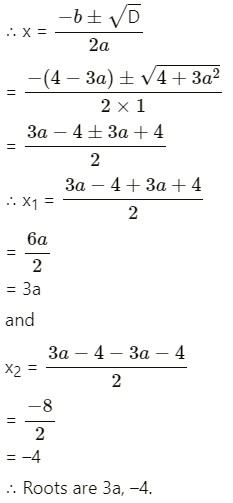
(ii) 10ax² – 6x + 15ax – 9 = 0,a≠0
Here a = 10a, b = –(6 – 15a), c = –9
D = b2 – 4ac
= [–(6 – 15a)]2 – 4 x 10a(–9)
= 36 – 180a + 225a2 + 360a
= 36 + 180a + 225a2 = (6 + 15a)2
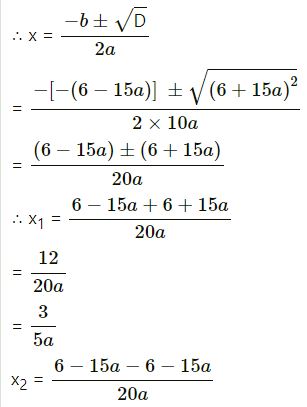
= -30a/20a
= -3/2
Hence x = 3a/ 5
or -3/2.
Question- 9 Solve for x using the quadratic formula. Write your answer correct to two significant figures: (x – 1)² – 3x + 4 = 0. (2014)
Answer -9
(x – 1)² – 3x + 4 = 0
x² + 1 – 2x – 3x + 4 = 0
x2 – 5x + 5 = 0
Here a = 1, b = – 5 and c = 5

= 3.618 or 1.382
∴ x = 3.618 ≈ 3.6
or 1.382 = 1.4(appr)
Question -10 Discuss the nature of the roots of the following equations:
(i) 3x² – 7x + 8 = 0
(ii) x² – x/2 – 4 = 0
(iii) 5x² – 6√5x + 9 = 0
(iv) √3x² – 2x – √3 = 0
Answer- 10
(i) 3x2 – 7x + 8 = 0
Here a = 3, b = –7, c = 8
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (–7)2 – 4 x 3 x 8
= 49 – 96
= –47
∵ D < 0
∴ Roots are not real.
(ii) x² – x/2 – 4 = 0
Here a = 1, b = 12, c = –4
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (1/2)2-4×1×(-4)
= (1/4)+16
= 65/4
∵ D > 0
∴ Roots are real and distinct.
(iii) 5x² – 6√5x + 9 = 0
Here a=5,b=-65,c=9
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (-6√5)2-4×5×9
= 180 – 180
= 0
∴ D = 0
∴ Roots are real and equal.
(iv) √3x² – 2x – √3 = 0
Here a=√3,b=-2,c=-√3
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (-2)2-4×√3×(-√3)
= 4 + 12
= 16
∵ D > 0
∴ Roots are real and distinct.
Question- 11 Find the values of k so that the quadratic equation (4 – k) x² + 2 (k + 2) x + (8k + 1) = 0 has equal roots.
Answer -11
(4 – k) x2 + 2 (k + 2) x + (8k + 1) = 0
Here a = (4 – k), b = 2 (k + 2), c = 8k + 1
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= [2(k + 2)]2 – 4 x (4 – k)(8k + 1) = 0
= 4(k + 2)2 – 4(32k + 4 – 8k2 – k)
= 4(k2 + 4k + 4) –4(32k + 4 – 8k2 – k)
= 4k2 + 16k + 16 – 128k – 16 + 32k2 + 4k
= 36k2 – 108k
= 36k(k – 3)
∵ Roots are equal
∴ D = 0
⇒ 36k(k – 3) = 0
⇒ k(k – 3) = 0
Either k = 0
or
k – 3 = 0,
then k= 3
k = 0, 3.
Answer -12
3x² – 5x – 2m = 0
Here a = 3, b = -5, c = -2m
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (5)2 –4 x 3 x (–2m)
= 25 + 24m
∵ Roots are real and distinct
∴ D> 0
25 + 24m > 0
24m > –25
m > -25/24.
page-95
Question -13 Find the value(s) of k for which each of the following quadratic equation has equal roots:
(i) 3kx² = 4 (kx – 1)
(ii) (k + 4)x² + (k + 1)x + 1 =0
Also, find the roots for that value (s) of k in each case.
Answer -13
(i)3kx² = 4(kx – 1)
⇒ 3kx² = 4kx – 4
⇒ 3kx² – 4kx + 4 = 0
Here a = 3k, b = –4k, c = 4
∴ D = b2 – 4ac
= (–4k)2 – 4 x 3k x 4
= 16k2 – 48k
∴ Roots are equal
∴ D = 0
⇒ 16k2 – 48k = 0
⇒ k2 – 3k = 0
⇒ k(k – 3) = 0
Either k = 0
or
k – 3 = 0
⇒ then k = 3
(k + 4)x2 + (k + 1)x + 1 =0
Here a = k + 4, b = k + 1, c = 1
∴ D = b2 4ac
= (k + 1)2 – 4 x (k + 4) x 1
= k2 + 2k + 1 – 4k – 16
= k2 – 2k – 15
∵ Root are equal
∴ k2 – 2k – 15 = 0
⇒ k2 – 5k + 3k – 15 = 0
⇒ k(k – 5) + 3(k – 5) = 0
⇒ (k – 5)(k + 3) = 0
Either k – 5 = 0,
then k = 5
or
k + 3 = 0,
then k = –3
Question -14 Find two natural numbers which differ by 3 and whose squares have the sum 117.
Answer- 14
Let first natural number = x
then second natural number = x + 3
According to the condition :
x² + (x + 3)² = 117
⇒ x2 + x2 + 6x + 9 = 117
⇒ 2x2 + 6x + 9 – 1117 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 6x – 108 = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x – 54 = 0 …(Dividing by 2)
⇒ x2 + 9x – 6x – 54 = 0
⇒ x(x + 9) –6(x + 9) 0
⇒ (x + 9)(x – 6) = 0
Either x + 9 = 0,
then x = –9,
but it is not a natural number.
or
x – 6 = 0,
then x = 6
∴ First natural number = 6
and second numberr = 6 + 3 = 9
Question -15 Divide 16 into two parts such that the twice the square of the larger part exceeds the square of the smaller part by 164.
Answer -15
Let larger part = x
then smaller part = 16 – x
(∵ sum = 16)
According to the condition
2x2 – (116 – x)2 = 164
⇒ 2x2 – (256 – 32x + x2) = 164
⇒ 2x2 – 256 + 32x – x2 = 164
⇒ x2 + 32x – 256 – 164 = 0
⇒ x2 + 32x – 420 = 0
⇒ x2 + 42x – 10x – 420 = 0
⇒ x(x + 42) – 10(x + 42) = 0
⇒ (x + 42)(x – 10) = 0
Either x + 42 = 0,
then x = –42,
but it is not possible.
or
x – 10 = 0,
then x = 10
∴ Larger part = 10
and smaller part = 16 – 10 = 6.
Question- 16 Two natural numbers are in the ratio 3 : 4. Find the numbers if the difference between their squares is 175.
Answer- 16
Ratio in two natural numbers = 3 : 4
Let the numbers be 3x and 4x
According to the condition,
According to the condition,
(4x)2 – (3x)2 = 175
⇒ 16x2 – 9x2 = 175
⇒ 7x2 = 175
⇒ x2 = 175/7 = 25 = (±5)2
∴ x = 5, -5
But x – 5 is not a natural number
∴ x = 5
∴ Natural numbers are 3x, 4x
= 3 x 5, 4 x 5
= 15, 20.
Question -17 Two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm. The sum of their areas is 656 sq. cm. Express this as an algebraic equation and solve it to find the sides of the squares.
Answer- 17
Side of first square = x cm .
and side of second square = (x + 4) cm
Now according to the condition,
(x)2 + (x + 4)2 = 656
⇒ x2 – x2 + 8x + 16 = 656
⇒ 2x2 + 8x + 16 – 656 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 8x – 640 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x – 320 = 0 …(Dividing by 2)
⇒ x2 + 20x – 16x – 320 = 0
⇒ x(x + 20) – 16(x + 20) = 0
⇒ (x + 20)(x – 16) = 0
EIther x + 20 = 0,
then x = –20,
but it not possible as it is in negative.
or
x – 16 = 0 then x = 16
Side of first square = 16 cm
and side of second square = 16 + 4 – 4 = 20 cm
Question- 18 The length of a rectangular garden is 12 m more than its breadth. The numerical value of its area is equal to 4 times the numerical value of its perimeter. Find the dimensions of the garden.
Answer -18
Let breadth = x m
then length = (x + 12) m
Area = l × b = x (x + 12) m²
and perimeter = 2 (l + b) = 2(x + 12 + x) = 2 (2x + 12) m
According to the condition.
x(x + 12) = 4 x 2(2x + 12)
⇒ x2 + 12x = 16x + 96
⇒ x2 + 12x – 16x – 96 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x – 96 = 0
⇒ x2 – 12x + 8x – 96 = 0
⇒ x(x – 12) + 8(x – 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12)(x + 8) = 0
Either x – 12 = 0,
then x = 12
or
x + 8 = 0,
then x = -8,
but it is not possible as it is in negative.
∴ Breadth = 12m
and length = 12 + 12 = 24m.
Question- 19 A farmer wishes to grow a 100 m² rectangular vegetable garden. Since he has with him only 30 m barbed wire, he fences three sides of the rectangular garden letting compound wall of his house act as the fourth side fence. Find the dimensions of his garden.
(this question is mis printed in text book as 18)
Answer -19
Area of rectangular garden = 100 m²
Length of barbed wire = 30 m
Let the length of the side opposite to wall = x
and length of other each side = (30-x)/2
According to the condition,
x(30-x)/2 = 100
⇒ x(30 – x) = 200
⇒ 30x – x2 = 200
⇒ x2 – 30x + 200 = 0
⇒ x2 – 20x – 10x + 200 = 0
⇒ x(x – 20) – 10(x – 20) = 0
⇒ (x – 20)(x – 10) = 0
Either x – 20 = 0,
then x = 20
or
x – 10 = 0,
then x = 10
(i) If x = 20,
then side opposite to the walI = 20m
and other side
= (30-20)/2
= 10/2
= 5m
(ii) If x = 10,
then side opposite to wall = 10m
and other side
= (30-10)/2
= 20/2
= 10m
∴ Sides are 20m, 5m or 10m.
Question- 20 The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is 1 m less than twice the shortest side. If the third side is 1 m more than the shortest side, find the sides of the triangle.
Answer -20
Let the length of shortest side = x m
Length of hypotenuse = 2x – 1
and third side = x + 1
Now according to the condition,
(2x – 1)2 = (x)2 + (x + 1)2 …(By Pythagorus Theorem)
⇒ 4x2 – 4x + 1 = x2 + x2 + 2x + 1
⇒ 4x2 – 4x + 1 = 2x2 – 2x – 1 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 6x = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) = 0 …(Dividing by 2)
Either x = 0,
but it is not possible
or
x – 3 = 0,
then x = 3
Shortest side = 3m
Hypotenuse = 2 x 3 – 1 = 6 – 1 – 5
Third side = x + 1 = 3 + 1 = 4
Hence sides are 3, 4, 5
Question -21 A wire ; 112 cm long is bent to form a right angled triangle. If the hypotenuse is 50 cm long, find the area of the triangle.
Answer -21
Perimeter of a right angled triangle = 112 cm
Hypotenuse = 50 cm
∴ Sum of other two sides = 112 – 50 = 62 cm
Let the length of first side = x
and length of other side = 62 – x
According to the condition
(x)2 + (62 – x)2 = (50)2 …(By Pythagorus Theorem)
⇒ x2 + 3844 – 124x + x2 = 2500
⇒ 2x2 – 124x + 3844 – 2500 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 124 + 1344 = 0
⇒ x2 – 62x + 672 = 0 …(Dividing by 2)
⇒ x2 – 48x – 14x + 672 = 0
⇒ x(x – 48) –14(x – 48) = 0
⇒ (x – 48)(x – 14) = 0
Either x – 48 = 0,
then x = 48
or
x – 14 = 0,
then x = 14
(i) If x = 48,
then one side = 48cm
and other side = 62 – 48 = 14cm
(ii) If x = 14,
then one side = 14cm
and other side = 62 – 14 = 48
Hence sides are 14cm, 48cm.
Question -22 The speed of a boat in still water is 11 km/ hr. It can go 12 km up-stream and return downstream to the original point in 2 hours 45 minutes. Find the speed of the stream
Answer -22
Speed of a boat in still water = 11 km/hr
Let the speed of stream = x km/hr.
Distance covered = 12 km.
Time taken = 2 hours 45 minutes
now according to the condition
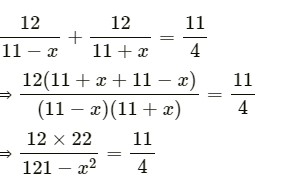
⇒ 1331 – 11x2 = 4 x 12 x 22 = 1056
⇒ 1331 – 11x2 = 1056
⇒ 1331 – 1056 – 11x2 = 0
⇒ -11x2 + 275 = 0
⇒ x2 – 25 = 0 …(Dividing by -11)
⇒ (x + 5)(x – 5) = 0
Either x + 5 = 0,
then x = –5,
but it is not possible as it is in negative.
or
x – 5 = 0,
then x = 5
Hence speed of stream = 5km/hr.
Question- 23 A man spent Rs. 2800 on buying a number of plants priced at Rs x each. Because of the number involved, the supplier reduced the price of each plant by Rupee 1.The man finally paid Rs. 2730 and received 10 more plants. Find x.
Answer- 23
Amount spent = Rs. 2800
Price of each plant = Rs. x
Reduced price = Rs. (x – 1)
No. of plants in first case = 2800/x
No. of plants received in second case = (2800/x)+10
Amount paid = Rs. 2730
According to the condition,
(2800/x +10)(x-1)=2730
(2800 +10 x)(x-1)=2730x
⇒ (2800 + 10)(x – 1) = 2730x
⇒ 2800x – 2800 + 10x2 – 10x – 2730 = 0
⇒ 10x2 + 2800x – 10x – 2730x – 2800 = 0
⇒ 10x2 + 60x – 2800 = 0
⇒ x2 + 60x – 280 = 0 …(Dividing by 10)
⇒ x2 + 20x – 14x – 280 = 0
⇒ x(x + 20) – 14(x + 20) = 0
⇒ (x + 20)(x – 14) = 0
Either x + 20 = 0,
then x = –20,
but it is not possible as it is in negative.
or
x – 14 = 0,
then x = 14.
Question- 24 Forty years hence, Mr. Pratap’s age will be the square of what it was 32 years ago. Find his present age.
Answer -24
Let Partap’s present age = x years
40 years hence his age = x + 40
and 32 years ago his age = x – 32
According to the condition
x + 40 = (x – 32)2
⇒ x + 40 = x2 – 64x + 1024
⇒ x2 – 64x + 1024 – x – 40 = 0
⇒ x2 – 65x + 1024 – x – 40 = 0
⇒ x2 – 65x + 984 = 0
⇒ x2 – 24x – 41x + 984 = 0
⇒ x(x – 24) – 41(x – 24) = 0
⇒ (x – 24)(x – 41) = 0
Either x – 24 = 0,
then x = 24
but it is not possible as it is less than 32
or
x – 41 = 0,
then x = 41
Hence present age = 41 years.
— : End of ML Aggarwal Solutions Quadratic Equations Ch-Test Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to :- ML Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-10
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends

In ques no. 19 there is an error and it is written 100cm2 instead of 100 m2.