RS Aggarwal Class-7 Representing 3D in 2D ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-20 Solutions. We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-20 Representing 3D in 2D for ICSE Class-7 RS Aggarwal Mathematics.
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-20 A and MCQs Exe-20 B to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-7 Mathematics.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal brothers Prakshan |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 7th |
| Chapter-20 | Representing 3D |
| Writer | RS Aggrawal |
| Book Name | Foundation |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-20 A and MCQs Exe-20 B to develop skill and confidence |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
RS Aggarwal Class-7 Representing 3D in 2D ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-20 Solutions
-: Select Topic :-
Introduction of Representing 3D in 2D
In Class VII, you have learnt about plane shapes and solid shapes. Plane shapes have two measurements like length and breadth and therefore they are called two-dimensional shapes whereas a solid object has three measurements like length, breadth, height or depth. Hence, they are called three-dimensional shapes. Also, a solid object occupies some space. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures can also be briefly named as 2-D and 3- D figures. You may recall that triangle, rectangle, circle etc., are 2-D figures while cubes, cylinders, cones, spheres etc. are three-dimensional figures.
However, in our practical life, many a times, we come across combinations of different shapes. For example, look at the following objects.
Views of 3D-Shapes
You have learnt that a 3-dimensional object can look differently from different positions so they can be drawn from different perspectives. For example, a given hut can have the following views.
Why is the top view of the glass a pair of concentric circles? Will the side view appear different if taken from some other direction? Think about this! Now look at the different views of a brick.
We can also get different views of figures made by joining cubes. For example.
Exe-20 A,
ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Page 222-223
Question 1:
State whether true (T) or false (F) :
(i) A cube has 8 edges.
(ii) A cuboid has more edges than vertices
(iii) A cube has all edges equal.
(iv) A cone has only one face.
(v) A cylinder has only one vertex.
(vi) A cylinder has two flat faces.
Answer :
(i) False.
(ii) True.
(iii) True.
(iv) False.
(v) False.
(vi) True.
Question 2:
Give two examples of each one of:
(i) a cuboid
(ii) a cube
(iii) a cylinder
(iv) a cone
Answer :
(i) A cuboid : A brick, an almirah, a pencil box, a match box, a room.
(ii) A cube : A dice, an ice cube, a sugar cube.
(iii) A cylinder : Circular pipes, circular pillars in buildings, circular pencils, measuring jars, road rollers and gas cylinders.
(iv) A cone : lce-cream cone, a conical tent, a funnel, a clown’s cap.
Question 3:
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A cuboid has ………………………. lateral faces.
(ii) The number of edges in a cube is …………….
(iii) A cylinder has .. …………. faces. The number of flat faces is ……………. and that of curved faces is ………….. .
(iv) A cylinder has ………………………. edges.
(v) A cone has one …………………. face and one ………………………. face.
(vi) A cuboid has six …………………….. faces,
Answer :
(i) A cuboid has 4 lateral faces.
(ii) The number of edges in a cube is 12.
(iii) A cylinder has 3 faces. The number of flat faces is 2 and that of curved faces is 1.
(iv) A cylinder has 2 edges.
(v) A cone has one curved face and one flat face.
(vi) A cuboid has six rectangular faces.
Question 4:
Draw any four possible nets for a cube.
Answer :
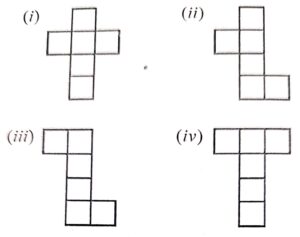
Question 5:
Analyses the following nets of cubes and fill in the blanks :
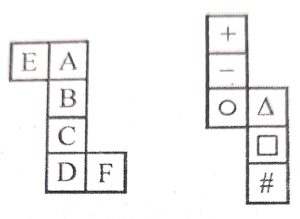
When Net (X) is folded to form a cube :
(i) A lies opposite ……….
(ii) F lies opposite. ………
When Net (Y) is folded to form a cube :
(iii) △ lies opposite …………
(ii) ▢ lies opposite ………….
Answer :
When Net (X) is folded to form a cube :
(i) A lies opposite C.
(ii) F lies opposite E.
When Net (Y) is folded to form a cube :
(iii) △ lies opposite #.
(ii) ▢ lies opposite -.
Exe-20 B,
ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Page 226
Question 1:
Draw a map to guide your friend telling him the way from his home to the venue of your birthday party. Use suitable symbols.
Answer :
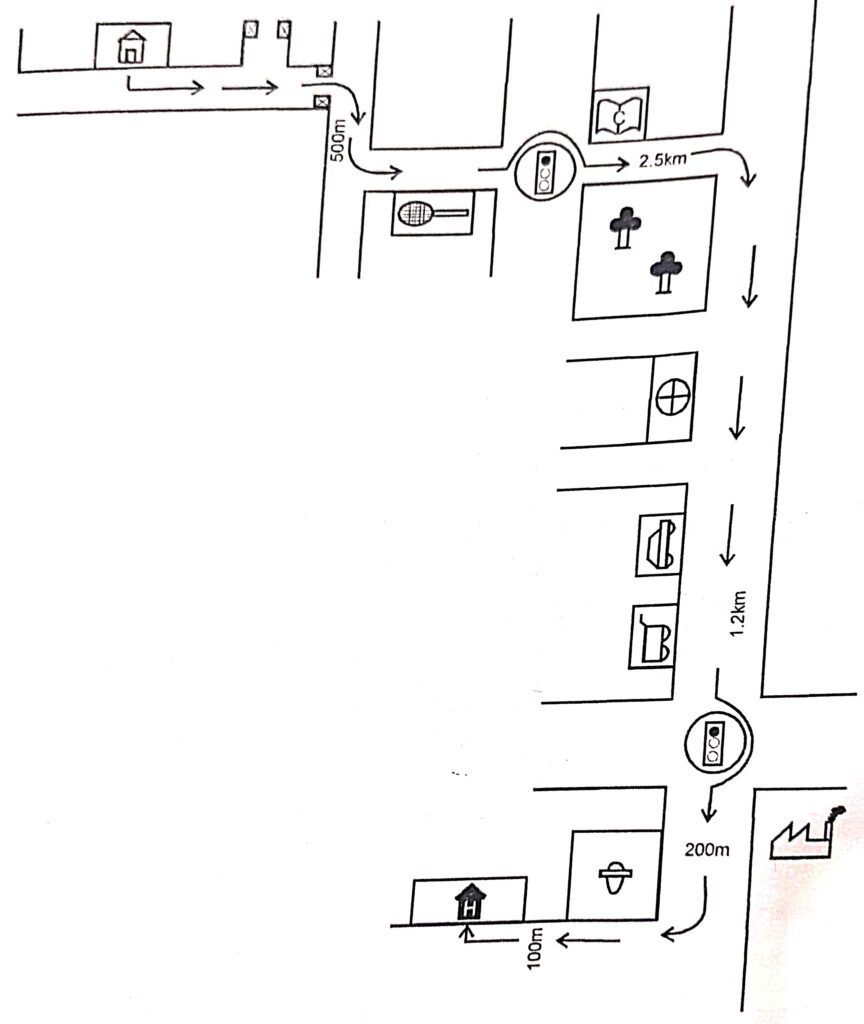
Question 2:
Draw a map of the post office near your house.
Answer :
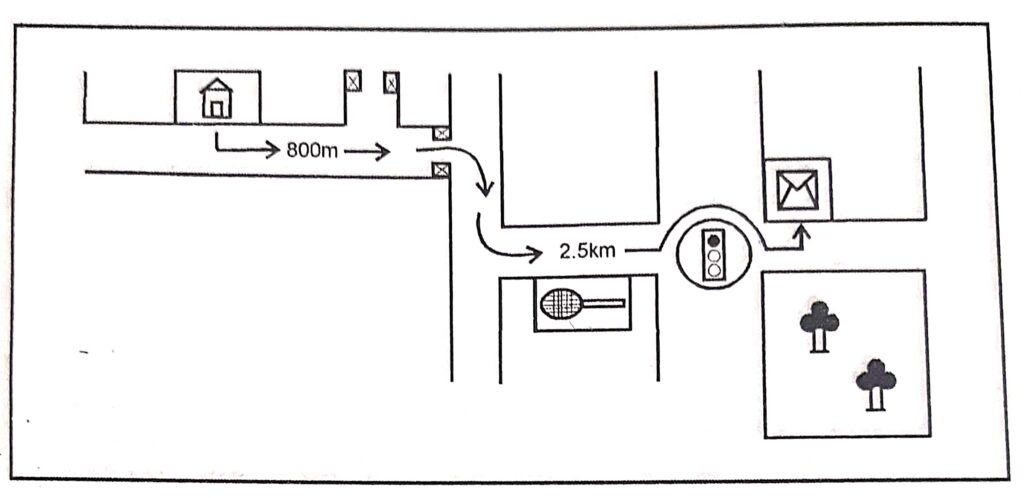
Question 3:
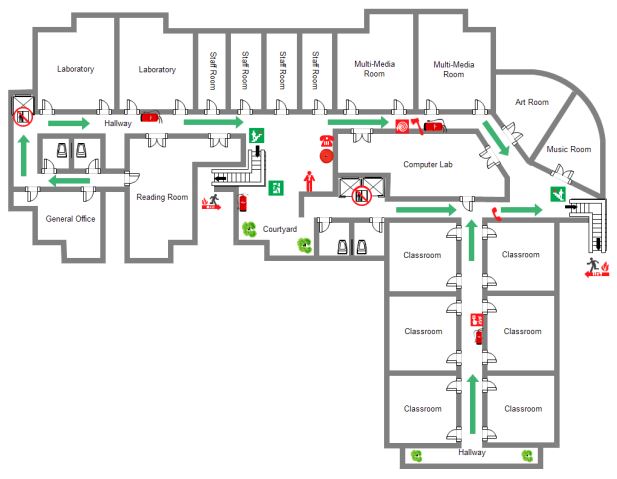
Draw a map of the ground floor of your school.
Answer :
–: End of RS Aggarwal Class-7 Representing 3D in 2D Solutions :–
Return to- RS Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-7 Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Thanks

Very good website it helps me too study in maths Very much