Nervous System Class 10 Concise Descriptive Answer ICSE Biology Selina Solutions Ch-10. In this article you will get the solutions of Descriptive Type Questions as council latest syllabus. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Nervous System Class 10 Concise Descriptive Answer ICSE Biology Selina Solutions Ch-10
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10 |
| Book | Selina Concise |
| Chapter-10 | Nervous System |
| Topics | Solutions of Descriptive Type Questions |
Descriptive Type Questions on Nervous System
Que-1: Define the following terms:
(a) Neuron
(b) Nerve
(c) Stimulus
(d) Synaptic cleft
(e) Reflex action
(f) Corpus callosum
Sol:
(a) Neuron – Neurons, also known as nerve cells, are the basic structural units of the nervous system, designed to transmit electrical signals that convey information across different parts of the body.
(b) Nerve – A nerve is a group of nerve fibers (axons) from multiple neurons, bundled together and surrounded by a protective sheath.
(c) Stimulus – A stimulus is any external or internal change in the environment that triggers a response in an organism or its body parts.
(d) Synaptic cleft – The synaptic cleft refers to the small gap between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron.
(e) Reflex action – Reflex action is an automatic, rapid, and involuntary response of the body to a stimulus, requiring little to no conscious thought.
(f) Corpus callosum – The corpus callosum is a large band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
Que-2: Distinguish between the following pairs:
(a) Cerebrum and cerebellum (function)
(b) Sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system (location and role)
(c) Sensory nerve and motor nerve (direction of impulse carried)
(d) Cerebrum and spinal cord (arrangement of cytons and axons of neurons)
(e) Cranial nerves and spinal nerves (number in pairs)
(f) Nerve impulse and flow of electricity (transmission and speed)
(g) Medulla oblongata and cerebellum (function)
Sol:
(a) Difference between the cerebrum and cerebellum (function)
| Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
|---|---|
| The cerebrum is responsible for intelligence, consciousness, and willpower. It controls voluntary actions and allows us to think, reason, plan, and memorize. | The cerebellum is responsible for maintaining the body’s balance and coordinating muscular activities. |
(b) Difference between the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system (location and role)
| Sympathetic Nervous System | Parasympathetic Nervous System |
|---|---|
| The sympathetic nervous system is located between the neck and waist regions. | The parasympathetic nervous system is located in the head, neck, and sacral regions. |
| It prepares the body for action during stressful or abnormal conditions. | It helps restore normal conditions after the stress response has subsided. |
(c) Difference between sensory nerves and motor nerves (direction of impulse carried)
| Sensory Nerve | Motor Nerve |
|---|---|
| Sensory nerves carry impulses from sensory receptors (sense organs) to the brain or spinal cord. | Motor nerves carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs like muscles or glands. |
(d) Difference between the cerebrum and spinal cord (arrangement of cytons and axons of neurons)
| Cerebrum | Spinal Cord |
|---|---|
| The grey matter, containing cytons (cell bodies), is located in the cortex (outer region), while the white matter, containing axons, is found in the medullary region (inner part). | The grey matter, containing cytons, is located in the medullary region (inner part), while the white matter, containing axons, is located in the cortex (outer part). |
(e) Difference between cranial nerves and spinal nerves (number in pairs)
| Cranial Nerves | Spinal Nerves |
|---|---|
| There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves. | There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. |
(f) Difference between nerve impulse and the flow of electricity (transmission and speed)
| Nerve Impulse | Flow of Electricity |
|---|---|
| In a nerve impulse, no substance or electrons move along the nerve fiber. | In the flow of electricity, electrons move along the wire. |
| Nerve impulses travel at approximately 100 meters per second. | Electricity is conducted at about 150,000 kilometers per second. |
(g) Difference between medulla oblongata and cerebellum (function)
| Medulla Oblongata | Cerebellum |
|---|---|
| The medulla oblongata controls the activities of internal organs, such as the peristaltic movement of the digestive tract and the regulation of breathing, along with other involuntary actions. | The cerebellum is responsible for maintaining balance and coordinating muscular movements. |
Que-3: While watching a scary movie, mention its effects on the following organs by the autonomous nervous system, in the table given below: (one has been done for you as an example).
| Organ | Sympathetic System | Parasympathetic System |
|---|---|---|
| e.g. Lungs | Dilates bronchi and bronchioles | Constricts bronchi and bronchioles |
| (1) Heart | ||
| (2) Pupil of the eye | ||
| (3) Salivary gland |
Sol:
| Organ | Sympathetic System | Parasympathetic System |
|---|---|---|
| e.g. Lungs | Dilates bronchi and bronchioles | Constricts bronchi and bronchioles |
| (1) Heart | Accelerates heartbeat | Retards heartbeat |
| (2) Pupil of the eye | Dilation | Constriction |
| (3) Salivary gland | Inhibits secretion of saliva (dryness of the mouth) | Stimulates secretion of saliva. |
Que-4: Give reasons:
(a) The brain and the spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system.
(b) Neurotransmitters are broken down by an enzyme just after passing an impulse from one neuron to the other.
Sol:
(a)The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord, both of which are protected within the vertebral column. These structures play a crucial role in regulating all bodily functions, as they control the body’s activities. Whenever a stimulus arises from any part of the body, it is transmitted to the brain or spinal cord, which then coordinates an appropriate response. Since the brain and spinal cord generate responses to stimuli, they are collectively referred to as the central nervous system.
(b)Neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes immediately after transmitting an impulse between neurons, ensuring that the synapse is ready for the next impulse transmission.
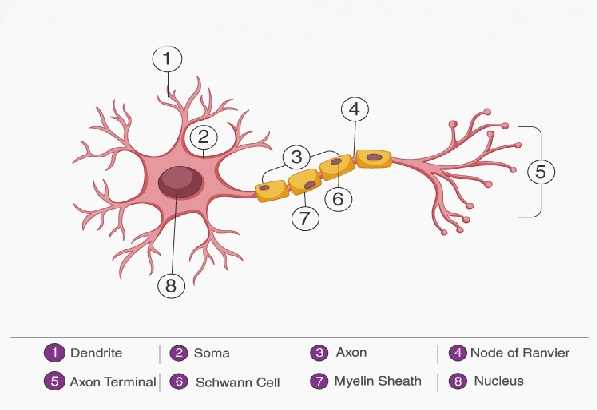
Que-5: Draw a labelled diagram of a myelinated neuron.
Sol: labelled diagram of a myelinated neuron:
Que-6: What are the advantages of having a nervous system?
Sol:
The nervous system provides several key advantages:
- It keeps us informed about the external environment through our sense organs.
- It allows us to remember, think, and reason.
- They controls and coordinates voluntary muscle activities, such as running, holding objects, and writing.
Que-7: What is the difference between reflex action and voluntary action?
Sol:
| Reflex Action | Voluntary Action |
|---|---|
| Triggered by a stimulus (such as touch, pain, pressure, heat, or light). | Triggered by conscious thought or will. |
| Primarily serves a self-protective function in response to the environment. | Aimed at achieving a specific goal or fulfilling a desire. |
| Commands mainly come from the spinal cord and autonomic nervous system, with some originating in the brain. | Commands originate primarily in the brain. |
| Involves muscles and glands. | Involves only muscles. |
–: End of Nervous System Class 10 Concise Descriptive Answer ICSE Biology Selina Solutions :–
Return to : Concise Biology for ICSE Class 10 Selina Solutions
Please share with your Friends if helpful
Thanks