Reflection of Light Exe-7C Long Answer Concise Physics ICSE Class-9 Selina Publishers. There is the solutions of Long Answer type Questions of your latest textbook which is applicable in 2025-26 academic session. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Reflection of Light Exe-7C Long Answer Type
Concise Physics ICSE Class-9 Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 9 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Writer / Publication | Concise Selina Publishers |
| Chapter-7 | Reflection of Light |
| Exe-7C | Spherical Mirrors |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-7(C) Long Answer Type |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Exercise- 7C Spherical Mirrors
page -190
Long Answer Type :
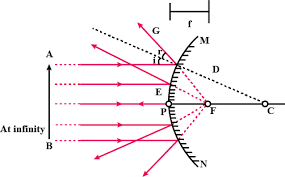
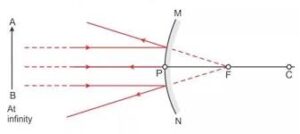
Que-1: Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate the action of (i) concave mirror and (ii) convex mirror on a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis.
Ans: (i)
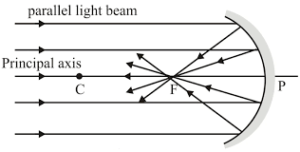
(ii)
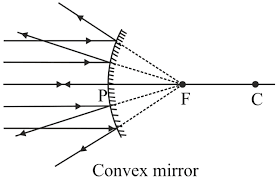
Que-2: Explain the meaning of the terms focus and focal length in case of a convex mirror, with the help of suitable ray diagram.
Ans: Focus of a convex mirror: The focus of a convex mirror is a point on the principal axis from which, the light rays incident parallel to principal axis, appear to come, after reflection from the mirror. Focal length of a convex mirror: The distance of the focus from the pole of the convex mirror is called its focal length.
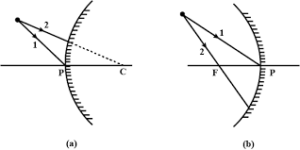
Que-3: (i) Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
(ii) In each case (a) and (b), draw reflected rays for the given incident rays and mark focus by the symbol F.
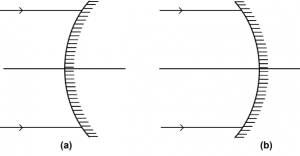
Ans: (i) Figure (a) has convex mirror. and in Figure (b) has concave mirror.
(ii) (a)
(b)
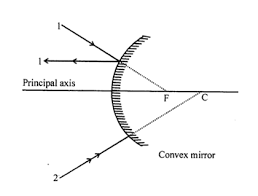
Que-4: Complete the following diagrams in Figure by drawing the reflected rays for the incident rays 1 and 2.
Ans:
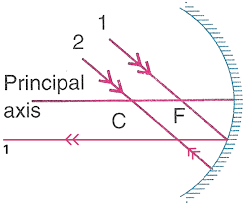
Que-5: Complete the following diagrams shown in Fig. by drawing the reflected ray for each of the incident ray A and B.
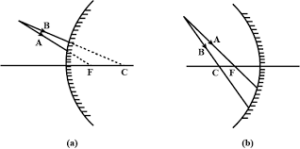
Ans:

Que-6: State the two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object? Explain your answer with the help of suitable ray diagrams.
Ans: Two convenient rays that are chosen to construct the image by a spherical mirror for a given object:
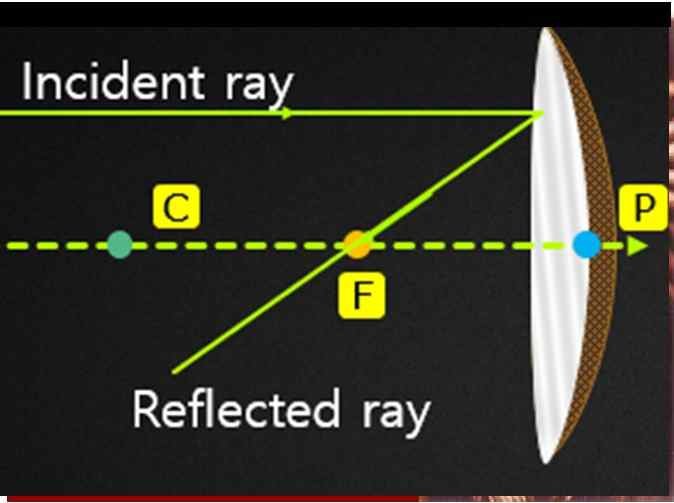
(1.) A ray passing through the centre of curvature: A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or a ray directed in the direction of centre of curvature of a convex mirror is reflected back along the same path after reflection.
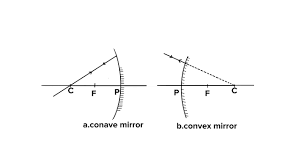
(2.) A ray parallel to the principal axis: A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, after reflection pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appears to diverge from it in case of convex mirror.
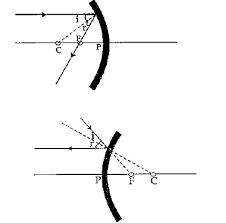
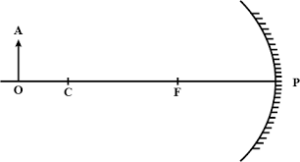
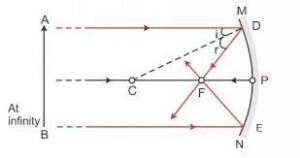
Que-7: Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
Ans:
Que-8: Figure shows a concave mirror with its pole at P, focus F and centre of curvature C. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object OA.
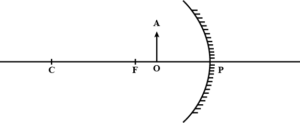
Ans:

Que-9: The diagram below in Fig.7.54, shows a convex mirror. C is its centre of curvature and F is its focus. (i) Draw two rays from A and hence locate the position of image of object OA. Label the image IB. (ii) State three characteristics of the image.
Ans: The ray diagram shows two light rays from A. The image of the object OA is formed between the focus and the pole on the other side of the mirror.
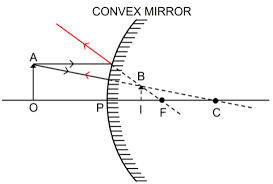
The image so formed is erect, virtual and diminished.
Que-10: Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus. State three characteristics of the image.
Ans: Ray diagram showing the formation of an image by a concave mirror for an object placed between its pole and focus:
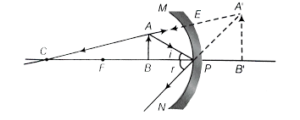
When the object is placed between focus F and pole P, the image is formed behind the mirror.
The image so formed is virtual, upright and magnified.
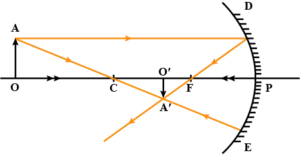
Que-11: Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave mirror for the object beyond its centre of curvature. State three characteristics of the image.
Ans: Ray diagram showing the formation of an image by a concave mirror for the object beyond its centre of curvature:
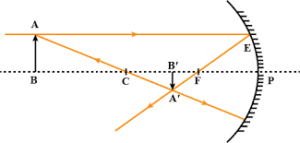
When the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature C, the image is formed between focus F and centre of curvature C. The image so formed is real, inverted and diminished
Que-12: Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object kept in front of a convex mirror. State three characteristics of the image.
Ans:
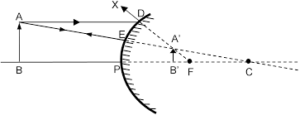
The image formed is virtual, erect and diminished
Que-13: Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a concave mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Ans: When an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror, the image formed moves away from the mirror. The image formed is real and inverted.
Page 191
Que-14: Discuss the position and nature of image formed by a convex mirror when an object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Ans: In a convex mirror, the image formed is always virtual, upright and diminished. It is always situated between its pole and focus, irrespective of the distance of object in front of the mirror.
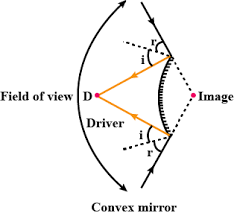
Que-15: Why does a driver use a convex mirror instead of a plane mirror as a rear view mirror? Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
Ans: A convex mirror diverges the incident beam and always forms a virtual, small and erect image between its pole and focus. Thus, a driver can see all the traffic approaching from behind. This fact enables the driver to use it as a rear view in vehicles to see all the traffic
approaching from behind.
— end of Reflection of Light Exe-7C Long Answer Concise Physics ICSE Class-9 Selina Publishers Solutions :—
Return to:- Concise Selina Physics ICSE Class-9 Solutions
Thanks