OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21. Step by step Solutions of OP Malhotra SK Gupta, Anubhuti Gangal S.Chand ISC Class-12 Mathematics with Exe-21(a), Exe-21(b), Exe-21(c), Exe-21(d), and Chapter Test Questions. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Mathematics.
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
| Class: | 12th |
| Subject: | Mathematics |
| Chapter : | Ch-21 Vectors of Section -B |
| Board | ISC |
| Writer | OP Malhotra, SK Gupta, Anubhuti Gangal |
| Publications | S.Chand Publications 2020-21 |
-: Included Topics :-
Exe-21(a),
Exe-21(b),
Exe-21(c),
Exe-21(d),
Chapter Test
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
Vector: Those quantities which have magnitude, as well as direction, are called vector quantities or vectors.
Note: Those quantities which have only magnitude and no direction, are called scalar quantities.
Representation of Vector: A directed line segment has magnitude as well as direction, so it is called vector denoted as 𝐴𝐵⃗ or simply as 𝑎⃗ . Here, the point A from where the vector 𝐴𝐵⃗ starts is called its initial point and the point B where it ends is called its terminal point.
Magnitude of a Vector: The length of the vector 𝐴𝐵⃗ or 𝑎⃗ is called magnitude of 𝐴𝐵⃗ or 𝑎⃗ and it is represented by |𝐴𝐵⃗| or |𝑎⃗ | or a.
Note: Since, the length is never negative, so the notation |𝑎⃗ |< 0 has no meaning.
Direction Cosines: If α, β and γ are the angles which a directed line segment OP makes with the positive directions of the coordinate axes OX, OY and OZ respectively, then cos α, cos β and cos γ are known as the direction cosines of OP and are generally denoted by the letters l, m and n respectively.
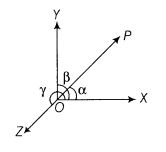
Types of Vectors :-
The various types of vectors included in vector algebra for class 12 concepts are
- Zero Vector
- Unit Vector
- Position Vector
- Co-initial Vectors
- Collinear Vectors
- Equal Vectors
- Negative of a Vector
Zero Vector :- A zero vector is a vector when the magnitude of the vector is zero and the starting point of the vector coincides with the terminal point. In other words, for a vector AB⃗ the co-ordinates of the point A are same as that of the point B then the vector is said to be a zero vector and is denoted by 0.
Unit Vector :-A vector which has a magnitude of unit length is called a unit vector. Suppose if x⃗ is a vector having a magnitude x then the unit vector is denoted by x̂ in the direction of the vector x⃗ and has the magnitude equal to 1.
Exe-21(a)
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
Question 1:
Draw a pair of directed segments vector AB and vector XY which are ………………… length, (ii) its direction ?
Question 2:
Simplify the triangle ABC and PQR
(i)………………
………………….
Question 3:
In Fig. given below the various ………………… of the following sums
……………
Question 4:
…………………
……………….
………………….
Question 6:
In fig. given below EFGH is a parallelogram simplify :
……………….
Exe-21(b)
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
Question 1:
Vector OA and vector OB are vectors a band b respectively ……………….
(i) vector OX and
(ii) vector OY
Question 2:
vector OA and OB are vector s a and b respectively ………………. terms of vector a and b.
(i)……………
(ii)…………..
Question 3:
………………….
………………….
Question 5:
Four point A, B, C, D with position vectors ………………. of line AC and BD.
Exe-21(c)
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
Question 1:
If the position vector of a point (-4, -3) be ………………
Question 2:
If P(-1, 3) and Q (2, -7) express the vector ……………….. the magnitude of r.
Question 3:
……………………
…………………..
…………………..
Question 16:
Show that the three point with position vector ……………….. collinear.
Position Vector :- If O is taken as reference origin and A is an arbitrary point in space then the vector O⃗A⃗ is called as the position vector of the point.
Position vector simply denotes the position or location of a point in the three-dimensional Cartesian system with respect to a reference origin.
Collinear Vectors :- Vectors which lie along the same line or parallel lines are known to be collinear vectors. They are also known as parallel vectors.
Equal Vectors :- Two or more vectors are said to be equal when their magnitude is equal and also their direction is the same.
Negative of a Vector :- If two vectors are the same in magnitude but exactly opposite in direction then both the vectors are negative of each other. Assume there are two vectors a and b, such that these vectors are exactly the same in magnitude but opposite in direction then these vectors can be given by
a = – b
Exe-21(d)
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
Question 1:
If ………… vectors AB and BA
Question 2:
If vector a = ……………….
Question 3:
Find the sum of the vector ………………. of these vectors.
Question 4:
……………………
……………………
……………………
Question 18:
Show that the points (2, -1, 3), …………………… are collinear.
Chapter Test
OP Malhotra Vectors ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions Ch-21
Question 1:
Find the magnitude of vector ……………
Question 2:
Find the direction ratio and the …………………
Question 3:
…………………..
……………………
…………………..
Question 10:
Show that the points A, B, and C with position vectors ……………. a right angled triangle.
-: End of Vectors S. Chand ISC Class-12 Maths Solution :-
Return to :- OP Malhotra S. Chand ISC Class-12 Maths Solutions
Thanks
Please share with your friends



VERY USEFUL STUDY GUIDE FOR STUDENTS AND TEACHERS.
thanks
Says “Alert: Content is Protected”
No protected, it is removed but soon upload it
Okay
Sir this chapter does not have a solution
our team uploading work is in progress
Sir you haven’t uploaded solutions for Vectors. If you can, please upload. Thank you
Thank you for reading my comment
keep in touch for any problems of icse isc
work in progress
uploading work is in progress
This chapter doesn’t have solutions
All chapter PDF solutions showing / working completely
please visit again for analysis