ML Aggarwal Quadratic Equations Exe-5.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions . We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exe-5.2 Questions for Quadratic Equations in One Variable as council prescribe guideline for upcoming board exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
ML Aggarwal Ch-5 Quadratic Equations in one Variable Exercise- 5.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-5 | Quadratic Equations |
| Writer / Book | Understanding |
| Topics | Solutions of Exe-5.2 |
| Academic Session | 2024-2025 |
Quadratic Equations in one Variable Exe-5.2
(Class 10 ICSE ML Aggarwal Maths Solutions)
Solve the following equations (1 to 18) by factorization
Question-1
(i) x² – 3x – 10 = 0
(ii) x(2x + 5) = 3
Answer -1
(i) x² – 3x – 10 = 0
⇒ x² – 5x + 2x – 10 = 0
⇒ x(x – 5) + 2(x – 5) = 0
(x + 2) (x – 5) =0
So now,
(x + 2) = 0 or (x – 5) =0
x = -2 or x = 5
∴ Value of x = -2, 5
(ii) x(2x + 5) = 3
Let us simplify the given expression,
2x2 + 5x – 3 = 0
Now, let us factorize
2x2 + 6x – x – 3 = 0
2x(x + 3) -1(x + 3) = 0
(2x – 1) (x + 3) = 0
So now,
(2x – 1) = 0 or (x + 3) = 0
2x = 1 or x = -3
x = ½ or x = -3
∴ Value of x = ½, -3
Question-2
(i) 3x² – 5x – 12 = 0
(ii) 21x² – 8x – 4 = 0
Answer -2
(i) 3x² – 5x – 12 = 0
⇒ 3x² – 9x + 4x – 12 = 0
⇒ 3x (x – 3) + 4(x – 3) = 0
(3x + 4) (x – 3) =0
So now,
(3x + 4) = 0 or (x – 3) =0
3x = -4 or x = 3
x = -4/3 or x = 3
∴ Value of x = -4/3, 3
(ii) 21x2 – 8x – 4 = 0
Let us simplify the given expression,
21x2 – 14x + 6x – 4 = 0
7x(3x – 2) + 2(3x – 2) = 0
(7x + 2) (3x – 2) = 0
So now,
(7x + 2) = 0 or (3x – 2) = 0
7x = -2 or 3x = 2
x = -2/7 or x = 2/3
∴ Value of x = -2/7, 2/3
Question -3
(i) 3x² = x + 4
(ii) x (6x – 1) = 35
Answer-3
(i) 3x² = x + 4
⇒ 3x² – x – 4 = 0
⇒ 3x² – 4x + 3x – 4 = 0
x(3x – 4) + 1(3x – 4) = 0
(x + 1) (3x – 4) = 0
So now,
(x + 1) = 0 or (3x – 4) = 0
x = -1 or 3x = 4
x = -1 or x = 4/3
∴ Value of x = -1, 4/3
(ii) x(6x – 1) = 35
Let us simplify the given expression,
6x2 – x – 35 = 0
Now, let us factorize
6x2 – 15x + 14x – 35 = 0
3x(2x – 5) + 7(2x – 5) = 0
(3x + 7) (2x – 5) = 0
So now,
(3x + 7) = 0 or (2x – 5) = 0
3x = -7 or 2x = 5
x = -7/3 or x = 5/2
∴ Value of x = -7/3, 5/2
Question -4
(i) 6p² + 11p – 10 = 0
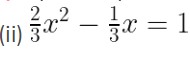
Answer -4
(i) 6p² + 11p – 10 = 0
⇒ 6p² + 15p – 4p – 10 = 0
⇒ 3p(2p + 5) – 2(2p + 5) = 0
(3p – 2) (2p + 5) = 0
So now, (3p – 2) = 0 or (2p + 5) = 0
3p = 2 or 2p = -5
p = 2/3 or p = -5/2
∴ Value of p = 2/3, -5/2
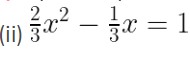
Let us simplify the given expression,
2x2 – x = 3
2x2 – x – 3 = 0
Let us factorize the given expression,
2x2 – 3x + 2x – 3 = 0
x(2x – 3) + 1(2x – 3) = 0
(x + 1) (2x – 3) = 0
(x + 1) = 0 or (2x – 3) = 0
x = -1 or 2x = 3
x = -1 or x = 3/2
∴ Value of x = -1, 3/2
Question -5
(i) 3(x – 2)² = 147
(ii) 1⁄7.(3x – 5)² = 28.
Answer-5
(i) 3(x – 2)² = 147
on expanding
3(x2 – 4x + 4) = 147
3x2 – 12x + 12 = 147
3x2 – 12x +12 – 147 = 0
3x2 – 12x – 135 = 0
Divide by 3, we get
x2 – 4x – 45 = 0
Let us factorize the expression,
x2 – 9x + 5x – 45 = 0
x(x – 9) + 5(x – 9) = 0
(x + 5) (x – 9) = 0
So now,
(x + 5) = 0 or (x – 9) = 0
x = -5 or x = 9
∴ Value of x = -5, 9
(ii) 1/7(3x – 5)2 = 28
Let us simplify the expression,
(3x – 5)2 = 28 × 7
(3x – 5)2 = 196
Now let us expand,
9x2 – 30x + 25 = 196
9x2 – 30x + 25 – 196 = 0
9x2 – 30x – 171 = 0
Divide by 3, we get
3x2 – 10x – 57 = 0
Let us factorize the expression,
3x2 – 19x + 9x – 57 = 0
x(3x – 19) + 3(3x – 19) = 0
(x + 3) (3x – 19) = 0
So now,
(x + 3) = 0 or (3x – 19) = 0
x = -3 or 3x = 19
∴ Value of x = -3, 19/3
ML Aggarwal Quadratic Equations in one Variable Exercise- 5.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions
Question-6
x² – 4x – 12 = 0,when x ∈ N
Answer-6
x² – 4x – 12 = 0
⇒ x² – 6x + 2x – 12 = 0
⇒ x (x – 6) + 2 (x – 6) = 0
⇒ (x – 6) (x + 2) = 0
Either x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
or x + 2 = 0, then x = -2
But -2 is not a natural number
∴ x = 6
Question -7
2x² – 9x + 10 = 0, When
(i) x ∈ N
(ii) x ∈ Q
Answer -7
2x² – 9x + 10 = 0
⇒ 2x² – 4x – 5x + 10 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 2) – 5(x – 2) = 0
(2x – 5) (x – 2) = 0
So now,
(2x – 5) = 0 or (x – 2) = 0
2x = 5 or x = 2
x = 5/2 or x = 2
(i) When, x ∈ N then, x = 2
(ii) When, x ∈ Q then, x = 2, 5/2
Question -8
(i) a²x² + 2ax + 1 = 0, a≠0
(ii) x² – (p + q)x + pq = 0
Answer -8
(i) a²x² + 2ax + 1 = 0
⇒ a²x² + ax + ax + 1 = 0
ax(ax + 1) + 1(ax + 1) = 0
(ax + 1) (ax + 1) = 0
So now,
(ax + 1) = 0 or (ax + 1) = 0
ax = -1 or ax = -1
x = -1/a or x = -1/a
∴ Value of x = -1/a, -1/a
(ii) x² – (p + q)x + pq = 0
Let us simplify the expression,
x² – (p + q)x + pq = 0
x2 – px – qx + pq = 0
x(x – p) – q(x – p) = 0
(x – q) (x – p) = 0
So now,
(x – q) = 0 or (x – p) = 0
x = q or x = p
Question-9
a²x² + (a² + b²)x + b² = 0, a≠0
Answer-9
a²x² + (a² + b²)x + b² = 0
⇒ a²x(x + 1) + b²(x + 1) = 0
(a2x + b2) (x + 1) = 0
So now,
(a2x + b2) = 0 or (x + 1) = 0
a2x = -b2 or x = -1
x = -b2/a2 or x = -1
∴ Value of x = -b2/a2, -1
Question-10
(i) √3x² + 10x + 7√3 = 0
(ii) 4√3x² + 5x – 2√3 = 0
Answer -10
(i) √3x² + 10x + 7√3 = 0
[ ∵ √3 x 7√3 = 7 x 3 = 21] ⇒ √3x(x + √3) + 7(x + √3) = 0
(√3x + 7) (x + √3) = 0
So now,
(√3x + 7) = 0 or (x + √3) = 0
√3x = -7 or x = -√3
x = -7/√3 or x = -√3
∴ Value of x = -7/√3, -√3
(ii) 4√3x2 + 5x – 2√3 = 0
on factorize
4√3x2 + 8x – 3x – 2√3 = 0 [As, 4√3 × (-2√3) = -8 × 3 = -24 and 8 × (-3) = -24]
4x(√3x + 2) – √3(√3x + 2) = 0
(4x – √3) (√3x + 2) = 0
So now,
(4x – √3) = 0 or (√3x + 2) = 0
4x = √3 or √3x = -2
x = √3/4 or x = -2/√3
ML Aggarwal Quadratic Equations in one Variable
(Exercise- 5.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions)
Question -11
(i) x² – (1 + √2)x + √2 = 0
(ii) x + 1/ x = 41/2
Answer -11
(i) x² – (1 + √2)x + √2 = 0
⇒ x² – x – √2x + √2 = 0
x(x – 1) – √2(x – 1) = 0
(x – 1) (x – √2) = 0
So now,
(x – 1) = 0 or (x + √2) = 0
x = 1 or x = -√2
∴ Value of x = 1, -√2
(ii) x + 1/x = 41/2
(x2 + 1)/x = 41/20
20(x2 + 1) = 41x
20x2 + 20 = 41x
20x2 – 41x + 20 = 0
on factorize
20x2 – 25x – 16x + 20 = 0
5x(4x – 5) – 4(4x – 5) = 0
(5x – 4) (4x – 5) = 0
So,
(5x – 4) = 0 or (4x – 5) = 0
5x = 4 or 4x = 5
x = 4/5 or x = 5/4
Question -12
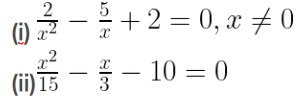
Answer -12
(i) 2/x2 – 5/x + 2 = 0
Taking L.C.M for the given expression,
(2 – 5x + 2x2)/x2 = 0
2x2 – 5x + 2 = 0
Now, on factorizing the above expression we get
2x2 – 4x – x + 2 = 0
2x(x – 2) – 1(x – 2) = 0
(2x – 1) (x – 2) = 0
So,
(2x – 1) = 0 or (x – 2) = 0
2x = 1 or x = 2
x = ½ or x = 2
∴ Value of x = ½, 2
(ii) x2/15 – x/3 – 10 = 0
Taking L.C.M for the given expression,
(x2 – 5x – 150)/15 = 0
x2 – 5x – 150 = 0
Now, on factorizing the above expression we get
x2 – 15x + 10x – 150 = 0
x(x – 15) + 10(x – 15) = 0
(x – 15) (x + 10) = 0
So,
(x – 15) = 0 or (x + 10) = 0
x = 15 or x = -10
Question-13
(i) 3x – 8/x = 2 (ii) (x + 2)/(x + 3) = (2x – 3)/(3x – 7).
Answer -13
(i) 3x – 8/x = 2
on L.C.M,
(3x2 – 8)/x = 2
3x2 – 8 = 2x
3x2 – 2x – 8 = 0
On factorizing
3x2 – 6x + 4x – 8 = 0
3x(x – 2) + 4(x – 2) = 0
(3x + 4) (x – 2) = 0
(3x – 4) = 0 or (x – 2) = 0
3x = 4 or x = 2
x = 4/3 or x = 2
∴ Value of x = 4/3, 2
(ii) (x + 2)/(x + 3) = (2x – 3)/(3x – 7)
(x + 2) (3x – 7) = (2x – 3) (x + 3)
3x2 – 7x + 6x – 14 = 2x2 + 6x – 3x – 9
3x2 – x – 14 = 2x2 + 3x – 9
3x2 – 2x2 – x – 3x – 14 + 9 = 0
x2 – 4x – 5 = 0
x2 – 5x + x – 5 = 0
x(x – 5) + 1(x – 5) = 0
(x + 1) (x – 5) = 0
x + 1 = 0 or x – 5 = 0
x = -1 or x = 5
Question -14
(i) 8/(x + 3) – 3/(2 – x) = 2
(ii) x/(x – 1) + (x – 1)/x = 2½
Answer -14
(i) 8/(x + 3) – 3/(2 – x) = 2
Taking L.C.M, we have
[8(2 – x) – 3(x + 3)]/[(x + 3)(2 – x)] = 2
16 – 8x – 3x – 9 = 2 (x + 3) (2 – x)
7 – 11x = 2 (2x + 6 – x2 – 3x)
7 – 11x = 2 (6 – x2 – x)
7 – 11x = 12 – 2x2 – 2x
2x2 – 11x + 2x + 7 – 12 = 0
2x2 – 9x – 5 = 0
2x2 – 10x + x – 5 = 0
2x(x – 5) + 1(x – 5) = 0
(2x + 1) (x – 5) = 0
2x + 1 = 0 or x – 5 = 0
x = -1/2 or x = 5
∴ Value of x = -1/2, 5
(ii) x/(x – 1) + (x – 1)/x = 2½
Taking L.C.M, we have
[x2 + (x – 1)2] / x(x- 1) = 5/2
(x2 + x2 – 2x + 1)/ (x2 – x) = 5/2
(2x2 – 2x + 1)/ (x2 – x) = 5/2
2 (2x2 – 2x + 1) = 5 (x2 – x)
4x2 – 4x + 2 = 5x2 – 5x
5x2 – 4x2 – 5x + 4x – 2 = 0
x2 – x – 2 = 0
x2 – 2x + x – 2 = 0
x(x – 2) + 1(x – 2) = 0
(x + 1) (x – 2) = 0
x + 1 = 0 or x – 2 = 0
x = -1 or x = 2
Question -15
(i) (x + 1)/(x – 1) + (x – 2)/(x + 2) = 3
(ii) 1/(x – 3) – 1/(x + 5) = 1/6
Answer -15
(i) (x + 1)/(x – 1) + (x – 2)/(x + 2) = 3
[(x + 1) (x + 2) + (x – 2) (x – 1)]/[(x – 1)(x + 2)] = 3
On expanding,
x2 + 3x + 2 + x2 – 3x + 2 = 3 (x – 1) (x + 2)
2x2 + 4 = 3 (x2 + x – 2)
2x2 + 4 = 3x2 + 3x – 6
3x2 – 2x2 + 3x – 6 – 4 = 0
x2 + 3x – 10 = 0
x2 + 5x – 2x – 10 = 0
x(x + 5) – 2(x – 5) = 0
(x + 5) (x – 5) = 0
x + 5 = 0 or x – 5 = 0
x = -5 or x = 5
(ii) 1/(x – 3) – 1/(x + 5) = 1/6
[x + 5 – (x – 3)] / [(x – 3) (x + 5)] = 1/6
(x + 5 – x + 3) / [(x – 3) (x + 5)] = 1/6
8/ [(x – 3) (x + 5)] = 1/6
8 × 6 = (x – 3) (x + 5)
48 = x2 + 5x – 3x – 15
x2 + 2x – 15 – 48 = 0
x2 + 2x – 63 = 0
x2 + 9x – 7x – 63 = 0
x(x + 9) – 7(x + 9) = 0
(x – 7) (x + 9) = 0
x – 7 = 0 or x + 9 = 0
x = 7 or x = -9
Quadratic Equations in one Variable Exercise- 5.2
(ML Aggarwal Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions)
Question-16
(i) a/(ax – 1) + b/(bx – 1) = a + b, a + b ≠ 0, ab ≠ 0
![]()
Answer -16
(i) a/(ax – 1) + b/(bx – 1) = a + b, a + b ≠ 0, ab ≠ 0
rearrange the equation
[a/(ax – 1) – b] + [b/(bx – 1) – a] = 0
[a – b(ax – 1)]/(ax – 1) + [b – a(bx – 1)]/(bx – 1) = 0
(a – abx + b)/(ax – 1) + (b – abx + a)/(bx – 1) = 0
(a – abx + b) [1/(ax – 1) + 1/(bx – 1)] = 0
(a – abx + b) [(bx – 1 + ax – 1)/(ax – 1)(bx – 1)] = 0
(a – abx + b) [(ax + bx – 2)/ (ax – 1)(bx – 1)] = 0
(a – abx + b) = 0 or (ax + bx – 2)/ [(ax – 1) (bx – 1)] = 0
If (a – abx + b) = 0,
a + b = abx
x = (a + b)/ab
if (ax + bx – 2)/ [(ax – 1) (bx – 1)] = 0
ax + bx – 2 = 0
(a + b)x = 2
x = 2/(a + b)
∴ Value of x = (a + b)/ab, 2/(a + b)
(ii)
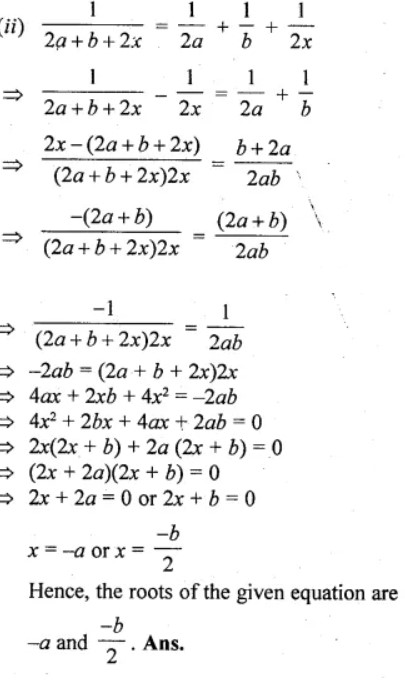
Question -17
1/(x + 6) + 1/(x – 10) = 3/(x – 4)
Answer -17
1/(x + 6) + 1/(x – 10) = 3/(x – 4)
[(x – 10) + (x + 6)]/ [(x + 6) (x – 10)] = 3/(x- 4)
(2x – 4)/ (x2 – 4x – 60) = 3/(x- 4)
(2x – 4) (x – 4) = 3(x2 – 4x – 60)
2x2 – 8x – 4x + 16 = 3x2 – 12x – 180
2x2 – 12x + 16 = 3x2 – 12x – 180
3x2 – 2x2 – 12x + 12x – 180 – 16 = 0
x2 – 196 = 0
x2 = 196
x = √196
∴ x = ± 14
Question-18
(i) √(3x + 4) = x
(ii) √[x(x – 7)] = 3√2
Answer -18
(i) √(3x + 4) = x
3x + 4 = x2
( squaring both sides,)
x2 – 3x – 4 = 0
x2 – 4x + x – 4 = 0
x(x – 4) + 1(x – 4) = 0
(x – 4) (x + 1) = 0
x – 4 = 0 or x + 1 = 0
x = 4 or x = -1
∴ Value of x = 4, -1
(ii) √[x(x – 7)] = 3√2
x(x – 7) = (3√2)2
(squaring on both sides)
x2 – 7x = 9 × 2
x2 – 7x – 18 = 0
x2 – 9x + 2x – 18 = 0
x(x – 9) + 2(x – 9) = 0
(x – 9) (x + 2) = 0
x – 9 = 0 or x + 2 = 0
x = 9 or x = -2
Question-19
Use the substitution y = 3x + 1 to solve for x : 5(3x + 1 )² + 6(3x + 1) – 8 = 0
Answer-19
y = 3x + 1
Now, 5(3x + 1)² + 6(3x + 1) – 8 = 0
5y2 + 6y – 8 = 0
5y2 + 10y – 4y – 8 = 0
5y(y + 2) – 4(y + 2) = 0
(5y – 4) (y + 2) = 0
5y – 4 = 0 or y + 2 = 0
5y = 4 or y = -2
y = 4/5 or y = -2
3x + 1 = 4/5 or 3x + 1 = -2
3x = 4/5 – 1 or 3x = -2 – 1
3x = (4 – 5)/5 or 3x = -3
3x = -1/5 or x = -3/3
x = -1/15 or x = -1
Question -20 Find the values of x if p + 1 =0 and x² + px – 6 = 0
Answer-20
p + 1 = 0, then p = – 1
Substituting the value of p in the given quadratic equation
x² + ( – 1)x – 6 = 0
⇒ x² – x – 6 = 0
⇒ x² – 3x + 2x – 6 = 0
⇒ x (x – 3) + 2 (x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 3) (x + 2) = 0
Either x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
or x + 2 = 0, then x = – 2
Hence x = 3, -2
Question- 21 Find the values of x if p + 7 = 0, q – 12 = 0 and x² + px + q = 0,
Answer- 21
p + 7 = 0, then p = – 7
and q – 12 = 0, then q = 12
Substituting the values of p and q in the given quadratic equation,
x² – 7x + 12 = 0
⇒ x² – 3x – 4x + 12 = 0
⇒ x (x – 3) – 4 (x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 3) (x – 4) = 0
Either x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
or x – 4 = 0, then x = 4
Hence x = 3, 4
Question -22 If x = p is a solution of the equation x(2x + 5) = 3, then find the value of p.
Answer -22
Given, x = p and x(2x + 5) = 3
Substituting the value of p,
p(2p + 5) = 3
⇒ 2p² + 5p – 3 = 0
⇒ 2p² + 6p – p – 3 = 0
2p(p + 3) – 1(p + 3) = 0
(2p – 1) (p + 3) = 0
2p – 1 = 0 or p + 3 = 0
2p = 1 or p = -3
p = ½ or p = -3
Question-23 if x = 3 is a solution of equation …(k+2)x².-kx+6=0 find value of k hence find other root of equation
Answer-23 substituting x = 3 it must satisfy the equation
(k + 2)(3)2 – k(3) + 6 = 0
(k + 2)(9) – 3k + 6 = 0
9k + 18 – 3k + 6 = 0
6k + 24 = 0
6(k + 4) = 0
So, k + 4 = 0
k = -4
putting k = -4
(-4 + 2)x2 – (-4)x + 6 = 0
-2x2 + 4x + 6 = 0
x2 – 2x – 3 = 0
x2 – 3x + x – 3 = 0
x(x – 3) + 1(x – 3) = 0
(x + 1)(x – 3) = 0
x + 1 = 0 or x – 3 = 0
— : End of ML Aggarwal Quadratic Equations Exe-5.2 Class 10 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to :- ML Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-10
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends