Newton Law of Motion Obj-1 HC Verma Solutions Concept of Physics Vol-1 Ch-5 for Class-11. Solution of Objective -1 (MCQ-1) Questions of Ch-5 Newton Law of Motion (Concept of Physics) .Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-11 Physics.
Newton Law of Motion Obj-1 (MCQ-1) HC Verma Solutions Concept of Physics Vol-1 Ch-5 for Class-11
| Board | ISC and other board |
| Publications | Bharti Bhawan Publishers |
| Ch-5 | Newton Law of Motion |
| Class | 11 |
| Vol | 1st |
| writer | H C Verma |
| Book Name | Concept of Physics |
| Topics | Solution of Objective-1 (MCQ-1) Questions |
| Page-Number | 77, 78 |
-: Select Topics :-
Objective-I (Currently Open)
Objective-II (update Soon)
Exercise (update Soon)
Newton Law of Motion Obj-1 (MCQ-1)
HC Verma Solutions Concept of Physics Vol-1 Ch-5 for Class-11
Page-77
Question-1
A body of weight w1 is suspended from the ceiling of a room by a chain of weight w2. The ceiling pulls the chain by a force.
(a) w1
(b) w2
(c) w1 + w2
(d) 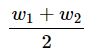
Answer-1
the option (c) w1 + w2 is correct
Explanation:
w1 + w2
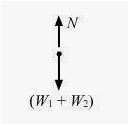
From the free-body diagram,
(w1 + w2) – N = 0
N = w1 + w2
The ceiling fan pulls the chain by a force w1 + w2
Question-2
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
(a) the cart on the horse
(b) the ground on the horse
(c) the ground on the cart
(d) the horse on the ground
Answer-2
the option (b) the ground on the horse is correct
Explanation:
The horse pushes the ground in the backward direction and, in turn, the ground pushes the horse in the forward direction, according to Newton’s third law of motion.
Question-3
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
(a) the engine of the car
(b) the driver of the car
(c) the earth
(d) the road
Answer-3
the option (d) the road is correct
Explanation:
The car pushes the ground in the backward direction and according to the third law of motion, reaction force of the ground in the forward direction acts on the car.
Question-4
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure (5-Q.2).
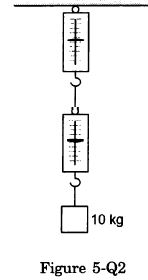
(a) Both the scales will read 10 kg.
(b) Both the scales will read 5 kg.
(c) The upper scale will read 10 kg and the lower zero.
(d) The readings may be anything but their sums will be 10 kg.
Answer-4
the option (a) Both the scales will read 10 kg. is correct
Explanation:
From the free-body diagram
K1x1 = mg = 10 x 9.8 = 98 N
K2x2 = K1x1
So, K1x1 = K2x2 = 98 N
Therefore, both the spring balances will read the same mass, i.e. 10 kg.
Question-5
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined plane of inclination θ with the horizontal. The force exerted by the plane on the block has a magnitude.
(a) mg
(b) mg / cosθ
(c) mg cosθ
(d) mg tanθ
Answer-5
the option (c) mg cosθ is correct
Explanation:

From the free-body diagram,
N = mg cosθ
Normal force exerted by the plane on the block is mg cosθ.
Question-6
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
(a) mg
(b) mg / cosθ
(c) mg cosθ
(d) mg tanθ
Answer-6
the option (b) mg / cosθ is correct
Explanation
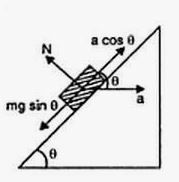
Free-body Diagram of the Small Block of Mass ‘m’
The block is at equilibrium w.r.t. to wedge. Therefore,
mg sinθ = m.a cosθ
⇒ a = g tanθ
Normal reaction on the block is
N = mg cosθ + ma sinθ
Putting the value of a, we get:
N = mg cosθ + mg tanθsinθ
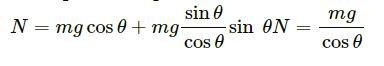
Question-7
Neglect the effect of rotation of the earth. Suppose the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface. A person standing on the surface of the earth will.
(a) fly up
(b) slip along the surface
(c) fly along a tangent to the earth’s surface
(d) remain standing
Answer-7
the option (d) remain standing is correct
Explanation
If the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface, the net force on the person will become zero and according to the first law of motion, the person will remain standing.
Question-8
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is
(a) zero
(b) 3.6 N
(c) 3.6√3 N
(d) 7.2 N
Answer-8
the option (a) zero is correct
Explanation
Using, Fnet = ma,
a = 0 ⇒ Fnet = 0
As the whole system is at rest, the resultant force on the charged particle at A is zero.
Page-78
Question-9
A force F1 acts on a particle accelerating it from rest to a velocity v. Force F1 is then replaced by F2 which decelerates the particle to rest.
(a) F1 must be equal to F2.
(b) F1 may be equal to F2.
(c) F1 must be unequal to F2
(d) None of these.
Answer-9
the option (b) F1 may be equal to F2. is correct
Explanation
Any force applied in the direction opposite the motion of the particle decelerates it to rest.
Question-10
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
(a) The two bodies will reach the same height.
(b) A will go higher than B.
(c) B will go higher than A.
(d) Any of the above three may happen depending on the speed with which the objects are thrown.
Answer-10
the option (b) A will go higher than B. is correct
Explanation
Let the air exert a constant resistance force = F (in downward direction).
Acceleration of particle A in downward direction due to air resistance, aA = F / mA.
Acceleration of particle B in downward direction due to air resistance, aB = F / mB.
mA > mB
aA < aB
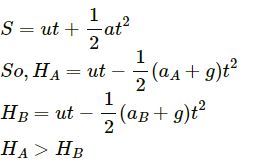
Hence, A will go higher than B
Question-11
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth’s surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
(a) take a time longer than T to slide down the wedge
(b) take a time shorter than T to slide down the wedge
(c) remain at the top of the wedge
(d) jump off the wedge
Answer-11
the option (c) remain at the top of the wedge. is correct
Explanation
Downward gravitational force will be balanced by the upward pseudo force (because of the motion of the wedge in downward direction). The block will remain at its position, as both the box and the inclined plane are falling with the same acceleration (g).
Question-12
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force F on any particle in the direction of the particle’s motion. A particle of mass m projected upward takes time t1 in reaching the maximum height and t2 in the return journey to the original point. Then.
(a) t1 < t2
(b) t1 > t2
(c) t1 = t2
(d) the relation between t1 and t2 depends on the mass of the particle
Answer-12
the option (b) t1 > t2. is correct
Explanation
Let acceleration due to air resistance force be a.
Let H be maximum height attained by the particle.
Direction of air resistance force is in the direction of motion.
case-1
In the upward direction of motion,
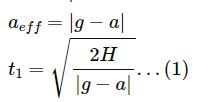
Case-2
In the downward direction of motion,
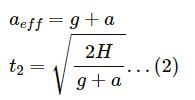
Therefore, t1 > t2.
Question-13
A person standing on the floor of an elevator drops a coin. The coin reaches the floor of the elevator in time t1 if the elevator is stationary and in time t2 if it is moving uniformly. Then
(a) t1 = t2
(b) t1 < t2
(c) t1 > t2
(d) t1 < t2 or t1 > t2 depending on whether the lift is going up or down.
Answer-13
the option (a) t1 = t2. is correct
Explanation
After the coin is dropped, the only force acting on it is gravity, which is same for both the cases.
Hence t1 = t2
Question-14
A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
(a) x + v t
(b) x − v t
(c) x
(d) depends on the direction of the train
Answer-14
the option (c) x. is correct
Explanation
The moving train does not put any extra force on the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus. So, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, will be same as before, i.e. x.
—: End of Newton Law of Motion Obj-1 HC Verma Solutions Vol-I Concept of Physics:–
Thanks