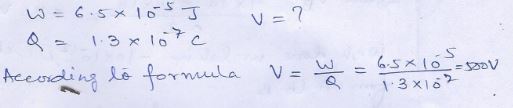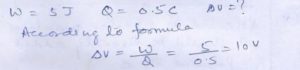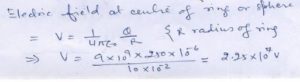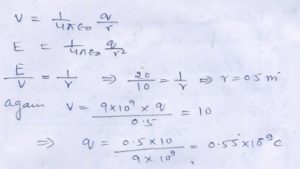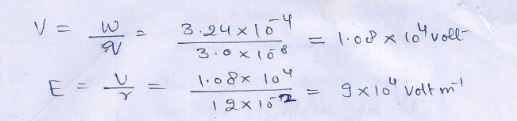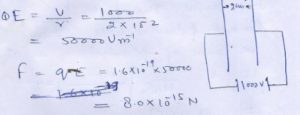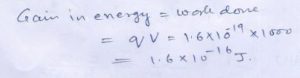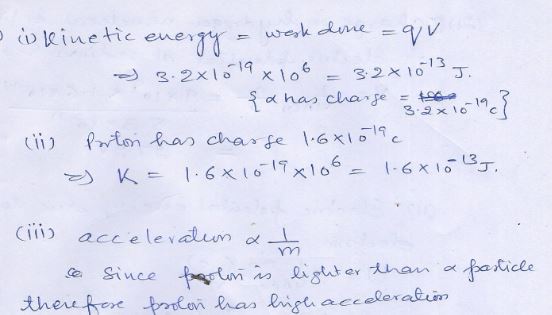Nootan Solutions Electric Potential Energy ISC Physics Class-12 Nageen Prakashan Chapter-3 Solved Numericals. Step by step Solutions of Kumar and Mittal ISC Physics Class-12 Nageen Prakashan Numericsls Questions. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics
Nootan Solutions Electric Potential Energy ISC Physics Class-12 Nageen Prakashan Chapter-3, Solved Numericals of Kumar and Mittal
| Class: | 12 |
| Subject: | Physics |
| Chapter 3: | Electric Potential and Potential Energy |
| Board | ISC |
| Writer /Publications | Nootan / Nageen Prakashan/Kumar and Mittal |
| Topics | Solved Numericals of page 110 , 111,112 |
Definition
Electric potential energy is posses by an object by the virtue of two elements, those being, the charge possessed by an object itself and the relative position of an object with respect to other electrically charged objects. The magnitude of electric potential depends on the amount of work done in moving the object from one point to another against the electric field
When an object is moved against the electric field it gains some amount of energy which is defined as the electric potential energy. For any charge, the electric potential is obtained by dividing the potential energy by the quantity of charge
There are two key elements on which the electric potential energy of an object depends.
- Its own electric charge,
- Its relative position with other electrically charged objects.
Electric Potential Formula:
A charge placed in an electric field possesses potential energy and is measured by the work done in moving the charge from infinity to that point against the electric field. If two charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance d, the electric potential energy of the system is;
U = 1/(4πεo) × [q1q2/d]
Electric Potential Derivation
Let us consider a charge q1. Let us say, they are placed at a distance ‘r’ from each other. The total electric potential of the charge is defined as the total work done by an external force in bringing the charge from infinity to the given point.
We can write it as, -∫ (ra→rb) F.dr = – (Ua – Ub)
Here, we see that the point rb is present at infinity and the point ra is r.
Substituting the values we can write, -∫ (r →∞) F.dr = – (Ur – U∞)
As we know that Uinfity is equal to zero.
Therefore, -∫ (r →∞) F.dr = -UR
Using Coulomb’s law, between the two charges we can write:
⇒ -∫ (r →∞) [-kqqo]/r2 dr = -UR
Or, -k × qqo × [1/r] = UR
Therefore, UR = -kqqo/r
Electric Potential of a Point Charge
Let us consider a point charge ‘q’ in the presence of another charge ‘Q’ with infinite separation between them.
UE (r) = ke × [qQ/r]
where, ke = 1/4πεo = Coloumb’s constant
Let us consider a point charge ‘q’ in the presence of several point charges Qi with infinite separation between them.
UE (r) = ke q × ∑ni = 1 [Qi /ri]
Important Points
- At a point midway between two equal and opposite charges, the electric potential is zero but the electric field is not zero.
- The electric potential at a point is said to be one volt if one joule of work is done in moving one Coloumb of the charge against the electric field.
- If a negative charge is moved from point A to B. The electric potential of system increases.
- The reference level used to define electric potential at a point is infinity. It signifies that the force on a test charge is zero at the reference level.
- The surface of the earth is taken to be at zero potential since the earth is so huge that addition or removal of charge from it will not alter its electrical state.
What is Electric Potential Difference?
In an electrical circuit, the potential between two points (E) is defined as the amount of work done (W) by an external agent in moving a unit charge (Q) from one point to another.
Mathematically we can say that,
E = W/Q
Where,
- E = Electrical potential difference between two points,
- W = Work done in moving a change from one point to another,
- Q = Quantity of charge in coulombs.
Solved Numericals of Electric Potential and Potential Energy Nootan Solutions, Nageen Prakashan Kumar and Mittal
(page-110)
Question 1
The amount ………….at the point .
Answer
Question 2
How much………….. is 4 v ?
Answer

Question 3
5 J work………………… the Points .
Answer
Question 4
Compute electric…………..charge of ……… .
Answer
Question 5
A wire …….. at its center .
Answer
Question 6
Calculate in …………………. A to B , ( OA = 0.10 m ,………)
Answer
Question 7
A charge A ……………..From D to C ?
Answer
Question 8
Two charges ………………………….the Charges .
Answer
Question 9
The Potential …………distance of 0.4 m?
Answer
Question 10
The electric ……………of the charges .
Answer
Question 11
A point ………………… the point x …………..
Answer

Question 12
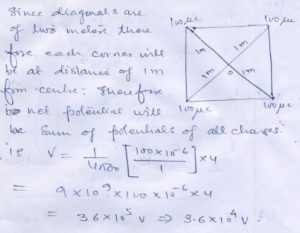
At each corner ……………………18 cm ?
Answer
Question 13
Electric charges …………………. of the square .
Answer
Question 14
10 J of …………………A and B ?
Answer
Question 15
……….. J of work ……………….the electric field .
Answer
Question 16
Two plane …………… two plates .
Answer
(page-111)
Question 17
The distance between ……………..to the order .
Answer

Question 18
How much kinetic ……………………answer in joule .
Answer
Question 19
An ..particle ……………………..J
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Answer
Question 20
The mutual …………… the protons .
Answer

Question 21
An electron ………….same radius .
Answer

Question 22
Three point ………….of the System .
Answer
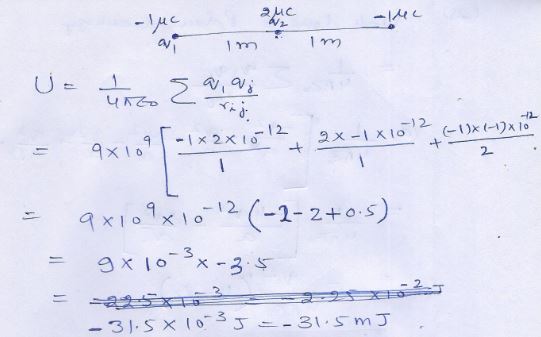
Question 23
Three equal …………….. of charges .
Answer
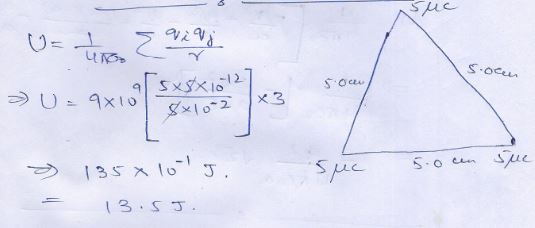
Question 24
Two positive …………….. by 2 cm .
Answer
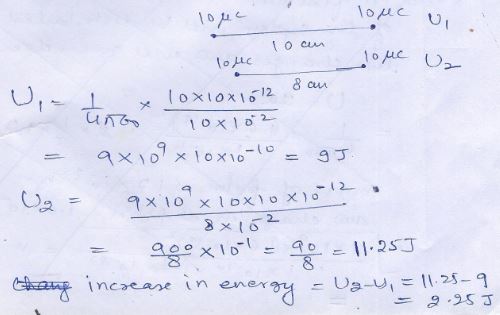
Question 25
(i)…………
(ii)………….
Answer
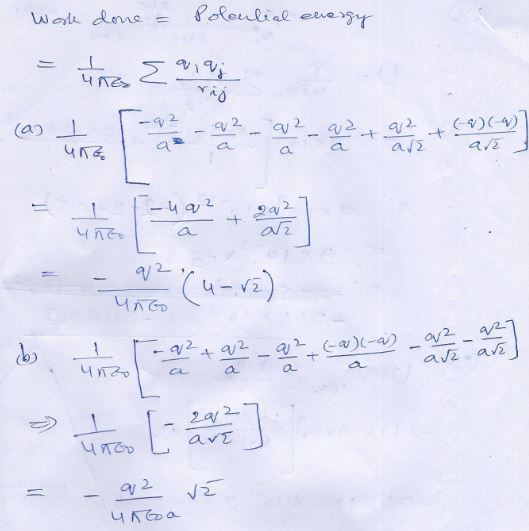
Question 26
The distance between ……………..kinetic Energy ?
Answer

Question 27
Two electrons ………………between them ?
Answer

Question 28
Two point ………….equilibrium position .
Answer
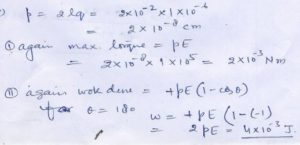
Question 29
An Electric ………………….calculate .
(i)…………
(ii)………….
Answer
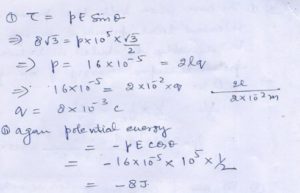
Question 30
Two point charges ………………….. dipole through 90 .
Answer

Question 31
Compare the electric ………………. silver is 47 .
Answer

Question 32
A hallow metallic ……………the sphere .
Answer
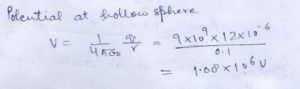
Question 33
A hallow spherical ……………….. of the Sphere .
Answer
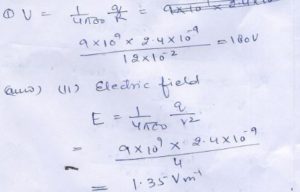
(page-112)
Question 34
The Electric potential……………………the center .
Answer

Question 35
The electric potential…………………….of the sphere .
Answer

Question 36
Eight charged drop ……………….the bigger drop .
Answer

Question 37
27 identical drops ………………………..to be spherical .
Answer

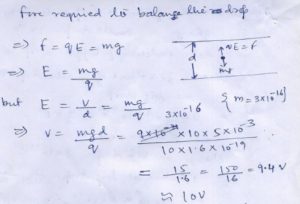
Question 38
Calculate ……………………..drop is …………..and ………….
Answer
— End of Nootan Solutions Electric Potential and Potential Energy of Numericals :–
Return to – Nootan Solutions for ISC Physics Class-12 Nageen Prakashan
Thanks