Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces Lenses Miscellaneous Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution Ch-16. Step by step solutions of Kumar and Mittal Physics of Nageen Prakashan as council latest prescribe guideline for upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ISC Board Class-12 Physics.
Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces Lenses Miscellaneous Numerical Class-12 Nootan ISC Physics Solution
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Book | Nootan |
| Chapter-16 | Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces Lenses |
| Topics | Miscellaneous Numerical |
| Academic Session | 2025-2026 |
Miscellaneous Numerical on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces Lenses
Que-60: Find the focal length and power of a convex lens which, when put in contact with a concave lens of focal length 25 cm forms a real image 5 times the size of an object placed 20 cm from the combination.
Ans- m = v/u = v/-20 = -5
= v = 100
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
=> f = uv/u-v
=> f = -20 x 100 / -20-100 = 50-3 cm
again 1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
=> 3/50 = 1/-25 + 1/f2
After solving,
=> 1/f2 = 10 cm
=> 0.1 m
P = 1/0.1 = 10 D
Que-61: A compound lens is formed with two lenses of powers + 15.5 D and – 5.5 D kept in contact. A 3 cm long object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. What is the length of the image?
Ans- P = 15.5-5.5 = 10D
f = 100/10 = 10 cm
m = f/f+u = v/u = I/O
=> 10/10-30 = I/3 = 10/-20
=> I = -1.5 cm
Que-62: Parallel rays of sun fall upon a concave lens of 10 cm focal length. At a distance of 20 cm from this lens, a convex lens of 15 cm focal length is placed. Where should the screen be placed to get the image of the sun?
Ans- for concave lens
u = -5 , f = -10 cm
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
=> -1/10 = 1/v + 1/5
=> v = -10
for convex lens u = -(20-10) = -10
f = 15 cm
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
=> 1/15 = 1/v – 1/-10
=> v = -30 cm
Que-63: A thin convex lens (L1) of focal length 60 cm and a thin concave lens (L2) of focal length f are kept co-axially, 15 cm apart as shown in figure below. When a narrow and parallel beam of light is incident on the convex lens, beam emerging from the concave lens is also a parallel beam. Find f.
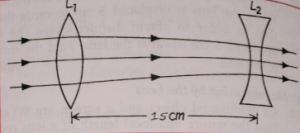
Ans- 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
=> 1/f = 1/∞ – 1/45 (1/∞ = 0)
=> 1/f = -1/45
Therefore, f = – 45 cm.
Que-64: Three lenses L1, L2 and L3 each of focal length 20 cm are placed co-axially as shown in figure. An object is held at 40 cm from the optic centre of lens L1. The final real image is formed at the focus I of L3. Calculate the separation between :
(i) L1 and L2 and (ii) L2 and L3.
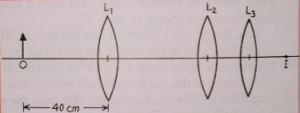
Ans- (i) Distance between L1 and L2 is 60 cm.
(ii) Distance between L2 and L3 can be any finite distance.
Que-65: A plano-convex lens (n = 3/2) of radius of curvature 5 cm is placed at a distance of ‘d2’ from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. What should be the distance ‘d1’ of a point-object ‘O’ from the plano-convex lens so that the position of final image is independent of ‘d2’? Also find the nature and position of final image from concave lens.
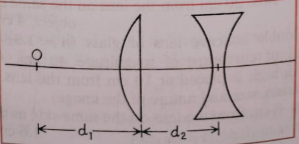
Ans- Object distance (d1)=> 10 cm
Nature of final image => Real
Position of final image from the concave lens => at infinity.
–: End of Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces Lenses Miscellaneous Numerical :–
Return to : – Nootan Solutions for ISC Class-12 Physics
Thanks
Please share with your friends


