Reproductive System Class-10 Long and Structured Questions Goyal Brothers Prakashan ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-12 . We Provide Solutions of Long and Structured Questions of Exercise-12 The Reproductive System. All solutions are given as council prescribe guideline for next upcoming exam. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Ch-12 The Reproductive System Class-10 Long and Structured Goyal Brothers ICSE Biology Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brothers publications |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| Writer | Dr. K.K. Aggrawal |
| Chapter-12 | The Reproductive System |
| Topics | Solutions of Long and Structured Questions |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
D. LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Ch-12 The Reproductive System Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-188)
Question 1. Describe the stages in the development of human embryo.
Answer :
- Fertilization.
- Cleavage.
- Blastulation.
- Implantation.
- Embryonic disc.
Question 2. Why are testes located in scrotal sacs outside the abdomen. Explain.
Answer : The testes is located outside the abdominal cavity because sperm formation requires a temperature lower than the body temperature. It is because scrotum has a temperature 1-3 degree Celsius lower than the normal body temperature, which is essential for the production of sperm or male gametes
Question 3. What are the secondary sexual characteristics in the male and female human beings.
Answer :
Secondary Sexual Characters in males:
(i) Appearance of facial hair (beard and moustache)
(ii) Pubic hair grows over the reproductive organs.
(iii) Pitch of the voice change
(iv) Increased development of musculature.
Secondary Sexual Characters in females:
(i) Development of mammary glands.
(ii) Pubic hair grows over the reproductive organs.
(iii) Menstrual cycle starts.
(iv) Increase in the subcutaneous fat particularly in thighs, buttocks and face.
Question 4. What are the accessory reproductive organs. Give a brief about them.
Answer :
In the male reproductive system, the essential organs of reproduction are called: The testes are the male gonads and are considered essential organs of the system. The seminal vesicles and Cowper glands are accessory glands and are not essential organs of the system.
Accessory reproductive glands of female include bartholin’s gland, skene’s gland and mammary glands. Bartholin’s gland or greater vestibular glands are two glands located at the left and right of the opening of the vagina.
E. STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
Ch-12 The Reproductive System Brothers Prakashan ICSE Class-10 Biology Solutions
(Page-188)
Question 1. The diagram given below represents two reproductive cells A and B. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) Identify the reproductive cells A and B.
(ii) Name the specific part of the reproductive system where the above cells are produced.
(iii) Where in the female reproductive system to these cells unite ?
Answer :
(i) A – Ovum
B – Sperm
(ii) Ovum is produced from the germinal layers in the ovary Sperm is produced from seminiferous tubules in the testis
(iii) In the fallopian tube
Question 2. Given below is a diagram of the lateral section of a testis of a man. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :
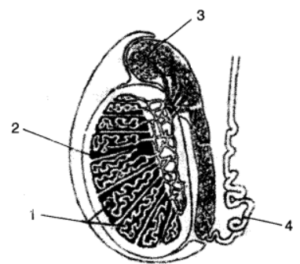
(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 of the diagram.
(ii) State the functions of the parts labelled 1 and 3.
(iii) What is the significance of the testes being located in the scrotal sac outside the abdomen ?
(iv) What is the role played by-the inguinal canal ?
(v) What is semen ?
Answer :
(i) (1) Seminiferous tubules.
(2) Testicular lobes
(3) Epidydymes
(4) Sperm duct/Vas deferens
(ii) Functions of Part 1 (Seminiferous tubules): The cells of seminiferous tubules keep on dividing and produce sperms by the process called spermatogenesis.
Function of Part 3 (Epidydymes):
(a) It helps in transportation of sperms from seminiferous tubules into vas deferens.
(b) It also helps the sperm to attain maturity.
(iii) Testis are located in scrotal sac because it provides 2-3 °C less temperture than the body temperature, which is required for maturation of sperms.
(iv) Inguinal canals facilitates the movement of testis from abdominal cavity into scrotal sac or vice-versa.
(v) Semen is an alkaline combination of sperms and seminal fluid.
Question 3. Given below are diagrams showing different stages in the process of fertilization of an egg in the female reproductive tract:
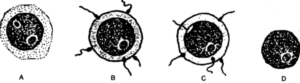
(i) Use the alphabets given below each diagram to show the correct order in the process of fertilization.
(ii) Where in the female reproductive system does this process normally take place ?
(iii) What is the biological term for the product of fusion ?
(iv) What is the chromosome number of (1) the egg (2) the fused product ?
(v) Draw a neat labelled diagram of a mature human sperm.
Answer :
(i) Correct order in the process of fertilization is D —> B —> C —> A.
(ii) In human fertilization takes place in fallopian tube.
(iii) The biological term for the product of fusion is ‘Zygote’.
(iv) The chromosome number of the egg is n and the chromosome number of the fused product is 2n.
(v)

Question 4. The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus in the womb. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :

(i) Name the part labelled 1.
(ii) Mention any two functions of the part labelled 2.
(iii) Explain the role played by the part labelled 3.
(iv) What is the norfhal gestation period (in days) of the developing foetus ?
(v) What’ is the role of the umbilical cord in the development of the foetus ?
(vi) Name the part in the diagram which is endocrine in nature.
Answer :
(i) Umbilical cord.
(ii) Part labelled 2 is placenta. It two functions are as follows :
(1) Provides diffusion for respiratory gases between mother and foetus.
(2) Removes urea produced by foetus.
(iii) Part labelled 3 is amniotic fluid. Its function is that it acts as a shock absorber and protects the developing embryo from mechanical injuries.
(iv) 280 days.
(iii) Umbilical cord contains blood vessels and connects the placenta with the foetus. It means it helps in providing nutrition to the embryo and O2 to foetus and removes CO2 and excretory wastes from foetus blood to maternal blood.
(iv) Endocrine part of this diagram is ‘placenta’.
Question 5. Given below is the outline of the male reproductive system :
(i) Name the parts labelled 1 to 5.
(ii) State the functions of the parts labelled 1 and 4.
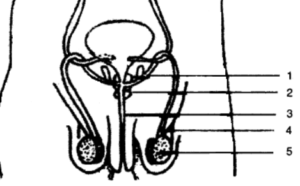
(iii) Name the cells of part 5 that produce testosterone.
(iv) Why is the structure 5 present outside the body in the scrotal sacs ?
(v) What is semen ?
Answer :
(i) 1—Seminal vesicle
2—Prostate gland
3— Urethra
4— Sperm duct/vas deferens
5—Testis.
(ii) Part 1—Its secretion serves as a medium for the transportation of the sperms.
Part 2—It carry the sperms.
(iii) Leydig cells or interstitial cells of part 5 produces testosterone.
(iv) The structure 5 is present outside the body in the scrotal sac because sperms are produced at 2 to 3°C lower than that of body temperature so, when too hot the skin of scrotal sac looses and testes are away from the body and when it is cold the skin contracts and testis are closer to the body for warmth.
(v) Semen—The mixture of seminal vesicles secretios and sperms produces a milky fluid, which is called semen.
Question 6. Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow :
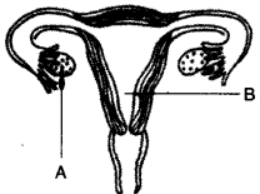
(i) Name the part labelled A. Name any two hormones produced by the part labelled A.
(ii) What happens to the part labelled B :
(1) If fertilisation takes place ? (2) If fertilisation does not take place ?
(iii) Where does fertilisation occur ?
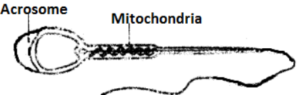
(iv) Draw a neat diagram of the human sperm as seen under high magnifi-cation and label the following parts.
(1) Acrosome (2) Mitochondria
Answer :
(i) A – Ovary: Two hormones are :
(1) Oesterogen (2) Progesteron
(ii) (1) If fertilisation takes place, part B i.e. uterus gets prepared to receieve the embryo. The endometrial lining thickens and gets highly vascularised.
(2) If fertilisation does not take place part B, then the endometrial lining of uterus erodes causing bleeding i.e., menstruation.
(iii) Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube/oviduct.
(iv)
Question 7. Copy and complete the following by filling in the blanks 1 to 5 with appropriate words:
The human female gonads are ovaries. A maturing egg in the ovary is present in a sac of cells called ……… (1). As the egg grows larger, the follicle enlarges and gets filled with a fluid and is now called the ……… (2) follice. The process of releasing the egg from the ovary is called ……… (3). The ovum is picked up by the oviducal funnel and fertilization takes place in the ……… (4). In about a week the blastocyst gets fixed in the endometrium of the uterus and this process is called …….. (5).
Answer :
The human female gonads are ovaries. A maturing egg in the ovary is present in a sac of cells called ovarian follicle (1). As the egg grows larger, the follicle enlarges and gets filled with a fluid and is now called the Graafian (2) follicle. The process of releasing the egg from the ovary is called ovulation (3). The ovum is picked up by the oviducal funnel and fertilization takes place in the oviduct (4). In about a week the blastocyst gets fixed in the endometrium of the uterus and this process is called implantation (5).
Question 8. The diagram given below shows the male urinogenital system of a human being. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow :
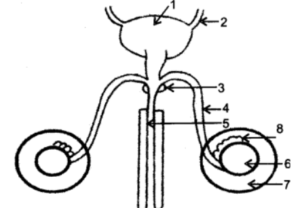
(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 8.
(ii) Name the corresponding structure of part (4) in female reproductive system.
(iii) What is the role of part 7 ?
Answer :
(i) 1. Urinary bladder
2. Ureter (left)
3. Prostate gland
4. Vas deferens/Sperm duct
5. Urethra
6. Testes
7. Scrotum
8. Epididymis
(ii) Fallopian tube/Oviduct.
(iii) It protects testis and regulate temperature of testes for sperm production.
Question 9. The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus. Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow :
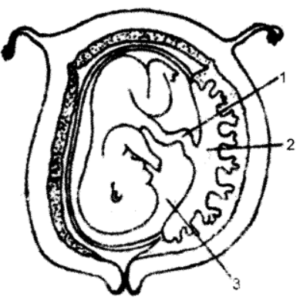
(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) Mention any two functions of the part labelled 2 in the diagram.
(iii) Explain the significance of the part numbered 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Define the term ‘Gestation’. What is the normal gestational period of the developing human embryo ?
(v) Mention the sex chromosomes in a male and female embryo.
Answer :
(i) 1. Umbilical cord 2. Placenta 3. Amniotic cavity/Amniotic fluid
(ii) Functions of Placenta:
1. Transfer nutrients and oxygen from mother’s blood to foetus.
2. Releases hormones called oestrogens, progesterone.
(iii) Significance of Amniotic Fluid:
1. Protects the foetus against jerks, mechanical shocks, and injury.
2. Allows foetus movements.
3. Keeps the pressure even, around the foetus.
4. Prevent sticking of foetus to the amnion.
(iv) Gestation : The full term of development of the embryo in the uterus.
In a developing human embryo gestational period is of 280 days.
(v) Male embryo = XY
Female embryo = XX.
Question 10. The diagram shown below Ls the longitudinal section of a testis of man. Study it carefully and answer the question that follow :

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) In which part of the testis are the sperms produced?
(iii) State the functions of the parts labelled 1 and 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Name the cells that. secrete Testosterone.
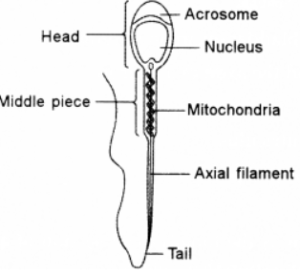
(v) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a sperm.
Answer :
(i)
- Scrotum
- Sperm duct/vasa deferens
- Epididymis
(ii) Seminiferous tubules.
(iii) Scrotum: Brings the temperature 2 – 3 °C for the maturation of sperms.
Epididymis: Store the sperms and help in their maturity.
(iv) Ley dig’s cells.
(v)
— : End of Reproductive System Class-10 Goyal Brothers Solutions :–
Return to :- ICSE Biology for Class 10 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
Thanks


