Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified ICSE Class-9 Solutions Chapter-9. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exercise /Lesson -9 Practical Chemistry with Additional Questions , Previous Year Questions and Unit Test-9 of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers New Simplified Chemistry . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified ICSE Class-9 Solutions Chapter-9
–: Select Topics :–
Previous Year Questions
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified
Question 1.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between the following gases:
(a) Hydrogen and oxygen
(b)Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide
(c) Hydrogen chloride and hydrogen sulphide
(d) Chlorine and nitrogen dioxide
(e) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride
(f) Sulphur dioxide and chlorine.
Answer:
Chemical test to distinguish between
(a)
Hydrogen: Bums with a pale-blue flame when a burning splint is brought near it. Oxygen : The gas turns an alkaline solution of pyrogallol dark brown.
(b)
Carbon dioxide [CO2]: Pass the gas through acidified potassium permanganate solution pink colour does not change.
Sulphur dioxide [SO2]: Potassium permanganate sol. pink colour changes to clear colourless.
(c)
Hydrogen chloride [HCl]: Turns silver nitrate sol. into curdy white ppt. This ppt. is soluble in NH4OH but insoluble in dil. HN03 does not show lead acetate paper test.
Hydrogen sulphide [H2S]: Shows no such test, with AgNO3[sol.] Put moist lead acetate paper in H2S gas. It turns silvery black.
(d)
Chlorine [Cl2]:
- Moist litmus [blue] turns red and gets bleached,
- Turns moist starch iodide paper blue black.
Nitrogen dioxide [NO2]:
- Turns blue litmus red.
- Displaces I2 from KI and turns potassium iodide paper brown.
(e)
Ammonia [NH3]: Bring a glass rod dipped in cone. HCl gives dense white fumes. Turns nessler’s reagent from colourless to pale-brown.
Hydrogen chloride [HCl]: Bring a glass rod dipped in cone. HCl, no white fumes. No-action with nessler’s reagent.
(f)
Sulphur dioxide [SO2]:
- Moist blue litmus paper turns red.
- turns acidified potassium permanganate from pink to colourless.
Chlorine [Cl2]:
- Moist blue paper turns red and gets bleached
- Turns moist starch iodide paper blue-black
Question 2.
On heating which of the following substances i.e. copper carbonate, zinc carbonate, washing soda, copper sulphate, zinc nitrate, copper nitrate, lead nitrate, ammonium chloride and ammonium dichromate – relate to the reactions given below.
(a) A white substance which leaves an amphoteric oxide as a residue [whose colour varies in the heated and in the cold state] and evolves a gas which turns lime water milky.
(b) An efflorescent substance which leaves a residue having the same colour as the substance and evolves a gas which changes the colour of cobalt chloride paper.
(c) A white solid which evolves two colourless gases which on cooling combine and condense on the cooler parts of the test tube.
(d) A coloured substance which decomposes violently leaving a coloured residue and evolving two neutral gases one of which is unreactive or inert in nature.
(e) A coloured substance which leaves a black residue and evolves two gases one of which is acidic and coloured and the other neutral and colourless.
(f) A coloured substance which leaves on strong heating a black residue and evolves two colourless gases one of which is acidic and the other neutral.
(g) A white crystalline solid which decrepitates on heating leaving a residue which fuses with the glass and evolves two gases one of which is coloured and acidic.
(h) An amorphous substance which turns from pale green to black on strong heating evolving a colourless, acidic gas as the only gaseous product.
Answer:
(a) Zinc carbonate [ZnCO3].
(b) Washing soda Na2CO3.10H2O Efflorescent substance.
(c) Ammonium chloride [NH4Cl].
(d) Ammonium dichromate [orange] [NH] Cr2Or
(e) Copper nitrate Cu[NO3]2.
(f) Copper sulphate [CuSOJ.
(g) lead nitrate Pb[NO3]2.
(h) Copper carbonate CuCO3.
Question 3.
Give balanced equations for the following conversions affected by heat alone on the substances:
(a) Copper carbonate to copper oxide;
(b) Hydrated copper sulphate to sulphur dioxide;
(c) Copper nitrate to nitrogen dioxide;
(d) Ammonium dichromate to nitrogen; .
(e) Zinc carbonate to zinc oxide;
(f) Zinc nitrate to nitrogen dioxide
Answer:
Action of heat on:
(a)
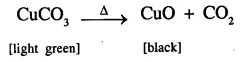
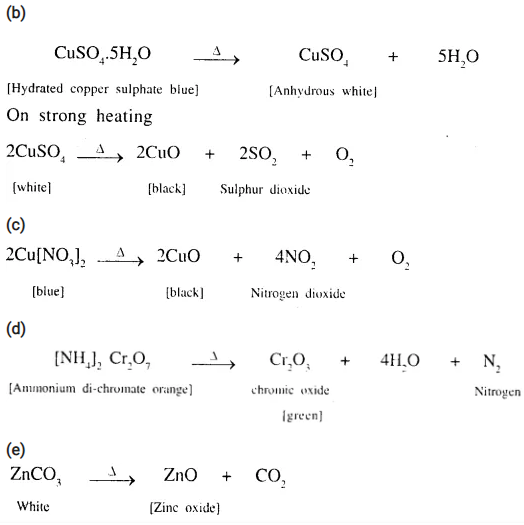

Question 4.
Using dilute sulphuric acid how would you differentiate between:
(a) Copper and magnesium.
(b) Sodium sulphide and sodium carbonate.
How would you identify the gaseous products evolved.
Answer:
Action of dil. H2SO4 on
(a) Copper — has no action
Magnesium — produces H2 burns with blue flame with pop-sound.
(b) Sodium sulphide → H2S
Na2S + H2SO4→ Na2S04 + H2 S→Turns lead acetate paper silvery black
Sodium carbonate → C02
Na CO + H9S04 → Na2SO4 + H20 + CO2
CO2 — Turns lime water milky.
Question 5.
Using a platinum wire, cone, hydrochloric acid and a Bunsen burner how would you distinguish between the three salts e. sodium chloride, potassium chloride and calcium chloride. Explain in brief the method used for the same.
Answer:
Application of flame test – to identify the metal in the substance
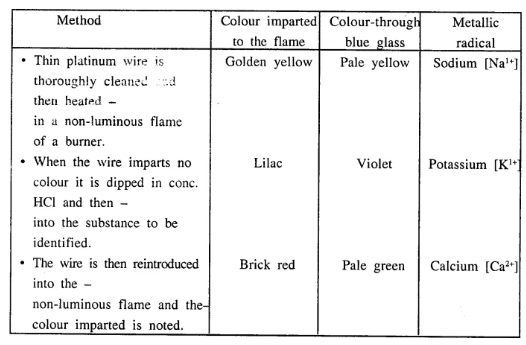
Question 6.
Using given samples of temporary and permanent hard water, soft water, ordinary soap, detergent and washing soda how would you
(a) distinguish between hard and soft water
(b) distinguish between temporary hard water and permanent hard water
(c) remove temporary hardness from water without using a chemical compound
(d) remove temporary hardness and permanent hardness from water using a chemical compound
(e) prove the advantage of detergent over soap.
Answer:
(a) Differentiating hard water from soft water
- Two unknown samples ‘X’ and ‘Y’ containing hard water and soft water are taken – separately in the trough or beaker.
- Ordinary soap is rubbed by the hands – inside each sample.
Observation
- One sample of water ‘X’ lathers with soap.
- The sample of water ‘Y’ does not lather with
Result
- Sample ‘X’ which lathers is – soft water.
- Sample ‘Y’ which does not lather is – hard
(b) Differentiating temporary and permanent hard water
- Two unknown samples ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing temporary and permanent hard water are taken – separately in a trough or beaker.
- The water is boiled slowly, gases allowed to escape out, and then the water is filtered.
- Ordinary soap is rubbed by the hands – inside each filtered sample.
Observation
- One sample of water ‘A’ – lathers with soap.
- The sample of water ‘B’ – does not lather with
Result
- The boiled and filtered sample ‘A’ which lathers is temporary hard water – whose hardness is removed by boiling. Sample ‘B’ is permanent hard water – whose hardness cannot be removed by boiling.
(c) Remove temporary hardness from water without using chemical compound. Temporary hardness can be removed by heating the hard water.
Experiment
Temporary hard water softened by heating
- Temporary hard water is taken in a beaker and heated
- After the gases escape out, the water is filtered through a filter paper.
- Ordinary soap is rubbed – inside the filtered solution.
Observation
- The boiled and filtered sample of – temporary hard water lathers readily with soap.
Result
Temporary hard water can be – softened by heating.
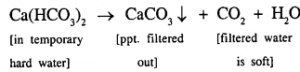
(d) To remove temporary hardness and permanent hardness using a chemical compound. Chemical compound used is washing soda which removes both kind of hardness.
Experiment
Temporary and permanent hard water softened by addition of washing soda
- Temporary and permanent hard water are taken separately in beakers and washing soda is added to each sample of water. The above solutions are filtered – to remove the precipitate formed.
- Ordinary soap is rubbed – inside the filtered solution.
Observation
- The filtered sample of temporary and permanent hard water lathers – readily with ordinary soap.
Result
- Temporary hard water and Permanent hard water can be – softened by using washing soda.
(e) To prove the advantage of detergent over soap.
Experiment
Advantage of using detergents over soap
- A sample of hard water ‘X’ is taken and ordinary soap is rubbed water.
- Another sample of hard water ‘Y’ is taken and detergent is rubbed water.
[Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonic acid and do not form scum.] Observation - Lather forms in ‘Y’ but not in ‘X’.
Result
- Detergents from lather even with hard water, while ordinary soap is wasted due to formation of scum.
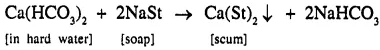
Question 7.
State the meaning of the term ‘water pollution’. State how you would find out, the different sources of pollution of water bodies in the locality.
Answer:
Water pollution — It is an undesirable change in the chemical, physical & biological conditions of water due to the presence of foreign substances in water. It leads to degrade the quality of water & makes it unsuitable for its designated use.
The main sources of pollution of water bodies in the locality are —
- Household detergents
- Sewage waste
SOURCES OF WATER POLLUTION IN THE LOCALITY
ontains Organic materials & inorganic materials such as phosphates & nitrates.
HOUSEHOLD DETERGENTS: They are household chemical cleaning organic compounds used for laundering & dish washing. They contain phosphates mainly sodium triphosphate. Phosphates are a major source of water pollution. Nutrients are added to the water in the form of nitrogen, carbon & phosphorus – generally from sewage.
DOMESTIC SEWAGE: It is waste water generated from household activities, (sewage also includes liquid waste industry and commerce)
Domestic sewage water cOrganic from food & vegetables & inorganic from soaps & detergents.
Question 8.
State in brief, the preventive steps to control the pollution of water bodies in the locality.
Answer:
PREVENTIVE STEPS TO – Control pollution of water bodies in the locality
Collection & Disposal of Domestic Sewage: A typical waste water system for sewage i.e. waste water generated from household activity consists of a network of waste water pipes.Sewer Lateral Pipe is the waste water pipe which collects sewage from household.
Server Main Pipe is the larger pipe on the main street which connects from sewer lateral pipe.
The waste water from sewer main pipe is then led to the Water treatment plant.
Water treatment plant: The waste water from sewer main pipe is then led to the water treatment plant.
It consists of –
Screen — Large waste materials such as leaves, rocks, twigs, etc. are easily removed.
Coagulation – Coagulated suspended impurities are removed by adding coagulants [e.g. alum], which settle down and are removed before filtration of ‘water. Sedimentation – Solid suspended particles settle down in the sedimentation tank. Filtration – Remaining pollutants are removed by passing water through sand & gravel filters.
Disinfection – Remaining pathogens are killed by liquid chlorine [ozone or bleaching powder]
UNIT TEST PAPER —9 , Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified
Question 1.
Select the correct gas from A to F which matches with the descriptions 1 to 5.
A: CO2 B: O02 C: NH3 D: Water vapour E: CI2 F : H2S
- Turns moist blue litmus red and then bleaches it.
- Turns moist red litmus paper blue.
- lime water milky and blue litmus paper slightly pink.
- Turns cobalt chloride paper from blue to pink.
- Turns lead acetate paper from white to silvery black.
Answer:
1. E: Cl2 2. C: NH, 3. A: C02 4. D : Water vapour 5. F: H2S
Question 2.
Select the correct salt from list II which on thermal decomposition exhibits the change in colour from list I – 1 to 5.

Question 3.
State which of the substances given below evolves oxygen gas on thermal decomposition.
- Zinc carbonate
- Washing soda
- Lead nitrate
- Ammonium dichromate
- Trilead tetroxide
- Zinc nitrate
- Mercury [II] oxide
- Anhydrous copper sulphate
Answer:
On thermal decomposition evolve oxygen are:
- Lead nitrate Pb[NO3]2
- Trilead oxide Pb3O4
- Zinc nitrate ZnfNO,],
- HgO Mercury [II] oxide
- Anhydrous copper sulphate [CuSO4]
Question 4.
Complete the table given below.
5. Select the correct answer from the words in bracket.
1 Hard and soft water can be distinguished using …………..
Hard and soft water can be distinguished using ordinary soap.
2 . Household detergents contain mainly ………. and pollute water bodies.
Household detergents contain mainly phosphates and pollute water bodies.
3. The type of water softened by addition of washing soda is …………
The type of water softened by addition of washing soda is both types.
4. Unpolluted water has ……..amount of dissolved oxygen.
Unpolluted water has high amount of dissolved oxygen.
5 . The sample of hard water which lathers with soap after boiling and filtration contains ………………………..
The sample of hard water which lathers with soap after boiling and filtration contains calcium bicarbonate.
.– : End of Practical Chemistry Dalal Simplified Solutions :–
Return to New Simplified Dalal ICSE Chemistry Class-9 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends


