Nootan Solutions Isothermal and Adiabatic Processes ISC Class-11 Physics Nageen Prakashan Chapter-20. Numericals of latest edition. Step by step Solutions of Kumar and Mittal ISC Physics Part-2 Class-11 Nageen Prakashan Numericals Questions. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-11 Physics.
Nootan Solutions Isothermal and Adiabatic Processes ISC Class-11 Physics Nageen Prakashan
| Class: | 11 |
| Subject: | Physics Part-2 |
| Chapter | 20 Isothermal and Adiabatic Processes |
| Board | ISC |
| Writer / Publications | Nootan / Nageen Prakashan / Kumar and Mittal |
| Topics | Solved Numericals of page 779, 780 |
Nootan Solutions Isothermal and Adiabatic Processes ISC Class-11 Physics Nageen Prakashan
Adiabatic Processes :-
- Adiabatic is a process in which there is no heat flow takes place between the system and the surroundings.
- These processes are sudden.
- The walls of the container should be adiabatic
- For an adiabatic process of an ideal gas
- From Boyle’s law
- PV γ = constant
Where γ = Cp/Cv Specific heat ratio
Example: – Hot tea in Thermos flask. It will remain hot as there is no exchange of heat takes place because the walls of thermos is insulating.
Adiabatic change of an ideal gas :-
- It implies how much work is done during adiabatic change of an ideal gas.
- Initially ideal gas is at Pressure P1, Volume V1 and Temperature T1 (P1,V1,T1)
- Final state of an ideal gas Pressure P2,Volume V2 and Temperature T2 (P2,V2,T2)
- P V γ = const
- γ =Cp/Cv
- If an ideal gas undergoes a change in its state adiabatically from (P1, V1) to (P2, V2)
- P1V1 γ = P2V2 γ
- The work done in an adiabatic change of an ideal gas from the
state (P1, V1, T1) to the state (P2, V2, T2).
W =∫ P V dV = P ∫V dV (Integrating between the limits V2 and V1)
For Adiabatic Process
- P V γ = constant This implies P= constant / V γ
- W = constant ∫dV/ V γ
- constant [V γ-1/- γ+1]
- constant/1- γ [V21- γ – V1 1-γ]
- = constant/1- γ[1/ V21- γ– 1/ V1 1-γ]
- By solving Work done W= R/ (γ-1)(T2-T1), where
- T2= final Temperature
- T1=initial temperature
- R=Universal gas constant
- γ = Specific heat ratio
- This is the work done during adiabatic change.
- Consider W= R/ (γ-1)(T2-T1)
Isothermal Processes :-
- Isothermal :- Iso means same and thermal related to temperature. In Isothermal process the temperature remains constant throughout while all other variables change.
- Temperature is constant throughout.
- For an ideal gas
- PV = nRT where
- n=no. of moles (constant), R = universal gas constant, T =constant for isothermal process.
- This implies PV=constant
- Pressure and volume are inversely proportional to each other.
- Graphically if we plot pressure and volume
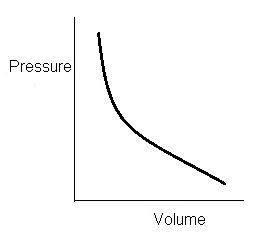
- We will get decreasing curve because if we increase pressure volume decreases and vice versa.
- This curve is known as Isothermal Curve.
Isothermal Expansion of an Ideal gas :-
- It can be described as amount of work done during isothermal expansion of an ideal gas under constant temperature.
- Initially ideal gas is at Pressure P1 and Volume V1 .
- At constant temperature the gas will expand from pressure P1 to P2 and volume changes from V1 to V2.So the final state (P2,V2).
- These all expansions are QuasiStatic processes.
- Consider any intermediate stage ,
- Pressure is P and volume is V1 + ΔV where ΔV increase in volume.
- ΔW=P ΔV where ΔW = small work done
- By solving and doing calculation the above equation the work done for an ideal gas the work done will be given as :-
W= RT lnV2/V1
Chapter-20
Nootan Solutions Isothermal and Adiabatic Processes ISC Class-11 Physics Nageen Prakashan
Page No 779, 780
CONTACT FOR LIVE CLASSES- 9335725646
-: End of Isothermal and Adiabatic Processes Nootan Solutions :-
Return to – Nootan Solutions for ISC Physics Class-11 Nageen Prakashan


