Refraction of light ICSE Class-10 Concise Physics Solutions Selina Publishers Chapter-4. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exercise-4(A), MCQs-4(A), Numericals-4(A), Exercise-4(B), MCQ-4(B), Numericals -4(B), Exercise-4(C), MCQ-4(C),Numericals -4(C), Exercise-4(D) and MCQ-4(D),Questions of Exercise-4 Refraction of light at Plane surfaces ICSE Class-10 . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Physics |
| Class | 10th |
| Chapter-4 | Refraction of light at Plane Surface |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-4(A), MCQs, Numericals, Exe-4(B), MCQs, Numericals, Exe-4(C), MCQs, Numericals, Exe-4(D) and MCQs |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Refraction of light ICSE Class-10 Concise Physics Solutions Selina Publishers Chapter-4
-: Select Topics :-
Exe-4(A), MCQs, Numericals, Exe-4(B), MCQs, Numericals,
Exe-4(C), MCQs, Numericals, Exe-4(D) and MCQs
Exercise – 4(A) Refraction of light at Plane Surfaces ICSE Class-10
Page 80
Question 1
What do you understand by refraction of light?
Answer 1
The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction of light.
Question 2
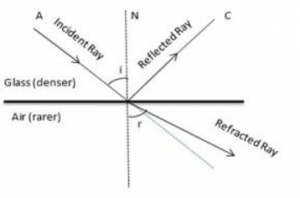
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from (i) air to glass, (ii) glass to air. In each diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r).
Answer 2
Diagram showing the refraction of light from Air to glass
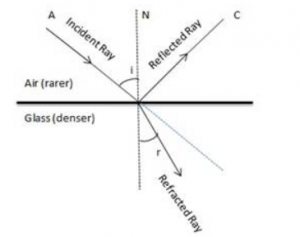
Diagram showing the refraction of light from Glass to Air
Question 3
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane glass slab. What will be (i) the angle of refraction and (ii) the angle of deviation for the ray?
Answer 3
The ray of light which is incident normally on a plane glass slab passes undeviated. That is such a ray suffers no bending at the surface because here the angle of incidence is 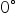 . Thus if angle of incidence
. Thus if angle of incidence ![]() , then the angle of refraction
, then the angle of refraction ![]() . And the angle of deviation of the ray will also be
. And the angle of deviation of the ray will also be 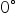 .
.
Question 4 (Refraction of light Physics)
An obliquely incident light ray bends at the surface due to change in speed, when passing from one medium to other. The ray does not bend when it is incident normally. Will the ray have different speed in the other medium?
Answer 4
Yes it will. When the medium changes, the speed of light changes.
Question 5
What is the cause of refraction of light when it passes from one medium to another?
Answer 5
The refraction of light (or change in the direction of path of light in other medium) occurs because light travels with different speeds in different media. When a ray of light passes from one medium to another, its direction (except for ![]() ) changes because of change in its speed.
) changes because of change in its speed.
Question 6
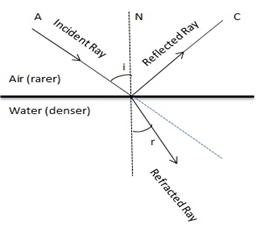
A light ray suffers reflection and refraction at the boundary in passing from air to water. Draw a neat labelled diagram to show it.
Answer 6
Air is a rarer medium while water is denser than air with refractive index of 1.33. Therefore when light ray will travel from air to water it will bend towards the normal.
Question 7 (Refraction of light Physics)
A ray of light passes from medium 1 to medium 2. Which of the following quantities of the refracted ray will differ from that of incident ray: speed, intensity, frequency, wavelength?
Answer 7
Speed, intensity and wavelength
Page 81
Question 8
State the Snell’s laws of refraction of light.
Answer 8
The Snell’s laws of refraction are:
1.The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
2.The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for the pair of the given media.
![]()
where ![]() is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
Question 9
Define the term refractive index of a medium. Can it be less than 1?
Answer 9
The refractive index of second medium with respect to first medium is defined as the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence in the first medium to the sine of the angle of refraction in the second medium.
Refractive index of a medium is always greater than 1 (it cannot be less than 1) because the speed of light in any medium is always less than that in vacuum
Question 10
(a) Compare the speeds of light of wavelength 4000  (i.e. violet light) and 8000
(i.e. violet light) and 8000  (i.e. red light) in vacuum.
(i.e. red light) in vacuum.
(b) How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it and in vacuum or air?
Answer 10
(a) Speed of light depends on medium not on wavelength hence speed will be same for both.
(b) Denser medium has a higher refractive index and therefore the speed of light in such medium is lower in comparison to the speed of light in a medium which has a lower refractive index.
Question 11
A light ray passes from water to (i) air, and (ii) glass. In each case, state how does the speed of light change.
Answer 11
Refractive index of water,![]()
Refractive index of air, ![]()
Refractive index of glass,![]()
This implies that![]()
The speed of light decreases when it enters from a rarer medium to denser medium and increases when it enters from a denser medium to rarer medium.
Therefore, the speed of light increases when light ray passes from water to air and the speed of light decreases when light ray passes from water to glass.
Question 12 (Refraction of light Physics)
A light ray in passing from water to a medium (a) speeds up (b) slows down. In each case, (i) give one example of the medium, (ii) State whether the refractive index of medium is equal to, less than or greater than the refractive index of water.
Answer 12
When the speed increases it means that the refractive index of the medium is less than that of water.
When the speed decreases it means that the refractive index of the medium is greater than that of water.
Question 13
What do you understand by the statement ‘the refractive index of the glass is 1.5 for white light’?
Answer 13
The refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light means white light travels in air 1.5 times faster than in glass.
Question 14
A monochromatic ray of light passes form air to glass. The wavelength of light in air is ![]() , the speed of light in air is c and in glass is v. If the refractive index of glass is 1.5, write down (a) the relationship between c and v, (b) the wavelength of light in glass.
, the speed of light in air is c and in glass is v. If the refractive index of glass is 1.5, write down (a) the relationship between c and v, (b) the wavelength of light in glass.
Answer 14
(a) The relation between speed of light in air c and in glass v is given by
![]()
(b) The wavelength of light in glass (![]() )
)
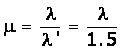
Question 15 (Refraction of light Physics)
A boy uses blue colour of the light to find the refractive index of glass. He then repeats the experiment using red colour of light. Will the refractive index be the same or different in the two cases? Give reason to support your answer.
Answer 15
The refractive index will be different. The speed of blue light in glass is less than that of red light and refractive index of glass is
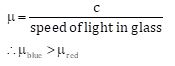
Question 16
(a) For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium (i) the least (ii) the most?
(b) Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Answer 16
(a) (i) The least for red colour and (ii) the most for violet colour.
(b) Red colour travels the fastest as its wavelength is the highest.
Question 17
Name two factors on which the refractive index of a medium depends? State how does it depends on the factor state by you.
Answer 17
The two factors on which the refractive index of a medium depends are:
1) Nature of a medium i.e. its optical density (e.g.![]() =1.5,
=1.5, ![]() =1.33) – Smaller the speed of light in a medium relative to air, higher is the refractive index of that medium.
=1.33) – Smaller the speed of light in a medium relative to air, higher is the refractive index of that medium.
2) Physical condition such as temperature – with increase in temperature, the speed of light in medium increases, so the refractive index of medium decreases.
Question 18
How does the refractive index of a medium depend on the wavelength of light used?
Answer 18
Refractive index of a medium decreases with increase in wavelength of light.
Refractive index of a medium for violet light (least wavelength) is greater than that for red light (greatest wavelength).
Question 19
How does the refractive index of a medium depend on its temperature?
Answer 19
Refractive index of a medium decreases with the increase in temperature.
With increase in temperature, the speed of light in that medium increases; thus, the refractive index (= velocity of light in vacuum/velocity of light in medium) decreases.
Question 20
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature, the glass piece is not seen.
(i) When is the glass piece not seen?
(ii) Why is the light of a single colour used?
Answer 20
(i) The glass piece is not seen when the refractive index of liquid becomes equal to the refractive index of glass.
(ii) Light of a single colour is used because the refractive index of a medium (glass or liquid) is different for the light of different colours.
Question 21
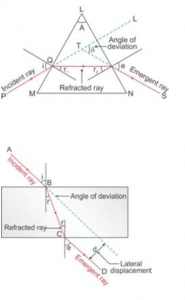
In the figure below 4.18 , a ray of light A incident from air suffers partial reflection and refraction at the boundary of water.
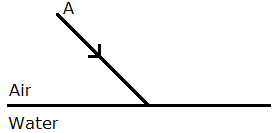
(a) Complete the diagram showing (i) the reflected ray B and (ii) the refracted ray C.
(b) How are the angles of incidence i and refraction r related?
Answer 21
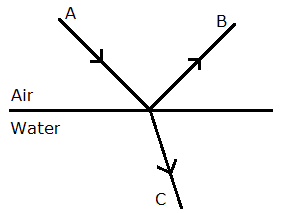
- The angles of incidence and refraction are related to each other by Snell’s law relation sin i/sin r = μw.
Question 22
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to liquid.
(a) Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, and (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
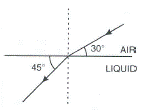
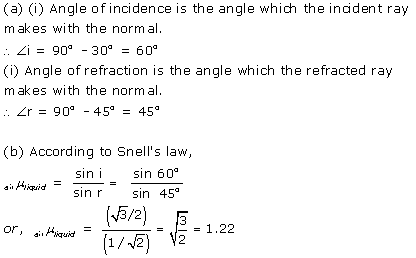
Answer 22
Question 23
The refractive index of water with respect to air is ![]() and of glass with respect to air is
and of glass with respect to air is![]() .Express the refractive index of glass with respect to water.
.Express the refractive index of glass with respect to water.
Answer 23
Refractive index of glass with respect to water ![]() is given by
is given by
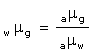
Question 24
What is lateral displacement? Draw a ray diagram showing the lateral displacement of a ray of light when it passes through a parallel sided glass slab.
Answer 24
The perpendicular distance between the path of emergent ray and the direction of the incident ray is called the lateral displacement.
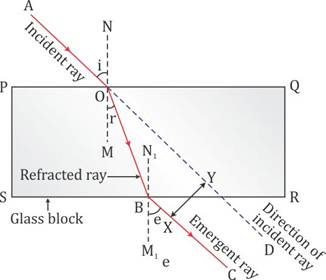
In the figure above, XY is the perpendicular distance or the lateral displacement.
Question 25 (Refraction of light Physics)
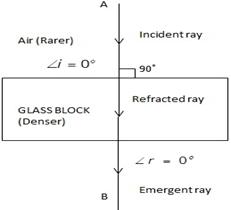
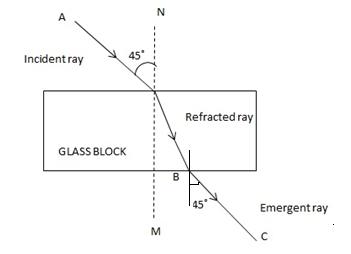
A ray of light strikes the surface at a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence is (i) 0o, (ii) 45o. In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
Answer 25
Case (i) when angle of incidence is 0o.
Case (ii) When angle of incidence is 45o.
Page 82
Question 26
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
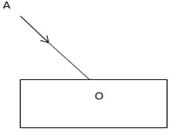
(a) Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
(b) In the ray diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first
interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to angles i and r ?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray.
Answer 26
(a)The complete path of incident ray in glass block is drawn in figure below.
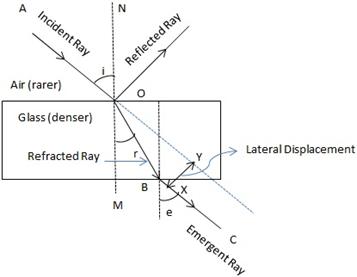
(b)Angle of incidence (i) and angle of refraction (r) are marked in part (a).
Refractive index ( ![]() ) of glass is related to the angles as
) of glass is related to the angles as
![]()
(c)Angle of emergence (e) is marked in part (a)
The two angles are related to each other by the relation
![]()
(d)Incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other.
(e)Lateral displacement is indicated in the figure by XY.
Question 27
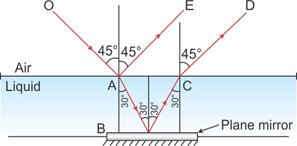
A ray of green light enters a liquid from air, as shown in the figure. The angle 1 is 45o and angle 2 is 30o.
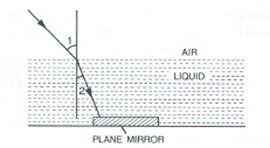
(a) Find the refractive index of liquid.
(b) Show in the diagram the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air. Mark in the diagram the angles wherever necessary.
(c) Redraw the diagram if plane mirror becomes normal to the refracted ray inside the liquid. State the principal used.
Answer 27
(a) Refractive index of the liquid =
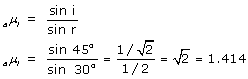
(b)
(c)
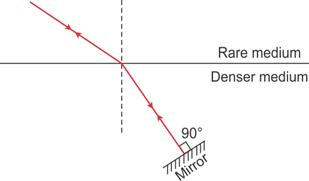
Here the ‘Principle of Reversibility’ is used.
Question 28 (Refraction of light Physics)
When an illuminated object is held in front of a thick plane glass mirror, several images are seen, out of which the second image is the brightest. Give reason.
Answer 28
When a ray of light from lighted candle fall on the surface of a thick plane glass mirror, a small part of light (nearly 4%) is reflected forming first image which is faint virtual image, while a large part of light (nearly 96%) is refracted inside the glass. This ray is now strongly reflected back by the silvered surface inside the glass. This ray is then partially refracted in air and this refracted ray forms another virtual image. This image is the brightest image because it is due to the light suffering a strong reflection at the silver surface.
Question 29
Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentences:
(a) When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed ………………….
(b) When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed ………………….
(c) The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be ………………….
Answer 29
(a) When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed decreases
(b) When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, its speed increases
(c) The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be 2/3
Refraction of light at Plane Surface “Selina Solution”
Multiple Choice Type – 4(A)
Page 82
Question 1
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it:
(a) Bends away from the normal
(b) Bends towards the normal
(c) Goes undeviated
(d) Is reflected back
Answer 1
The ray of light bends towards the normal.
Reason: As the speed of light decreases in the denser medium, it bends towards the normal.
Question 2
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incidence is:
(a) 0°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Answer 2
(a) 0°
Reason: A ray of light which is incident normally (i.e. at angle of incidence = 0°) on the surface separating the two media, passes undeviated.
Question 3
The highest refractive index is of:
(a) Glass
(b) Water
(c) Diamond
(d) Ruby
Answer 3
Diamond
Reason: As the speed of light in diamond is the least, diamond has the highest refractive index.
Numericals 4(A) Selina Solution – Refraction of light at Plane Surface
Page 82
Question 1
The speed of light in air is 3 x 108 m s-1. Calculate the speed of light in glass. The refractive index of glass is 1.5.
Answer 1

Question 2
The speed of light in diamond is 125,000 km s-1. What is the refractive index? (speed of light in air = 3 x 108 m s-1).
Answer 2

Question 3
The refractive index of water with respect to air is 4/3. What is the refractive index of air with respect to water?
Answer 3
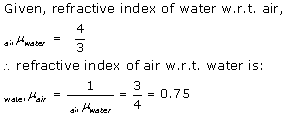
Question 4
A ray of light of wavelength 5400 ![]() suffers refraction from air to glass. Taking =
suffers refraction from air to glass. Taking = ![]() =3/2, find the wavelength of light in glass.
=3/2, find the wavelength of light in glass.
Answer 4

Selina Solution “Refraction of light at plane surface”
Exercise 4 (B)
Page 87
Question 1
What is a prism ? With the help of a diagram of a prism, indicate its refracting surfaces, refracting edges and base.
Answer 1
A prism is a transparent refracting medium bounded by five plane surfaces inclined at some angle.
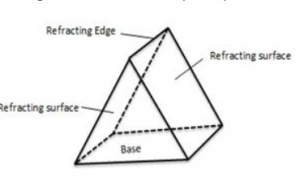
Question 2
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Fig. below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and prism, respectively.
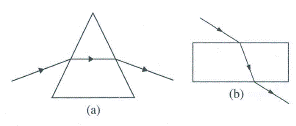
(a) In each diagram, label the incident, refracted, emergent rays and the
(b) In what way the direction of emergent ray in the two cases differ with respect to the incident ray? Explain your answer.
Answer 2
(a)
(b) For the prism, the emergent ray is not parallel to the incident ray but for the glass block it is parallel. This is because, in a prism, refraction takes place at two inclined surfaces while in a glass block refraction takes place at two parallel surfaces.
Question 3
Define the term angle of deviation.
Answer 3
The angle between the direction of incident ray and the emergent ray, is called the angle of deviation.
Question 4
Complete the following sentence:
Angle of deviation is the angle which the ________ ray makes with the direction of ________ ray.
Answer 4
Angle of deviation is the angle which the emergent ray makes with the direction of incident ray.
Question 5
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism? Why is it caused? State three factors on which angle of deviation depends.
Answer 5
In a prism the ray of light suffers refraction at two faces. The prism produces a deviation at the first surface and another deviation at the second surface. Thus a prism produces a deviation in the path of light.
The value of the angle of deviation (or the deviation produced by a prism) depends on the following four factors:
(a)the angle of incidence (i),
(b)the material of prism(i.e., on refractive index  ),
),
(c)the angle of prism (A),
(d)The colour or wavelength (![]() ) of light used.
) of light used.
Question 6 (Refraction of light Physics)
(a) How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism change with increase in the angle of incidence. Draw a curve showing the variation in the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence at a prism surface.
(b) Using the curve in part (a) above, how do you infer that for given prism, the angle of minimum deviation δmin is unique for the given light.
Answer 6
(a) As the angle of incidence increases, the angle of deviation decreases first and reaches to a minimum value (![]() ) for a certain angle of incidence. By further increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation is found to increase.
) for a certain angle of incidence. By further increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation is found to increase.
Variation of angle of deviation (![]() ) with angle of incidence(i):
) with angle of incidence(i):
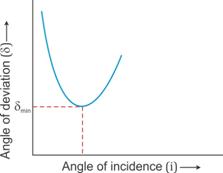
(b) For a given prism and given colour of light, angle of minimum deviation is unique since only one horizontal line can be drawn parallel to the i-axis at the lowest point of i-δ curve.
Question 7
State whether the following statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’.
The deviation produced by a prism is independent of the angle of incidence and is same for all the colours of light.
Answer 7
False.
With the increase in the angle of incidence, the deviation produced by a prism first decreases and then increases.
A given prism deviates the violet light most and the red light least.
Question 8
How does the deviation produced by a prism depend on (i) the refraction index of its material, and (ii) the wavelength of incident light
Answer 8
(i) For a given angle of incidence, the prism with a higher refractive index produces a greater deviation than a prism with a lower refractive index.
(ii) The refractive index of a medium is different for light of different colours. It increases with decrease in wavelength. Thus, the refractive index of the material of prism is maximum for violet and least for red light. Hence, the prism deviates violet light the most and red light the least, i.e., δviolet > δred.
Question 9
How does the angle of minimum deviation produced by a prism change with increase in (i) the wavelength of incident light and (ii) the refracting angle of the prism?
Answer 9
Changes in the angle of deviation as we increase
(i) The wavelength of incident light
As we increase the wavelength, angle of deviation decreases.
(ii) The refracting angle of the prism
The angle of deviation increases with the increase in the angle of prism.
Question 10 (Refraction of light Physics)
Write a relation for the angle of deviation (δ) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism in terms of angle of incident (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of prism (A).
Answer 10
The relation between the angle of incident (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of prism (A) and angle of deviation (![]() ) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism is
) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism is
![]()
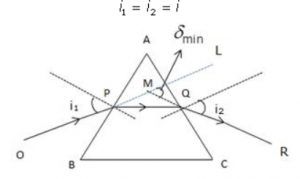
Question 11
A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence i1 passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges at an angle of emergence i2.
(i) How is the angle of emergence ‘i2‘ related to the angle of incidence ‘i1‘.
(ii) What can you say about the angle of deviation in such a situation?
Answer 11
(i) i2 = i1
(ii) Angle of deviation is minimum
Explanation: In minimum deviation position, the refracted ray inside the prism travels parallel to it if the prism is equilateral and the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence.
Question 12
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation. How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence in this position.
Answer 12
In case of an equilateral prism, when the prism is in the position of minimum ![]() deviation, the angle of incidence i1 is equal to the angle of emergence i2.
deviation, the angle of incidence i1 is equal to the angle of emergence i2.
Question 13
A light ray of yellow colour is incident on an equilateral glass prism at an angle of incidence equal to 48o and suffers minimum deviation by an angle of 36o. (i) What will be the angle of emergence? (ii) If the angle of incidence is changed to (a) 30o, (b) 60o, state whether the angle of deviation will be equal to less than or more than 36o.
Answer 13
(i) As the ray is suffering minimum deviation in an equilateral glass prism so
![]()
![]()
(ii) If the angle of incidence is changed to
(a) 30o, the angle of deviation will be more than 36o.
(b) 60o, the angle of deviation will be more than 36o.
Question 14
Name the colour of white light which is deviated (i) the most, (ii) the least, on passing through a prism.
Answer 14
(i) Violet colour will deviate the most and (ii) Red colour will deviate the least.
Question 15 (Refraction of light Physics)
Which of the two prisms, A made of crown glass and B made of flint glass, deviate a ray of light more?
Answer 15
B made of flint glass. Because it has higher refractive index.
Question 16
How does the angle of deviation depend on refracting angle of the prism?
Answer 16
The angle of deviation () increases with the increase in the angle of prism (A).
Question 17 (Refraction of light Physics)
An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of its image seen by the observer.
Answer 17
Let two rays OA and OL from a source O are incident on the prism. They are refracted along AB and LM from first face of the prism. These two rays again refract from the second face of the prism emerge out along BC and MN respectively such that they appear to come from I.
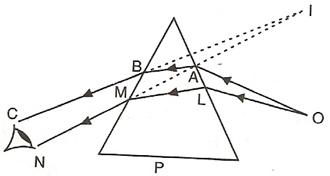
Thus, observer sees the object O raised to the position I.
Page 88
Question 18 (Refraction of light Physics)
A ray of light is normally incident on one face of an equilateral glass prism. Answer the following:
(a) What is the angle of incidence on the first face of the prism?
(b) What is the angle of refraction from the first face of the prism?
(c) What will be the angle of incidence at the second face of the prism?
(d) Will the light ray suffer minimum deviation by the prism?
Answer 18
(a) If the incident ray normal to prism then angle of incidence is 0o.
(b) In this case the angle of refraction from the first face r1= 0o.
(c) As the prism is equilateral so A=60o and r1=0o. So at the second face of the prism, the angle of incidence will be 60o.
(d) No the light will not suffer minimum deviation.
Question 19
The diagram below shows two identical prisms A and B placed with their faces parallel to each other. A ray of light of single colour PQ is incident at the face of the prism A. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray till it emerges out of the prism B.
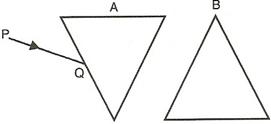
[Hint: The emergent ray out of the prism B will be parallel to the incident ray PQ]
Answer 19
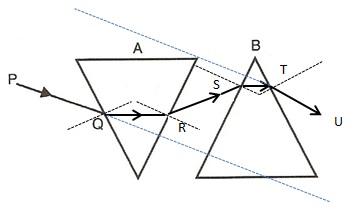
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces “Selina Solution
Multiple Choice Type 4(B)
Page 88
Question 1
In refraction of light through a prism, the light ray:
(a) Suffers refraction only at one face of the prism
(b) Emerges out from the prism in a direction parallel to the incident ray
(c) Bends at both the surfaces of prism towards its base
(d) Bends at both the surfaces of prism opposite to its base.
Answer 1
The light ray bends at both the surfaces of prism towards its base.
Question 2
A ray of light suffers refraction through an equilateral prism. The deviation produced by the prism does not depend on the:
(a) Angle of incidence
(b) Colour of light
(c) Material of prism
(d) Size of prism
Answer 2
The deviation produced by the prism does not depend on the size of prism.
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces “Selina Solution
Numericals 4(B)
Page 88
Question 1
A ray of light incident at an angle 48o on a prism of refracting angle 60o suffers minimum deviation. Calculate the angle of minimum deviation.
[Hint: δmin = 2i – A]
Answer 1
Angle of incidence, i = 480
Refracting angle, A = 600
Angle of minimum deviation, 𝛿min =?
We know that
𝛿min = 2i – A
𝛿min = 2(48) – 60
𝛿min = 96 – 60
𝛿min = 360
Question 2 (Refraction of light Physics)
What should be the angle of incidence for a ray of light which suffers a minimum deviation of 36o through an equilateral prism?
[Hint: A = 60°, i = (A + δmin)/2]
Answer 2
Angle of prism, A = 600
Angle of minimum deviation, 𝛿min = 360
Angle of incidence, i = ?
We know that
𝛿min = 2i – A
360 = 2i – 600
i = 480