Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures Class 9 RS Aggarwal Exe-17B Goyal Brothers ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17. In this article you will learn how to solve problems on Perimeter and Area of Quadrilateral. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9 Mathematics.
Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures Class 9 RS Aggarwal Exe-17B Goyal Brothers ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-17 | Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures |
| Writer | RS Aggrawal |
| Topics | Area and Perimeter of Quadrilateral |
| Academic Session | 2024-2025 |
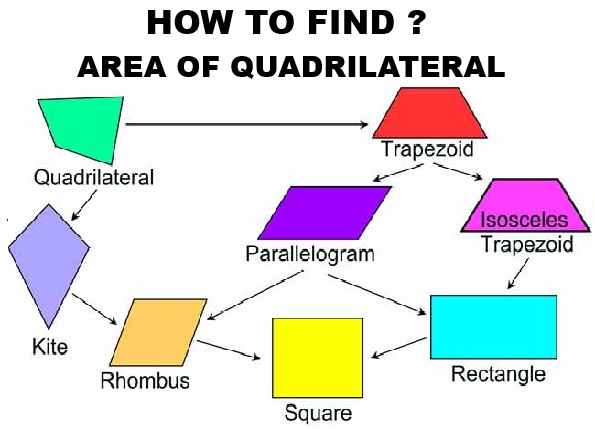
How to Find Area of Any Quadrilateral
For a general quadrilateral with sides a, b, c, and d, and diagonals p and q:
1. Calculate semi-perimeter (s) = (a + b + c + d) / 2
2. Area = √[(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)(s-d) – (pq/4)²]
Rectangle
For a rectangle with length (l) and width (w):
Area = l × w
Square
For a square with side (s):
Area = s²
Rhombus
For a rhombus with diagonals p and q:
Area = (p × q) / 2
Trapezoid
For a trapezoid with parallel sides a and b, and height (h):
Area = (a + b) × h / 2
Parallelogram
For a parallelogram with base (b) and height (h):
Area = b × h
Kite
For a kite with diagonals p and q:
Area = (p × q) / 2
Exercise- 17B
(Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures Class 9 RS Aggarwal Exe-17B Goyal Brothers ICSE Maths Solutions Ch-17)
Que-1: Find the area of a quadrilateral one of whose diagonals is 25cm long and the lengths of perpendiculars from the other two vertices are 16.4 cm and 11.6 cm respectively.
Sol: Area = (1/2) × one diagonal × Sum of the lengths of the perpendiculars drawn from it on the remaining two vertices.
= (1/2) × 25 × (16.4+11.6)
= (25/2)×28 = 25×14 = 350 cm²
Que-2: The diagonals of a quadrilateral intersect each other at right angles. If the lengths of these diagonals be 14cm and 19cm respectively, find the area of quadrilateral.
Sol: Since we have given that
The diagonal of a quadrilateral intersect each other at right angle.
So, the quadrilateral becomes “Rhombus”.
Length of first diagonal = 14 cm
Length of another diagonal = 19 cm
So, the area of rhombus becomes
= (1/2)×d1×d2
= (1/2)×14×19
= 133 cm².
Que-3: Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 29cm, BC = 21cm, AC = 20cm, CD = 34cm and DA = 42cm.
Sol: Given that
Sides of a quadrilateral are AB = 42 cm, BC = 21 cm, CD = 29 cm
DA = 34 cm and diagonal BD = 20 cm
Area of quadrilateral = area of ΔADB + area of ΔBCD.
Now, area of ΔABD
Perimeter of ΔABD
We know that
⇒ S = (1/2)(𝐴𝐵+𝐵𝐷+𝐷𝐴)
= (1/2)(34+42+20)=96
= 96/2
= 48 𝑐𝑚
Area of ΔABD = √{S(S-AB)(S-BD)(S-DA)}
= √{48(48-42)(48-20)(48-34)}
= √{48(14)(6)(28)}
= 336cm2
Also for area of ΔBCD,
Perimeter of ΔBCD
2s = BC+CD+BD
⇒ S = (1/2)(29+21+20)+35cm
By using heron’s formulae
Area of ΔBCD = √{s(s-bc)(s-cd)(s-db)}
= √{35(35-21)(53-29)(35-20)}
= √(210×210)
= 210 cm²
∴ Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 336 + 210 = 546.
Que-4: Find the perimeter and area of quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 9cm, AD = 12cm, BD = 15cm, CD = 17cm and ∠CBD = 90°
Sol: In the right angled : ΔACB
AB² = BC²+AC²
⇒ 17² = BC²+15²
⇒ 17²-15² = BC²
⇒ 64 = BC²
⇒ BC = 8cm
Perimeter = AB+BC+CD+AD
= 17+8+12+9
= 46 cm
Area of ΔABC = (1/2)(b×h)
= (1/2)(8×15)
= 60 cm²
In : ΔADC
AC² = AD²+CD²
So, ΔADC is a right- angled triangle at D
Area of ΔADC = (1/2)×b×h
= (1/2)×9×12
= 54 cm²
∴ Area of the quadrilateral = Area of ΔABC + Area of ΔADC
= 60+54
= 114 cm²
Que-5: Calculate the area of quadrilateral ABCD in which : AB = 24cm, AD = 32cm, ∠BAD = 90°, and BC = CD = 52cm.
Sol: Here ABD is a right triangle. So the area will be :
ΔABD = (1/2)(24)(32)
= 384
Again
BD = √(24²+32²)
= 8√(3²+4²)
= 8 ( 5 )
= 40
Now BCD is an isosceles triangle and BP is perpendicular to BD, therefore
DP = (1/2) BD
= (1/2) (40)
= 20
From the right triangle DPC we have
PC = √(52² – 20²)
= 4√(13²-5²)
= 4(12)
= 48
So
ΔDPC = (1/2)(40)(48)
= 960
Hence the area of the quadrilateral will be :
ΔABD + ΔDPC = 960 + 384
= 1344 cm2
Que-6: Calculate the area of quadrilateral ABCD in which ΔBCD is equilateral with each side equal to 26cm, ∠BAD = 90° and AD = 24 cm.
Sol: ΔBDC is an equilateral triangle with side a=26 cm
Area of ΔBDC = (√3/4) a²
= (√3/4)×26²
= 1.734×676
= 292.37 cm²
By using Pythagoras theorem in the right – angled triangle ΔDAB,We get
AD²+AB² = BD²
⇒ 24²+AB² = 26²
⇒ AB² = 26²-24²
⇒ AB² = 676-576
⇒ AB² = 100
⇒ AB = 10cm
Area of the ΔABD = (1/2)×b×h
= (1/2)×10×24
= 120 cm²
Area of the quadrilateral
= Area of the quadrilateral
= Are of ΔBCD+Area of ΔABD
= 292.37+120
= 412.37cm
Que-7: In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is right angled at A, BC = 7.5cm and AB = 4.5cm. If the area of quad. ABCD is 30 cm² and DL is the altitude of ΔDAC, calculate the length DL.
Sol: BC = 7.5cm and AB = 4.5cm
∠A = 90°
Area of quad. ABCD = 30 cm²
Using the Pythagorean theorem,
BC² = AB² + AC²
(7.5)² = (4.5)² + AC²
56.25 = 20.25 + AC²
AC² = 36
AC = 6 cm
Area of ΔABC = (1/2) × AB × AC
= (1/2) × 4.5 × 6
= 13.5 cm²
Area of ΔDAC = 30 – 13.5
= 16.5 cm²
Area of ΔDAC = (1/2) × AC × DL
16.5 = (1/2) × 6 × DL
16.5 = 3 × DL
DL = 16.5/3
DL = 5.5 cm
Que-8: The perimeter of a rectangle is 81 m and its breadth is 12 m. Find the length and area.
Sol: PERIMETER =81 m
BREADTH = 12 m.
TO FIND LENGTH AND AREA, WE DO…
2(L+B)=P
81 = 2(x + 12)
2x+24 = 81
2x = 57
x = 57/2
x = 28.5 m
AREA = 57/2×12
= 57×6
= 342 m²
Que-9: The perimeter of a rectangular field is (3/5)km and its length is twice its breadth. Find the area of a field in m².
Sol: Let the width be x and length 2x km.
Hence
2(x+2x) = 35
x = 110 km
= 100 m
Hence the width is 100m and length is 200m
The required area is given by
A = length x width
= 100 x 200
= 20,000 m²
Que-10: A rectangular plot 30m long and 18m wide is to be covered with grass leaving 2.5 m all around it. Find the area to be laid with grass.
Sol: Area of big rectangle = (30×18) m²
leaving 2.5m each side that mean 2×2.5 = 5m
Subtracting 5m from each side (25×15) m² = 325 m²
∴ Area of grass = 325 m²
Hence, the answer is 325 m².
Que-11: A foot path of uniform width runs all around inside of a rectangular field 45m long and 36m wide. If the area of the path is 234 m², find the width of the path.
Sol: Area = Length x Breadth
Area = 45 x 36
Area = 1620 m²
Area of the path = 234 m²
Area of the field without the path = 1620 – 234 = 1386 m²
Width = x m
Length = 45 – x – x = 45 – 2x
Width = 36 – x – x= 36 – 2x
Area = length x Breadth
(45 – 2x)(36 – 2x) = 1386
1620 – 90x – 72x + 4x² = 1386
4x² – 162x + 234 = 0
2x² – 81x + 117 = 0
(2x – 3)(x – 39) = 0
x = 1.5 or x = 39 (rejected, 39 will result in negative length)
Width of the path = x = 1.5 m.
Que-12: The adjoining diagram shows two cross paths drawn inside a rectangular field 45m long and 38m wide, one parallel to length and the other parallel to breadth. The width of each path is 4m. Find the cost of gravelling the paths at Rs5.60 per m².
Sol: Two cross paths drawn inside a rectangular field 45 m long and 38 m wide.
The width of each path is 4 m.
area of path – area of rectangle formed by overlapping of two paths
(45 x 4) + (38 x 4) – (4 x 4) m²
180 + 152 – 16 m²
332 – 16 m²
316 m²
Now the cost of graveling the paths will be:
316 m² x 5.60
Rs 1769.6
Que-13: A rectangle of area 144 cm² has its length equal to x cm. Write down its breadth in terms of x. Given that its perimeter is 52 cm, write down an equation in x and solve it to determine the dimensions of the rectangle.
Sol: Area of the rectangle = 144 cm²
Length = x cm
Perimeter = 52 cm
area = length × breadth
⇒ x × b = 144
⇒ b = 144/x
Hence, breadth in terms of ‘x’ is 144/x .
Perimeter = 2(l+b)
⇒ 2( x + 144/x ) = 52
⇒ 2x + 288/x = 52
⇒ 2x² + 288 = 52x
⇒ 2x² – 52x + 288 = 0
⇒ 2(x² – 26x + 144) = 0
⇒ 2(x² – 8x – 18x + 144) = 0
⇒2[x(x – 8) – 18(x – 8)] = 0
⇒ 2(x – 18)(x – 8) = 0
⇒ x = 18 ; x = 8
Que-14: The perimeter of a rectangular plot is 130m and its area is 1000 m². Take the length of the plot as x metres. Use the perimeter to write the value of breadth in terms of x. Use the values of length, breadth and area to write an equation in x. Solve the equation and calculate the length and breadth of the plot.
Sol: Perimeter = 2(length + breadth)
→ 130 = 2(x + breadth)
→ (130/2) = x + breadth
→ 65 – x = breadth {breadth}
Given, Area = 1000 m²
= > length * breadth = 1000
= > x * (65 – x) = 1000
= > 65x – x² = 1000
= > x² – 65x + 1000 = 0 {equation}
= > x² – 25x – 40x + 1000 = 0
= > x(x – 25) – 40(x – 25) = 0
= > (x – 25)(x – 40) = 0
= > x = 25 or 40
Que-15: If the length of a rectangle is increased by 10 cm and the breadth decreased by 5cm, the area remains unchanged. If the length is decreased by 5cm and the breadth is increased by 4cm, even then the rea remains unchanged. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
Sol: Let the length of the rectangle be l and breadth be b.
Now, (l+10)(b-5) = lb
lb+10b-5l-50 = lb
10b-5l = 50
2b-l = 10
Multiply by 4 we get
8b-4l = 40 ……………(i)
(l-5)(b+4) = lb
lb-5b+4l-20 = lb
-5b+4l = 20 …………….(ii)
Subtracting eq(i) and (ii) we get
3b = 60
b = 20
2×20 – l = 10
l = 40-10
l = 30.
Que-16: A room is 13m long and 9m wide. Find the cost of carpeting the room with a carpet 75 cm wide at Rs12.50 per metre.
Sol: Given
Length of the room = 13 m
Breadth of the room = 9 m
Area of the room = (length × breadth)
= (13×9) m²
= 117 m²
Let the length required of the carpet be x m
Breadth of the carpet = 75 cm = 0.75 m
Area of the carpet =(0.75×x) m²
= 0.75x m²
For carpeting the room
Area converted by the carpet = Area of the room
0.75x = 117
x = 117/0.75
x = 156 m
Hence, length of the carpet = 15 m
1 m carpet cost = rupees 12.50
156 m carpet cost will be = (156×12.50)
= Rupees 1950.
Que-17: A rectangular courtyard 3.78 m long and 5.25 m broad is to be paved exactly with square tiles, all of the same size. What is the largest side of such a tile? Also, find the number of tiles.
Sol: Length of rectangular courtyard = 3.78 m = 378 cm
Breadth of rectangular courtyard = 5.25 m = 525 cm
Highest possible dimension of square = HCF of 378 and 525
⇒ 21 cm
Minimum number of tiles = (Area of rectangular courtyard)/(Area of square)
⇒ (l × b)/a²
⇒ (378 × 525)/(21)2
⇒ 450
Que-18: The cost of cultivating a square field at the rate of Rs160per hectare is Rs1440. Find the cost of putting a fence around it at the rate of 75 paise per metre.
Sol: Area = 1440 / 160 hectares
= 9 hectares
= 90000 m2
∴ One side = √90000 m
= 300 m
So perimeter = 4 x 300 m
= 1200 m
∴ Cost of fencing = Rs (1200 x 75) / 100
= Rs. 900
Que-19: Find the area of parallelogram, if its two adjacent side are 12 cm and 14 cm, and if the diagonal connecting their ends is 18 cm.
Sol: Perimeter of one triangle formed = 14 + 12 + 18 = 44
2s = 44cm
s = 22cm
Area of Triangle = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c) where a,b and c are the sides of the triangle.
= √22(22-12)(22-14)(22-18)
=√22 x 10 x 8 x 4
=√2 x 11 x 2 x 5 x 2 x 4 x 4
=2 x 4 √110 = 8√110 cm²
Therefore area of parallelogram = 2 x Area of Triangle
= 2 x 8√110
= 16√110 cm²
≈ 167.80 cm²
Que-20: Find the length of a diagonal of a square of area 200 cm².
Sol: We know that,
Area of a square = (1/2)×(diagonal)²
200 = (1/2) × (diagonal)²
(Diagonal)² = 200×(2/1)
Diagonal = √400
Diagonal = 20 cm.
Que-21: The area of square field is 8 hectares. How long would a man take to cross it diagonally by walking at the rate of 4 kmph?
Sol: Given, area of square field = 8 hectares
= 8×0.01 [1hectare=0.01km²]
= 0.08 km²
Now, area of square field = (side of square)² = 0.08
⇒ side of square field = √0.08 = (2√2)/10 = √2/5 = km
Distance covered by man along the diagonal of square field = length of diagonal
√2 side = √2 × (√2/5) = 2/5 km
Speed of walking = 4 km/h
∴ Time taken = distance/ speed = 2/(5×4) = 2/20 = 1/10
= 0.1 hour
= (1/10) × 60min = 6 minutes.
Que-22: Find the area and perimeter of square plot of land whose diagonal is 15m. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.
Sol: Let a be the length of each side of the square.
Hence
2a2 = ( diagonal )2
a2 = 1522
a2 = 112.5
a = 10.60
Hence
Area = a2
= 112.5 sq . m
And
Perimeter = 4a = 42.43 m
Que-23: The area of parallelogram is 338 m². If its altitude is twice the corresponding base, determine the base and altitude.
Sol: Let the base of the parallelogram be a.
According to the question altitude is twice the corresponding base.
∴ Altitude = 2a
Area of parallelogram = base × altitude = 338 m2
∴ a × 2a = 338
⇒ a = 13 m
Altitude = 2a = 26 m.
Que-24: Find the area of rhombus one side of each measures 20 cm and one of whose diagonals is 24 cm.
Sol: Side of a rhombus is 20 cm.
One diagonal is 24 cm
We know that all sides of a rhombus are equal
⇒ AB = BD = DC = CA = 20 cm
Two diagonals are AD and BC
Now,
BM = MC = BC/2 =24/2 = 12 cm (As in rhombus diagonals bisect each other at 90 degrees)
Hence,
Consider triangle AMC,
As it is a right-angled triangle
⇒ AC² = AM² + MC²
⇒ ( 20)² = AM² + (12)²
⇒ AM² = 400 – 144 = 256
⇒ AM = √256 = 16 cm
Now,
AM = MD = 16 cm
AD = (AM +MD) = (16 + 16) = 32 cm
Area of a rhombus =1/2 × product of diagonals
⇒ 1/2 × ( AD × BC)
⇒ 1/2 × 32 × 24 = 384 cm²
Que-25: The two parallel side of trapezium are 58m and 42m long. The other two sides are equal, each being 17m. Find its area.
Sol: In this case, a = 58 m and b = 42 m, and the two other sides of equal length are 17 m each. We can use these values to find the height of the trapezium using the Pythagorean Theorem:
h² = (17 m)² – (8 m)²
h² = 289 – 64
h = √225
h = 15 m
Area = {(a + b)/2} × h
Area = {(58 m + 42 m)/2} × 15 m
Area = (100 m/2) × 15 m
Area = 50 m × 15 m
Area = 850 m²
Que-26: The perimeter of a rhombus is 52cm. If one of its diagonal is 24 cm long, find :
(i) the length of the other diagonal (ii) the area of the rhombus
Sol: Let a be the length of each side of the rhombus.
4a = perimeter
4a = 52
a = 13 cm
(i) It is given that,
AC = 24 cm
We have to find BD.
Now
a² = (AC/2)² + (BD/2)²
13² = 12² + (BD/2)²
(BD/2)² = 5²
BD = 10 cm
Hence the other diagonal is 10cm.
(ii) Area of the rhombus = (1/2) x AC x BD
= (1/2) x 24 x 10
= 120 sq.cm.
Que-27: The area of a rhombus id 216 cm² and one its diagonals measures 24 cm. Find :
(i) the length of the other diagonal (ii) the length of each of its side (iii) its perimeter
Sol: (i) We know that,
Area of Rhombus = (1/2) x AC x BD
Here
A = 216 sq.cm
AC = 24 cm
BD = ?
Now,
A = (1/2) x AC x BD
216 = (1/2) x 24 x BD
BD = 18 cm.
(ii) Let a be the length of each side of the rhombus.
a2 = (AC/2)² + (BD/2)²
a2 = 122 + 92
a2 = 225
a = 15 cm
(iii) Perimeter of the rhombus = 4a = 60 cm.
Que-28: Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 36 cm and 25 cm. If the distance between longer sides is 15cm, find the distance between the shorter sides.
Sol: Longer side = 36 cm
Shorter side = 25 cm
Distance between the longer sides = 15 cm
Area = Base × Height
Area = 36 × 15 = 540 cm²
Now, using the same area formula but taking 25 cm as the base and h as the required height:
Area = 25 × h
25×h = 540
h = 540/25
h = 21.6 cm.
Que-29: In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium in which AD = 13cm, BC = 5cm, CD = 17cm and ∠A = ∠B = 90°.
Calculate : (i) AB (ii) Area of trap. ABCD
Sol: Given, AD = 13cm,BC = 5cm, CD = 17cm ,∠A =∠B =90°
(i) Since, BC = BE + EC
= 13cm = 5cm + 8 cm
Also, AD = 5cm
Since ∠A = ∠B = 90°
⇒AD ║ BC.
Now, In ΔDEC
∠DEC = 90°
By applying Pythagoras Theorem
DC² = DE² + EC²
17² = DE² + 8²
DE² = 17² – 8²
DE² = 289-64
DE = √225 = 15cm.
(ii) In trapezium ABCD
AB is the height of trapezium parallel to BC.
Now,
Area of trapezium = (1/2) × (sum of opposite parallel side) × height
= (1/2) × (13+5) × 15
= (1/2) × 18 × 15
= 135 cm²
Que-30: The adjoining figure shows a field with the measurements given in metres. Find the area of the field.
Sol: From figure,
Area of right angled △AXB = (1/2) × base × height
= (1/2) × BX × AX
= (1/2) × 30 × 12
= 180 m².
Area of trapezium XZCB = (1/2)× (sum of parallel sides) × distance between them
= (1/2) × (BX + CZ) × 15
= (1/2) × (30 + 25) × 15
= (1/2) × 55 × 15
= 412.5 cm².
Area of right angled △CZD = (1/2) × base × height
= (1/2) × CZ × ZD
= (1/2) × 25 × 10
= 125 m².
Area of △AED = (1/2) × base × height
= (1/2) × AD × EY
= (1/2) × 37 × 20
= 370 m².
Area of field = Area of right angled △AXB + Area of trapezium XZCB + Area of right angled △CZD + Area of △AED
= 180 + 412.5 + 125 + 370 = 1087.5 m².
– : End of Perimeter and Area of Plane Figures Class 9 RS Aggarwal Exe-17B Goyal Brothers ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to : – RS Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-9 Mathematics
Thanks
Please Share with your friends if helpful


