Skeleton-Movement and Locomotion Goyal Brothers ICSE Class 9 Biology Solutions Ch-14. We Provide Solutions of Exercise-14 Skeleton-Movement and Locomotion Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Ch-14. All Type exercise question such as name the following, difference between, MCQs, Answer the question. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Ch-14 Skeleton-Movement and Locomotion
Solutions of ICSE Class-9 Biology
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brother Prakashan |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| Writer | Dr. S.K. Aggarwal |
| Chapter-14 | Skeleton-Movement and Locomotion |
| Topics | Solutions of Exercises-14 |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Ch-14 Skeleton-Movement and Locomotion
(Page-144)
Questions 1. Name the following:
(i) Parts of the axial skeleton.
Ans– The five parts of your axial skeleton include the bones in your skull, ossicles (small bones) of your middle ear, hyoid bone of your neck, vertebra (bones of your spine) and thoracic cage (ribcage).
(ii) Parts of the appendicular system.
Ans– The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the shoulder girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs.
(iii) Type of joint present in the skull.
Ans– The type of joint present in between them is called sutures. Suture is a type of fibrous immovable joint present only in skull. The bones are connected by a fiber called Sharpey’s fibers
(iv) Type of joint present between the fore arm and the wrist.
Ans– The wrist joint also referred to as the radiocarpal joint is a condyloid synovial joint of the distal upper limb that connects and serves as a transition point between the forearm and hand. A condyloid joint is a modified ball and socket joint that allows for flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction movements.
(v) Bones comprising the backbone.
Ans– Vertebrae: The spine has 33 stacked vertebrae (small bones) that form the spinal canal. The spinal canal is a tunnel that houses the spinal cord and nerves, protecting them from injury. Most vertebrae move to allow for a range of motion. The lowest vertebrae (sacrum and coccyx) are fused together and don’t move.
(vi) Bones of pectoral girdle.
Ans– The shoulder, or pectoral, girdle is composed of the clavicles (collarbones) and the scapulae (shoulder blades). In humans the clavicles join the sternum (breastbone) medially and the scapulae laterally; the scapulae, however, are joined to the trunk only by muscles.
(vii) Bones of pelvic girdle.
Ans– The pelvic girdle, also known as the os coxae, Latin for “bone of the hip,” consists of the fused bones identified individually as the ilium, ischium, and pubis
Questions 2. Define the following
(i) Locomotion– Locomotion is directional movement that enables someone or something to move from one location to another. The word derives from the Latin words locō (place) and mōtiō (to move).
(ii) Movement– motion is the change in position of an object with respect to its surroundings in a given interval of time
(iii) Skeleton– The skeletal system is your body’s central framework. It consists of bones and connective tissue, including cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It’s also called the musculoskeletal system.
(iv) Joints– A joint is the part of the body where two or more bones meet to allow movement.
(v) Ligaments– A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
Questions 3. Distinguish between the following:
(i) Movement and Locomotion
Ans– Locomotion is the displacement of a body from one place to another. On the contrary, movement is the displacement of a body or a part of the body from its original position.
(ii) True ribs and floating ribs
Ans–
| True Ribs | Floating ribs |
|---|---|
| The first seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs. | The 11th and 12th pair of ribs are called floating ribs because one end of the rib is attached to the vertebral column and the other end is free. |
(iii) Pectoral girdle and Pelvic girdle
Ans–
| Pectoral girdle | Pelvic girdle |
|---|---|
| The glenoid cavity present in the pectoral girdle is comparatively shallow. | Acetabulum cavity present in the pelvic girdle is comparatively deep. |
| It gives articulation to forelimb bones. | It gives articulation to hindlimb bones. |
(iv) Ball and Socket joint and Hinge joint
Ans–
Ball-and-Socket joints are the most mobile of all synovial joints. They allow the bone with the ball head to be moved freely in all planes, Whereas hinge joints allow restricted movements in one plane only.
Questions 4. Choose the correct answer from each of the four options given below:
(i) A change in position of any part of an organism’s body is called
(a) Locomotion
(b) Movement
(c) Fertilisation
(ii) The skull, the vertebral column, the ribs and the sternum form
(a) Appendicular skeleton
(b) Axial skeletion
(c) Ribcage
(iii) The first seven pairs of ribs in humans are called
(a) False ribs
(b) Floating ribs
(c) True ribs
(iv) Ilium, ischium and pubis bones are the parts of
(a) Pelvic girdle
(b) Pectoral girdle
(c) Pentadactyl limbs
Questions 5. Answer the following:
(i) State the functions of skeleton.
Ans– The skeletal system works as a support structure for your body. It gives the body its shape, allows movement, makes blood cells, provides protection for organs and stores minerals. The skeletal system is also called the musculoskeletal system
(ii) Write about the human axial skeleton, giving suitable labelled diagrams.
Ans– Your axial skeleton is made up of the 80 bones within the central core of your body. This includes bones in your skull (cranial and facial bones), ears, neck, back (vertebrae, sacrum and tailbone) and ribcage (sternum and ribs)
(iii) Describe the human appendicular skeleton.
Ans– The bones of the appendicular skeleton make up the rest of the skeleton, and are so called because they are appendages of the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the shoulder girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs.
(iv) Describe the structure of a typical vertebra.
Ans– A typical vertebra consists of a body and a vertebral arch. The arch is formed by the paired pedicles and paired laminae. Arising from the vertebral arch are the transverse, spinous, superior articular, and inferior articular processes. The vertebral foramen provides for passage of the spinal cord.
(v) Write in brief about the ribs.
Ans– The ribs are the bony framework of the thoracic cavity. The ribs form the main structure of the thoracic cage protecting the thoracic organs, however their main function is to aid respiration. There are twelve pairs of ribs. Each rib articulates posteriorly with two thoracic vertebrae by the costovertebral joint.
(vi) What are joints? List the different types of joints giving one example in each case.
Ans–
| Types of joints | Example |
|---|---|
| Freely movable joint | Hip joint |
| Gliding joint | Ankle bones |
| Pivot joint | Joint between atlas and axis vertebrae |
| Hinge joint | Elbow |
(vii) Give a brief of the joint found in our skull.
Ans– A suture is a type of fibrous joint that is only found in the skull (cranial suture). The bones are bound together by Sharpey’s fibres. A tiny amount of movement is permitted at sutures, which contributes to the compliance and elasticity of the skull. These joints are synarthroses.
Questions 6. Observe the figure given below and answer the following questions:
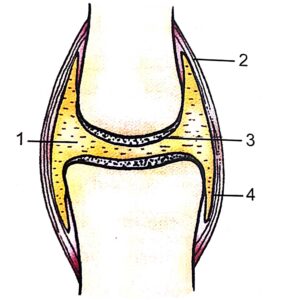
(i) Name the type of joint shown in the figure.
Ans– Moveable Joint
(ii) Name the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Ans– 1-synovial fluid 2- joint capsule 3- cartilage 4- synovial membrane
(iii) Where does the above type of joint found in human body?–
Ans:- At leg
–: End of Skeleton-Movement and Locomotion Goyal Brothers ICSE Class 9 Biology Solutions :–
Return to:- ICSE Biology for Class 9 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
thanks


