Solving Simple Problems Concise Solution Chapter 6 ICSE Maths Class 10th is available here. All Solution of Concise of Chapter 6 Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) in One Variable has been solved according instruction given by council. This is the Solution of Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) in one variable for ICSE Class 10th .ICSE Maths text book of Concise is In series of famous ICSE writer in maths. Selina Publishers Maths is most famous among students. With the help of Concise Maths , student can achieve their goal in 2020 exam of council.
The Solution of Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) for ICSE Class 10 have been solved by experience teachers from across the globe to help students of class 10th ICSE board exams conducted by the ICSE (Indian Council of Secondary Education) board papering in 2020. Therefore the ICSE Class 10th Concise Maths Solutions of Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) solve problems of exercise and Chapter test related to various topics which are prescribed in most ICSE Maths textbooks.
Solving Simple Problems Concise Solution Chapter 6 ICSE Maths Class 10th
-: Select Topic :-
Note:- Before viewing Solving Simple Problems Concise Solution Chapter 6 which is based on Quadratic Equations read the Chapter Carefully then solve all example of your Concise text book. The Solving Simple Problems Concise Solution Chapter 6 is main Chapter in ICSE board .
Chapter-6,Solving Simple Problems Concise Solution Exercise 6 (A)
Question 1
The product of two consecutive integers is 56. Find the integers.
Answer 1
Let the two consecutive integers be x and x + 1.
From the given information,
x(x + 1) = 56
x2 + x – 56 = 0
(x + 8) (x – 7) = 0
x = -8 or 7
Thus, the required integers are – 8 and -7; 7 and 8.
Question 2
The sum of the squares of two consecutive natural numbers is 41. Find the numbers.
Answer 2
Let the numbers be x and x + 1.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 1)2 = 41
2x2 + 2x + 1 – 41 = 0
x2 + x – 20 = 0
(x + 5) (x – 4) = 0
x = -5, 4
But, -5 is not a natural number. So, x = 4.
Thus, the numbers are 4 and 5.
Question 3
Find the two natural numbers which differ by 5 and the sum of whose squares is 97.
Answer 3
Let the two numbers be x and x + 5.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 5)2 = 97
2x2 + 10x + 25 – 97 = 0
2x2 + 10x – 72 = 0
x2 + 5x – 36 = 0
(x + 9) (x – 4) = 0
x = -9 or 4
Since, -9 is not a natural number. So, x = 4.
Thus, the numbers are 4 and 9.
Question 4
The sum of a number and its reciprocal is 4.25. Find the number.
Answer 4
Let the numbers be x and 1/x
From the given information,
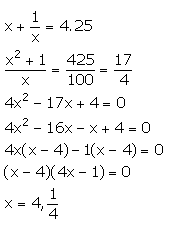
x = 4 ![]()
x = ![]() x = 4
x = 4
Thus, the numbers are 4 and ![]()
Question 5
Two natural numbers differ by 3. Find the numbers, if the sum of their reciprocals is ![]()
Answer 5
Let the numbers be x and x + 3.
From the given information,
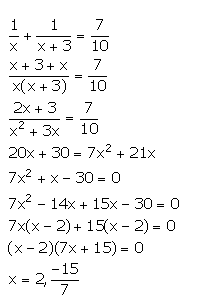
Since, x is a natural number, so x = 2.
Thus, the numbers are 2 and 5.
Question 6
Divide 15 into two parts such that the sum of their reciprocals is ![]()
Answer 6
Let the two parts be x and x – 15.
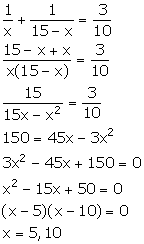
x = 5 ⇒ One part = 5 and other part = 10
x = 10 ⇒ One part = 10 and other part = 5
Thus, the required two parts are 5 and 10.
Question 7
The sum of the square of two positive integers is 208. If the square of larger number is 18 times the smaller number, find the numbers.
Answer 7
Let the two numbers be x and y, y being the bigger number. From the given information,
x2 + y2 = 208 ….. (i)
y2 = 18x ….. (ii)
From (i), we get y2=208 – x2. Putting this in (ii), we get,
208 – x2 = 18x
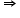 x2 + 18x – 208 = 0
x2 + 18x – 208 = 0
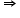 x2 + 26X – 8X – 208 = 0
x2 + 26X – 8X – 208 = 0
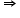 x(x + 26) – 8(x + 26) = 0
x(x + 26) – 8(x + 26) = 0
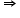 (x – 8)(x + 26) = 0
(x – 8)(x + 26) = 0
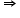 x can’t be a negative number , hence x = 8
x can’t be a negative number , hence x = 8
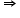 Putting x = 8 in (ii), we get y2 = 18 x 8=144
Putting x = 8 in (ii), we get y2 = 18 x 8=144
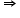 y = 12, since y is a positive integer
y = 12, since y is a positive integer
Hence, the two numbers are 8 and 12.
Question 8
The sum of the squares of two consecutive positive even numbers is 52. Find the numbers.
Answer 8
Let the consecutive positive even numbers be x and x + 2.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 2)2 = 52
2x2 + 4x + 4 = 52
2x2 + 4x – 48 = 0
x2 + 2x – 24 = 0
(x + 6) (x – 4) = 0
x = -6, 4
Since, the numbers are positive, so x = 4.
Thus, the numbers are 4 and 6.
Question 9
Find two consecutive positive odd numbers, the sum of whose squares is 74.
Answer 9
Let the consecutive positive odd numbers be x and x + 2.
From the given information,
x2 + (x + 2)2 = 74
2x2 + 4x + 4 = 74
2x2 + 4x – 70 = 0
x2 + 2x – 35 = 0
(x + 7)(x – 5) = 0
x = -7, 5
Since, the numbers are positive, so, x = 5.
Thus, the numbers are 5 and 7.
Question 10
The denominator of a positive fraction is one more than twice the numerator. If the sum of the fraction and its reciprocal is 2.9; find the fraction.
Answer 10
Let the required fraction be.![]()
From the given information,
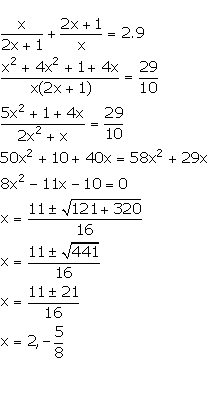
Thus, the required fraction is .2/5
Question 11
Three positive numbers are in the ratio ………. Find the numbers if the sum of their squares is 244.
Answer 11
Given, three positive numbers are in the ratio 6:4:3
Let the numbers be 6x, 4x and 3x.
From the given information,
(6x)2 + (4x)2 + (3x)2 = 244
36x2 + 16x2 + 9x2 = 244
61x2 = 244
x2 = 4
x = ![]()
Since, the numbers are positive, so x = 2.
Thus, the numbers are 12, 8 and 6.
Question 12
Divide 20 into two parts such that three times the square of one part exceeds the other part by 10.
Answer 12
Let the two parts be x and y.
From the given information,
x + y = 20 ![]()
3x2 = (20 – x) + 10
3x2 = 30 – x
3x2 + x – 30 = 0
3x2 – 9x + 10x – 30 = 0
3x(x – 3) + 10(x – 3) = 0
(x – 3) (3x + 10) = 0
x = 3, -10/3
Since, x cannot be equal to -10/3, so, x = 3.
Thus, one part is 3 and other part is 20 – 3 = 17.
Question 13
Three consecutive natural numbers are such that the square of the middle number exceeds the difference of the squares of the other two by 60.
Assume the middle number to be x and form a quadratic equation satisfying the above statement. Hence; find the three numbers.
Answer 13
Let the numbers be x – 1, x and x + 1.
From the given information,
x2 = (x + 1)2 – (x – 1)2 + 60
x2 = x2 + 1 + 2x – x2 – 1 + 2x + 60
x2 = 4x + 60
x2 – 4x – 60 = 0
(x – 10) (x + 6) = 0
x = 10, -6
Since, x is a natural number, so x = 10.
Thus, the three numbers are 9, 10 and 11.
Question 14
Out of three consecutive positive integers, the middle number is p. If three times the square of the largest is greater than the sum of the squares of the other two numbers by 67; calculate the value of p.
Answer 14
Let the numbers be p – 1, p and p + 1.
From the given information,
3(p + 1)2 = (p – 1)2 + p2 + 67
3p2 + 6p + 3 = p2 + 1 – 2p + p2 + 67
p2 + 8p – 65 = 0
(p + 13)(p – 5) = 0
p = -13, 5
Since, the numbers are positive so p cannot be equal to -13.
Thus, p = 5.
Question 15
A can do a piece of work in ‘x’ days and B can do the same work in (x + 16) days. If both working together can do it in 15 days; calculate ‘x’.
Answer 15
Work done by A in one day =1/6
Work done by B in one day = 1/x+16
Together A and B can do the work in 15 days. Therefore, we have:
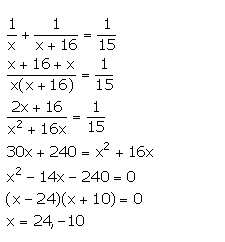
Since, x cannot be negative.
Thus, x = 24.
Question 16
One pipe can fill a cistern in 3 hours less than the other. The two pipes together can fill the cistern in 6 hours 40 minutes. Find the time that each pipe will take to fill the cistern.
Answer 16
Let one pipe fill the cistern in x hours and the other fills it in (x – 3) hours.
Given that the two pipes together can fill the cistern in 6 hours 40 minutes, i.e.,
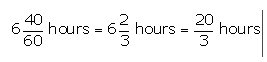
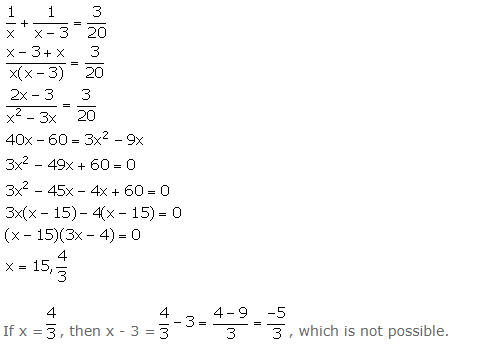
So, x = 15.
Thus, one pipe fill the cistern in 15 hours and the other fills in (x – 3) = 15 – 3 = 12 hours.
Question 17
A positive number is divided into two parts such that the sum of the squares of the two parts is 20. The square of the larger part is 8 times the smaller part. Taking x as the smaller part of the two parts, find the number.
Answer 17
Let the smaller part be x.
Then, (larger part)2 = 8x
\ larger part = √8x
Now, the sum of the squares of both the terms is given to be 208
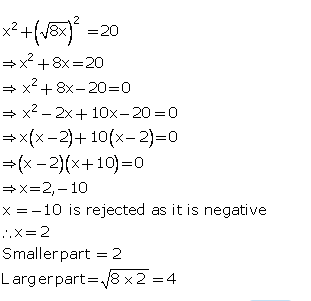
Concise Solution Chapter 6 Solving Simple Problems ICSE Maths Class 10th Exercise – 6 (B)
Question 1
The sides of a right-angled triangle containing the right angle are 4x cm and (2x – 1) cm. If the area of the triangle is 30 cm2; calculate the lengths of its sides.
Answer 1
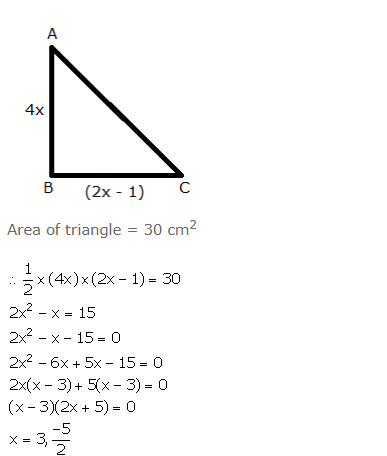
But, x cannot be negative, so x = 3.
Thus, we have:
AB = 4 3 cm = 12 cm
BC = (2 3 – 1) cm = 5 cm
CA = ![]() (Using Pythagoras theorem)
(Using Pythagoras theorem)
Question 2
The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is 26 cm and the sum of other two sides is 34 cm. Find the lengths of its sides.
Answer 2
Hypotenuse = 26 cm
The sum of other two sides is 34 cm.
So, let the other two sides be x cm and (34 – x) cm.
Using Pythagoras theorem,
(26)2 = x2 + (34 – x)2
676 = x2 + x2 + 1156 – 68x
2x2 – 68x + 480 = 0
x2 – 34x + 240 = 0
x2 – 10x – 24x + 240 = 0
x(x – 10) – 24(x – 10) = 0
(x – 10) (x – 24) = 0
x = 10, 24
When x = 10, (34 – x) = 24
When x = 24, (34 – x) = 10
Thus, the lengths the three sides of the right-angled triangle are 10 cm, 24 cm and 26 cm.
Question 3
The sides of a right-angled triangle are (x – 1) cm, 3x cm and (3x + 1) cm. Find:
(i) the value of x,
(ii) the lengths of its sides,
(iii) its area.
Solution 3
Longer side = Hypotenuse = (3x + 1) cm
Lengths of other two sides are (x – 1) cm and 3x cm.
Using Pythagoras theorem,
(3x + 1)2 = (x – 1)2 + (3x)2
9x2 + 1 + 6x = x2 + 1 – 2x + 9x2
x2 – 8x = 0
x(x – 8) = 0
x = 0, 8
But, if x = 0, then one side = 3x = 0, which is not possible.
So, x = 8
Thus, the lengths of the sides of the triangle are (x – 1) cm = 7 cm, 3x cm = 24 cm and (3x + 1) cm = 25 cm.
Area of the triangle = ![]()
Question 4
The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle exceeds one side by 1 cm and the other side by 18 cm; find the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
Solution 4
Let one hypotenuse of the triangle be x cm.
From the given information,
Length of one side = (x – 1) cm
Length of other side = (x – 18) cm
Using Pythagoras theorem,
x2 = (x – 1)2 + (x – 18)2
x2 = x2 + 1 – 2x + x2 + 324 – 36x
x2 – 38x + 325 = 0
x2 – 13x – 25x + 325 = 0
x(x – 13) – 25(x – 13) = 0
(x – 13) (x – 25) = 0
x = 13, 25
When x = 13, x – 18 = 13 – 18 = -5, which being negative, is not possible.
So, x = 25
Thus, the lengths of the sides of the triangle are x = 25 cm, (x – 1) = 24 cm and (x – 18) = 7 cm.
Question 5
The diagonal of a rectangle is 60 m more than its shorter side and the larger side is 30 m more than the shorter side. Find the sides of the rectangle.
Answer 5
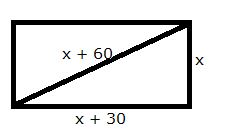
Let the shorter side be x m.
Length of the other side = (x + 30) m
Length of hypotenuse = (x + 60) m
Using Pythagoras theorem,
(x + 60)2 = x2 + (x + 30)2
x2 + 3600 + 120x = x2 + x2 + 900 + 60x
x2 – 60x – 2700 = 0
x2 – 90x + 30x – 2700 = 0
x(x – 90) + 30(x – 90) = 0
(x – 90) (x + 30) = 0
x = 90, -30
But, x cannot be negative. So, x = 90.
Thus, the sides of the rectangle are 90 m and (90 + 30) m = 120 m.
Question 6
The perimeter of a rectangle is 104 m and its area is 640 m2. Find its length and breadth.
Answer 6
Let the length and the breadth of the rectangle be x m and y m.
Perimeter = 2(x + y) m
104 = 2(x + y)
x + y = 52
y = 52 – x
Area = 640 m2
xy = 640
x(52 – x) = 640
x2 – 52x + 640 = 0
x2 – 32x – 20x + 640 = 0
x(x – 32) – 20 (x – 32) = 0
(x – 32) (x – 20) = 0
x = 32, 20
When x = 32, y = 52 – 32 = 20
When x = 20, y = 52 – 20 = 32
Thus, the length and breadth of the rectangle are 32 m and 20 m.
Question 7
A footpath of uniform width runs round the inside of a rectangular field 32 m long and 24 m wide. If the path occupies 208 m2, find the width of the footpath.
Answer 7
Let w be the width of the footpath.
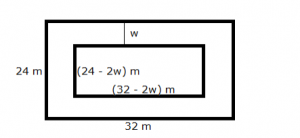
Area of the path = Area of outer rectangle – Area of inner rectangle
208 = (32)(24) – (32 – 2w)(24 – 2w)
208 = 768 – 768 + 64w + 48w – 4w2
4w2 – 112w + 208 = 0
w2 – 28w + 52 = 0
w2 – 26w – 2w + 52 = 0
w(w – 26) – 2(w – 26) = 0
(w – 26) (w – 2) = 0
w = 26, 2
If w = 26, then breadth of inner rectangle = (24 – 52) m = -28 m, which is not possible.
Hence, the width of the footpath is 2 m.
Question 8
Two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm. The sum of their area is 656 sq. cm. Express this as an algebraic equation in x and solve the equation to find the sides of the squares.
Answer 8
Given that, two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm.
Sum of their area = 656 cm2
x2 + (x + 4)2 = 656
x2 + x2 + 16 + 8x = 656
2x2 + 8x – 640 = 0
x2 + 4x – 320 = 0
x2 + 20x – 16x – 320 = 0
x(x + 20) – 16(x + 20) = 0
(x + 20) (x – 16) = 0
x = -20, 16
But, x being side, cannot be negative.
So, x = 16
Thus, the sides of the two squares are 16 cm and 20 cm.
Question 9
The dimensions of a rectangular field are 50 m and 40 m. A flower bed is prepared inside this field leaving a gravel path of uniform width all around the flower bed. The total cost of laying the flower bed and graveling the path at Rs 30 and Rs 20 per square meter, respectively, is Rs 52,000. Find the width of the gravel path.
Answer 9
Let the width of the gravel path be w m.
Length of the rectangular field = 50 m
Breadth of the rectangular field = 40 m
Let the length and breadth of the flower bed be x m and y m respectively.
Therefore, we have:
x + 2w = 50 … (1)
y + 2w = 40 … (2)
Also, area of rectangular field = 50 m 40 m = 2000 m2
Area of the flower bed = xy m2
Area of gravel path = Area of rectangular field – Area of flower bed = (2000 – xy) m2
Cost of laying flower bed + Gravel path = Area x cost of laying per sq. m
52000 = 30 xy + 20 (2000 – xy)
52000 = 10xy + 40000
xy = 1200
Using (1) and (2), we have:
(50 – 2w) (40 – 2w) = 1200
2000 – 180w + 4w2 = 1200
4w2 – 180w + 800 = 0
w2 – 45w + 200 = 0
w2 – 5w – 40w + 200 = 0
w(w – 5) – 40(w – 5) = 0
(w – 5) (w – 40) = 0
w = 5, 40
If w = 40, then x = 50 – 2w = -30, which is not possible.
Thus, the width of the gravel path is 5 m.
Question 10
An area is paved with square tiles of a certain size and the number required is 128. If the tiles had been 2 cm smaller each way, 200 tiles would have been needed to pave the same area. Find the size of the larger tiles.
Answer 10
Let the size of the larger tiles be x cm.
Area of larger tiles = x2 cm2
Number of larger tiles required to pave an area is 128.
So, the area needed to be paved = 128 x2 cm2 …. (1)
Size of smaller tiles = (x – 2)cm
Area of smaller tiles = (x – 2)2 cm2
Number of larger tiles required to pave an area is 200.
So, the area needed to be paved = 200 (x – 2)2 cm2 …. (2)
Therefore, from (1) and (2), we have:
128 x2 = 200 (x – 2)2
128 x2 = 200x2 + 800 – 800x
72x2 – 800x + 800 = 0
9x2 – 100x + 100 = 0
9x2 – 90x – 10x + 100 = 0
9x(x – 10) – 10(x – 10) = 0
(x – 10)(9x – 10) = 0
x = 10, ![]()
If  ,then
,then  , which is not possible.
, which is not possible.
Hence, the size of the larger tiles is 10 cm.
Question 11
A farmer has 70 m of fencing, with which he encloses three sides of a rectangular sheep pen; the fourth side being a wall. If the area of the pen is 600 sq. m, find the length of its shorter side.
Answer 11
Let the length and breadth of the rectangular sheep pen be x and y respectively.
From the given information,
x + y + x = 70
2x + y = 70 … (1)
Also, area = xy = 600
Using (1), we have:
x (70 – 2x) = 600
70x – 2x2 = 600
2x2 – 70x + 600 = 0
x2 – 35x + 300 = 0
x2 – 15x – 20x + 300 = 0
x(x – 15) – 20(x – 15) = 0
(x – 15)(x – 20) = 0
x = 15, 20
If x = 15, then y = 70 – 2x = 70 – 30 = 40
If x = 20, then y = 70 – 2x = 70 – 40 = 30
Thus, the length of the shorter side is 15 m when the longer side is 40 m. The length of the shorter side is 20 m when the longer side is 30 m.
Question 12
A square lawn is bounded on three sides by a path 4 m wide. If the area of the path ![]() is that of the lawn, find the dimensions of the lawn.
is that of the lawn, find the dimensions of the lawn.
Answer 12
Let the side of the square lawn be x m.
Area of the square lawn = x2 m2
The square lawn is bounded on three sides by a path which is 4 m wide.
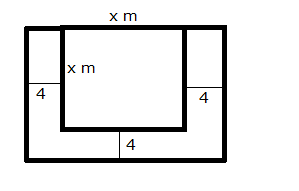
Area of outer rectangle = (x + 4) (x + 8) = x2 + 12x + 32
Area of path = x2 + 12x + 32 – x2 = 12x + 32
From the given information, we have:
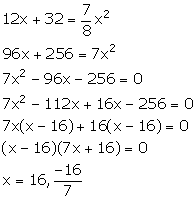
Since, x cannot be negative. So, x = 16 m.
Thus, each side of the square lawn is 16 m.
Question 13
The area of a big rectangular room is 300 m2. If the length were decreased by 5 m and the breadth increased by 5 m; the area would be unaltered. Find the length of the room.
Answer 13
Let the original length and breadth of the rectangular room be x m and y m respectively.
Area of the rectangular room = xy = 300

New length = (x – 5) m
New breadth = (y + 5) m
New area = (x – 5) (y + 5) = 300 (given)
Using (1), we have:
But, x cannot be negative. So, x = 20.
Thus, the length of the room is 20 m.
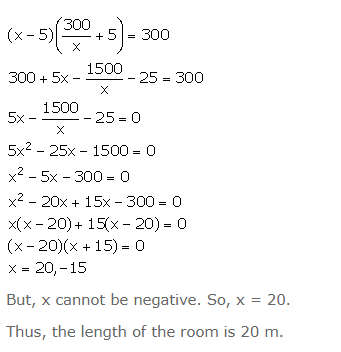
Thus, the required number is 2 + 4 = 6.
Exercise 6 (C), Chapter 6 – Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Concise Maths Solutions
Question 1
The speed of an ordinary train is x km per hr and that of an express train is (x + 25) km per hr.
(i) Find the time taken by each train to cover 300 km.
(ii) If the ordinary train takes 2 hrs more than the express train; calculate speed of the express train.
Answer 1
(i) Speed of ordinary train = x km/hr
Speed of express train = (x + 25) km/hr
Distance = 300 km
We know:
![]()
Time taken by ordinary train to cover 300 km = ![]()
Time taken by express train to cover 300 km = ![]()
(ii) Given that the ordinary train takes 2 hours more than the express train to cover the distance.
Therefore,
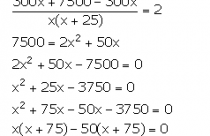
But, speed cannot be negative. So, x = 50.
Speed of the express train = (x + 25) km/hr = 75 km/hr
Question 2
If the speed of a car is increased by 10 km per hr, it takes 18 minutes less to cover a distance of 36 km. Find the speed of the car.
Answer 2
Let the speed of the car be x km/hr.
Distance = 36 km
Time taken to cover a distance of 36 km = ![]()
![]()
New speed of the car = (x + 10) km/hr
New time taken by the car to cover a distance of 36 km = ![]()
From the given information, we have:
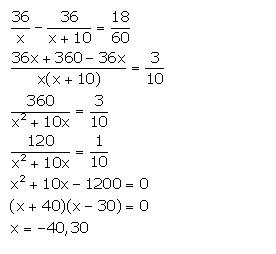
But, speed cannot be negative. So, x = 30.
Hence, the original speed of the car is 30 km/hr.
Question 3
If the speed of an aeroplane is reduced by 40 km/hr, it takes 20 minutes more to cover 1200 km. Find the speed of the aeroplane.
Answer 3
Let the original speed of the aeroplane be x km/hr.
Time taken to cover a distance of 1200 km = ![]()
Let the new speed of the aeroplane be (x – 40) km/hr.
![]()
Time taken to cover a distance of 1200 km = ![]()
From the given information, we have:
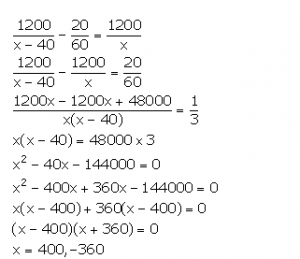
But, speed cannot be negative. So, x = 400.
Thus, the original speed of the aeroplane is 400 km/hr.
Question 4
A car covers a distance of 400 km at a certain speed. Had the speed been 12 km/h more, the time taken for the journey would have been 1 hour 40 minutes less. Find the original speed of the car.
Answer 4
Let x km/h be the original speed of the car.
We know that,
![]()
It is given that the car covers a distance of 400 km with the speed of x km/h.
Thus, the time taken by the car to complete 400 km is
![]()
Now, the speed is increased by 12 km.
Also given that, increasing the speed of the car will decrease the time taken by 1 hour 40 minutes.
![]()
Hence,
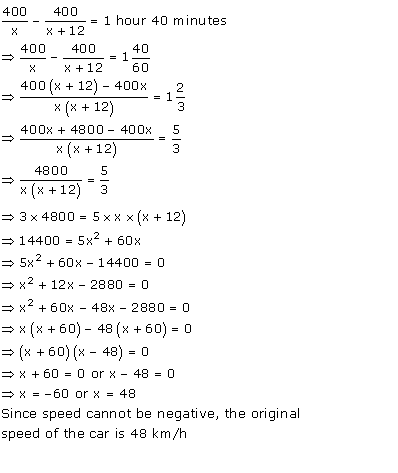
Question 5
A girl goes to her friend’s house, which is at a distance of 12 km. She covers half of the distance at a speed of x km/hr and the remaining distance at a speed of (x + 2) km/hr. If she takes 2 hrs 30 minutes to cover the whole distance, find ‘x’.
Answer 5
We know:
![]()
Given, the girl covers a distance of 6 km at a speed x km/ hr.
Time taken to cover first 6 km = ![]()
Also, the girl covers the remaining 6 km distance at a speed (x + 2) km/ hr.
Time taken to cover next 6 km = ![]()
Total time taken to cover the whole distance = 2 hrs 30 mins = ![]()
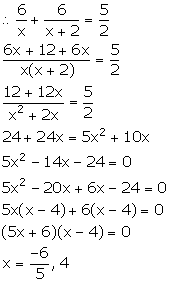
Since, speed cannot be negative. Therefore, x = 4.
Question 6
A car made a run of 390 km in ‘x’ hours. If the speed had been 4 km/hour more, it would have taken 2 hours less for the journey. Find ‘x’.
Answer 6
Let the original speed of the car be y km/hr.
We know:
![]()
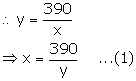
New speed of the car = (y + 4) km/hr
New time taken by the car to cover 390 km = ![]()
From the given information,
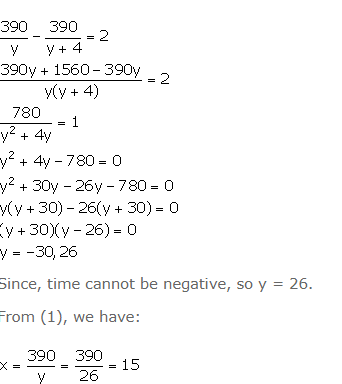
Since, time cannot be negative, so y = 26.
From (1), we have:
Question 7
A goods train leaves a station at 6 p.m., followed by an express train which leaved at 8 p.m. and travels 20 km/hour faster than the goods train. The express train arrives at a station, 1040 km away, 36 minutes before the goods train. Assuming that the speeds of both the train remain constant between the two stations; calculate their speeds.
Answer 7
Let the speed of goods train be x km/hr. So, the speed of express train will be (x + 20) km/hr.
Distance = 1040 km
We know:
![]()
Time taken by goods train to cover a distance of 1040 km = ![]()
Time taken by express train to cover a distance of 1040 km = ![]()
It is given that the express train arrives at a station 36 minutes before the goods train. Also, the express train leaves the station 2 hours after the goods train. This means that the express train arrives at the station ![]() before the goods train.
before the goods train.
Therefore, we have:
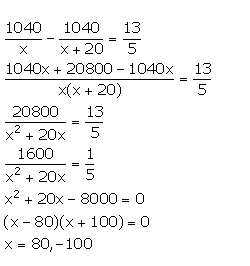
Since, the speed cannot be negative. So, x = 80.
Thus, the speed of goods train is 80 km/hr and the speed of express train is 100 km/hr.
Question 8
A man bought an article for Rs x and sold it for Rs 16. If his loss was x per cent, find the cost price of the article.
Answer 8
C.P. of the article = Rs x
S.P. of the article = Rs 16
Loss = Rs (x – 16)
We know:
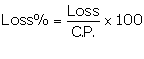
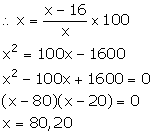
Thus, the cost price of the article is Rs 20 or Rs 80.
Question 9
A trader bought an article for Rs x and sold it for Rs 52, thereby making a profit of (x – 10) per cent on his outlay. Calculate the cost price.
Answer 9
C.P. of the article = Rs x
S.P. of the article = Rs 52
Profit = Rs (52 – x)
We know:
![]()
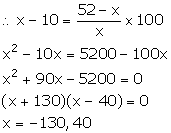
Since, C.P. cannot be negative. So, x = 40.
Thus, the cost price of the article is Rs 40.
Question 10
By selling a chair for Rs 75, Mohan gained as much per cent as its cost. Calculate the cost of the chair.
Answer 10
Let the C.P. of the chair be Rs x
S.P. of chair = Rs 75
Profit = Rs (75 – x)
We know:

But, C.P. cannot be negative. So, x = 50.
Hence, the cost of the chair is Rs 50.
Concise Maths Solution Chapter 6 – Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise 6 (D)
Question 1
The sum S of n successive odd numbers starting from 3 is given by the relation: S = n(n + 2). Determine n, if the sum is 168.
Answer 1
From the given information, we have:
n(n + 2) = 168
n2 + 2n – 168 = 0
n2 + 14n – 12n – 168 = 0
n(n + 14) – 12(n + 14) = 0
(n + 14) (n – 12) = 0
n = -14, 12
But, n cannot be negative.
Therefore, n = 12.
Question 2
A stone is thrown vertically downwards and the formula d = 16t2 + 4t gives the distance, d metres, that it falls in t seconds. How long does it take to fall 420 metres?
Answer 2
From the given information,
16t2 + 4t = 420
4t2 + t – 105 = 0
4t2 – 20t + 21t – 105 = 0
4t(t – 5) + 21(t – 5) = 0
(4t + 21)(t – 5) = 0
t = ![]() , 5
, 5
But, time cannot be negative.
Thus, the required time taken is 5 seconds.
Question 3
The product of the digits of a two digit number is 24. If its unit’s digit exceeds twice its ten’s digit by 2; find the number.
Answer 3
Let the ten’s and unit’s digit of the required number be x and y respectively.
From the given information,
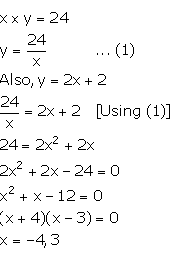
The digit of a number cannot be negative, so, x = 3.
![]()
Thus, the required number is 38.
Question 4
The ages of two sisters are 11 years and 14 years. In how many years time will the product of their ages be 304?
Answer 4
The ages of two sisters are 11 years and 14 years.
Let in x number of years the product of their ages be 304.
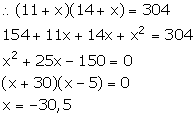
But, the number of years cannot be negative. So, x = 5.
Hence, the required number of years is 5 years.
Question 5
One year ago, a man was 8 times as old as his son. Now his age is equal to the square of his son’s age. Find their present ages.
Answer 5
Let the present age of the son be x years.
Present age of man = x2 years
One year ago,
Son’s age = (x – 1) years
Man’s age = (x2 – 1) years
It is given that one year ago; a man was 8 times as old as his son.
(x2 – 1) = 8(x – 1)
x2 – 8x – 1 + 8 = 0
x2 – 8x + 7 = 0
(x – 7) (x – 1) = 0
x = 7, 1
If x = 1, then x2 = 1, which is not possible as father’s age cannot be equal to son’s age.
So, x = 7.
Present age of son = x years = 7 years
Present age of man = x2 years = 49 years
Question 6
The age of the father is twice the square of the age of his son. Eight years hence, the age of the father will be 4 years more than three times the age of the son. Find their present ages.
Answer 6
Let the present age of the son be x years.
Present age of father = 2x2 years
Eight years hence,
Son’s age = (x + 8) years
Father’s age = (2x2 + 8) years
It is given that eight years hence, the age of the father will be 4 years more than three times the age of the son.
2x2 + 8 = 3(x + 8) +4
2x2 + 8 = 3x + 24 +4
2x2 – 3x – 20 = 0
2x2 – 8x + 5x – 20 = 0
2x(x – 4) + 5(x – 4) = 0
(x – 4) (2x + 5) = 0
x = 4, ![]()
But, the age cannot be negative, so, x = 4.
Present age of son = 4 years
Present age of father = 2(4)2 years = 32 years
Question 7
The speed of a boat in still water is 15 km/hr. It can go 30 km upstream and return downstream to the original point in 4 hours 30 minutes. Find the speed of the stream.
Answer 7
Let the speed of the stream be x km/hr.
Speed of the boat downstream = (15 + x) km/hr
Speed of the boat upstream = (15 – x) km/hr
Time taken to go 30 km downstream = ![]()
Time taken to come back = ![]()
From the given information,
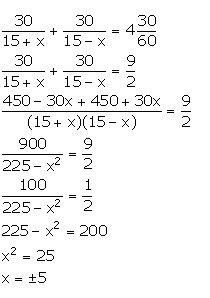
But, x cannot be negative, so, x = 5.
Thus, the speed of the stream is 5 km/hr.
Question 8
Mr. Mehra sends his servant to the market to buy oranges worth Rs 15. The servant having eaten three oranges on the way. Mr. Mehra pays Rs 25 paise per orange more than the market price.
Taking x to be the number of oranges which Mr. Mehra receives, form a quadratic equation in x. Hence, find the value of x.
Answer 8
Number of oranges = y
Cost of one orange = 
The servant ate 3 oranges, so Mr. Mehra received (y – 3) oranges.
So, x = y – 3 ⇒ y = x + 3 …(1)
Cost of one orange paid by Mr. Mehra = 
=
Now, Mr. Mehra pays a total of Rs 15.
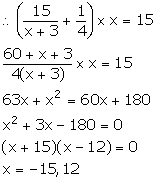
But, the number of oranges cannot be negative. So, x = 12.
Question 9
Rs 250 is divided equally among a certain number of children. If there were 25 children more, each would have received 50 paise less. Find the number of children.
Answer 9
Let the number of children be x.
It is given that Rs 250 is divided amongst x students.
So, money received by each child = Rs![]()
If there were 25 children more, then
Money received by each child = Rs![]()
From the given information,
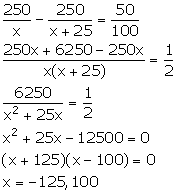
Since, the number of students cannot be negative, so, x = 100.
Hence, the number of students is 100.
Question 10
An employer finds that if he increased the weekly wages of each worker by Rs 5 and employs five workers less, he increases his weekly wage bill from Rs 3,150 to Rs 3,250. Taking the original weekly wage of each worker as Rs x; obtain an equation in x and then solve it to find the weekly wages of each worker.
Answer10
Original weekly wage of each worker = Rs x
Original weekly wage bill of employer = Rs 3150
Number of workers = ![]()
New weekly wage of each worker = Rs (x + 5)
New weekly wage bill of employer = Rs 3250
Number of workers = ![]()
From the given condition,
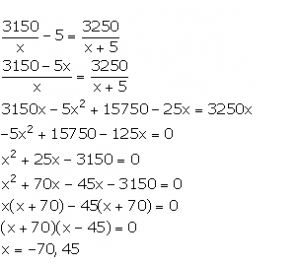
Since, wage cannot be negative, x = 45.
Thus, the original weekly wage of each worker is Rs 45.
Question 11
A trader bought a number of articles for Rs 1,200. Ten were damaged and he sold each of the remaining articles at Rs 2 more than what he paid for it, thus getting a profit of Rs 60 on whole transaction.
Taking the number of articles he bought as x, form an equation in x and solve it.
Answer 11
Number of articles bought by the trader = x
It is given that the trader bought the articles for Rs 1200.
So, cost of one article = Rs![]()
Ten articles were damaged. So, number of articles left = x – 10
Selling price of each of (x – 10) articles = Rs![]()
Selling price of (x – 10) articles = Rs (x – 10) ![]()
Profit = Rs 60
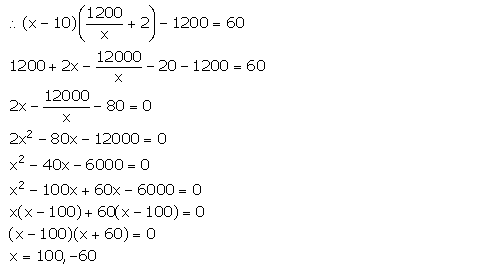
Number of articles cannot be negative. So, x = 100.
Question 12
The total cost price of a certain number of identical articles is Rs 4800. By selling the articles at Rs 100 each, a profit equal to the cost price of 15 articles is made. Find the number of articles bought.
Answer 12
Let the number of articles bought be x.
Total cost price of x articles = Rs 4800
Cost price of one article = Rs![]()
Selling price of each article = Rs 100
Selling price of x articles = Rs 100x
Given, Profit = C.P. of 15 articles
100x – 4800 = 15 ![]()
100x2 – 4800x = 15 x 4800
x2 – 48x – 720 = 0
x2 – 60x + 12x – 720 = 0
x(x – 60) + 12(x – 60) = 0
(x – 60) (x + 12) = 0
x = 60, -12
Since, number of articles cannot be negative. So, x = 60.
Thus, the number of articles bought is 60.
Chapter 6 – Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Exercise 6 (E)
Question 1
The distance by road between two towns A and B is 216 km, and by rail it is 208 km. A car travels at a speed of x km/hr and the train travels at a speed which is 16 km/hr faster than the car. Calculate:
(i) the time taken by the car to reach town B from A, in terms of x;
(ii) the time taken by the train to reach town B from A, in terms of x.
(iii) If the train takes 2 hours less than the car, to reach town B, obtain an equation in x and solve it.
(iv) Hence, find the speed of the train.
Answer 1

Question 2
A trader buys x articles for a total cost of Rs 600.
(i) Write down the cost of one article in terms of x.
If the cost per article were Rs 5 more, the number of articles that can be bought for Rs 600 would be four less.
(ii) Write down the equation in x for the above situation and solve it for x.
Answer 2

Question 3
A hotel bill for a number of people for overnight stay is Rs 4800. If there were 4 people more, the bill each person had to pay, would have reduced by Rs 200. Find the number of people staying overnight.
Answer 3

Question 4
An Aero plane travelled a distance of 400 km at an average speed of x km/hr. On the return journey, the speed was increased by 40 km/hr. Write down an expression for the time taken for:
(i) the onward journey;
(ii) the return journey.
If the return journey took 30 minutes less than the onward journey, write down an equation in x and find its value.
Answer 4

Question 5
Rs 6500 was divided equally among a certain number of persons. Had there been 15 persons more, each would have got Rs 30 less. Find the original number of persons.
Answer 5

Question 6
A plane left 30 minutes later than the schedule time and in order to reach its destination 1500 km away in time, it has to increase its speed by 250 km/hr from its usual speed. Find its usual speed.
Answer 6

Question 7
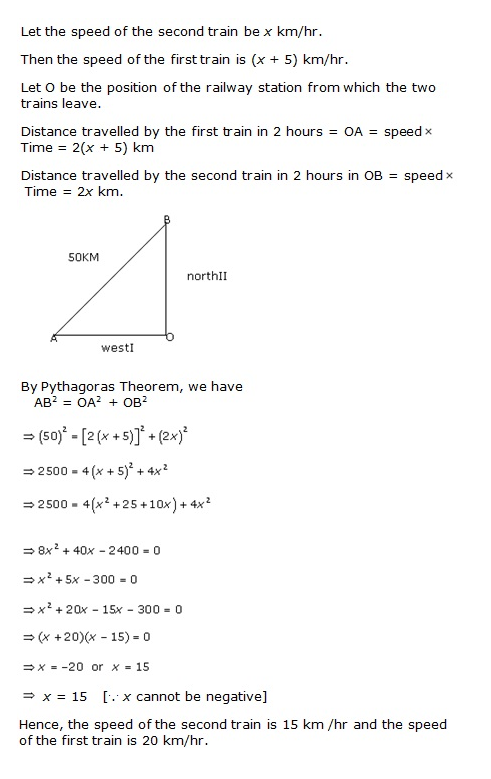
Two trains leave a railway station at the same time. The first train travels due west and the second train due north. The first train travels 5 km/hr faster than the second train. If after 2 hours, they are 50 km apart, find the speed of each train.
Answer 7
Question 8
The sum S of first n even natural numbers is given by the relation S = n(n + 1). Find n, if the sum is 420.
Answer 8
S = n(n + 1)
Given, S = 420
n(n + 1) = 420
n2 + n – 420 = 0
n2 + 21n – 20n – 420 = 0
n(n + 21) – 20(n + 21) = 0
(n + 21) (n – 20) = 0
n = -21, 20
Since, n cannot be negative.
Hence, n = 20.
Question 9
The sum of the ages of a father and his son is 45 years. Five years ago, the product of their ages (in years) was 124. Determine their present ages.
Answer 9
Let the present ages of father and his son be x years and (45 – x) years respectively.
Five years ago,
Father’s age = (x – 5) years
Son’s age = (45 – x – 5) years = (40 – x) years
From the given information, we have:
(x – 5) (40 – x) = 124
40x – x2 – 200 + 5x = 124
x2 – 45x +324 = 0
x2 – 36x – 9x +324 = 0
x(x – 36) – 9(x – 36) = 0
(x – 36) (x – 9) = 0
x = 36, 9
If x = 9,
Father’s age = 9 years, Son’s age = (45 – x) = 36 years
This is not possible.
Hence, x = 36
Father’s age = 36 years
Son’s age = (45 – 36) years = 9 years
Question 10
In an auditorium, seats were arranged in rows and columns. The number of rows was equal to the number of seats in each row. When the number of rows was doubled and the number of seats in each row was reduced by 10, the total number of seats increased by 300. Find:
(i) the number of rows in the original arrangement.
(ii) the number of seats in the auditorium after re-arrangement.
Answer 10
Let the number of rows in the original arrangement be x.
Then, the number of seats in each row in original arrangement = x
Total number of seats =
From the given information,
2x(x – 10) = x2 + 300
2x2 – 20x = x2 + 300
x2 – 20x – 300 = 0
(x – 30) (x + 10) = 0
x = 30, -10
Since, the number of rows or seats cannot be negative. So, x = 30.
(i) The number of rows in the original arrangement = x = 30
(ii) The number of seats after re-arrangement = x2 + 300 = 900 + 300 = 1200
Question 11
Mohan takes 16 days less than Manoj to do a piece of work. If both working together can do it in 15 days, in how many days will Mohan alone complete the work?
Answer 11
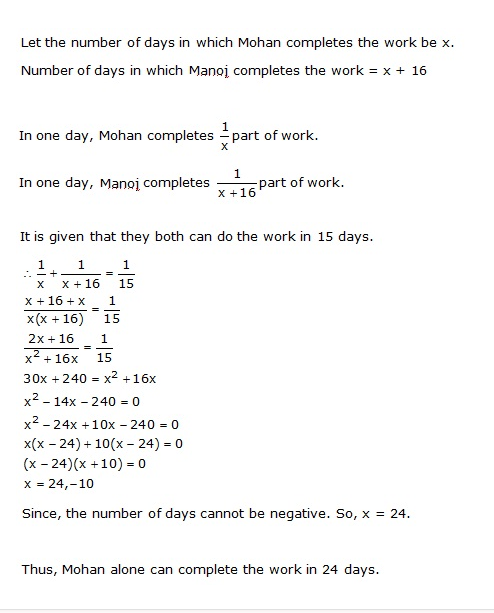
Question 12
Two years ago, a man’s age was three times the square of his son’s age. In three years time, his age will be four times his son’s age. Find their present ages.
Answer 12
Let the age of son 2 years ago be x years.
Then, father’s age 2 years ago = 3x2 years
Present age of son = (x + 2) years
Present age of father = (3x2 + 2) years
3 years hence:
Son’s age = (x + 2 + 3) years = (x + 5) years
Father’s age = (3x2 + 2 + 3) years = (3x2 + 5) years
From the given information,
3x2 + 5 = 4(x + 5)
3x2 – 4x – 15 = 0
3x2 – 9x + 5x – 15 = 0
3x(x – 3) + 5(x – 3) = 0
(x – 3) (3x + 5) = 0
x = 3,
Since, age cannot be negative. So, x = 3.
Present age of son = (x + 2) years = 5 years
Present age of father = (3x2 + 2) years = 29 years
Question 13
In a certain positive fraction, the denominator is greater than the numerator by 3. If 1 is subtracted from the numerator and the denominator both, the fraction reduces by 1/14. Find the fraction.
Answer 13

Question 14
In a two digit number, the ten’s digit is bigger. The product of the digits is 27 and the difference between two digits is 6. Find the number.
Answer 14
Given, the difference between two digits is 6 and the ten’s digit is bigger than the unit’s digit.
So, let the unit’s digit be x and ten’s digit be (x + 6).
From the given condition, we have:
x(x + 6) = 27
x2 + 6x – 27 = 0
x2 + 9x – 3x – 27 = 0
x(x + 9) – 3(x + 9) = 0
(x + 9) (x – 3) = 0
x = -9, 3
Since, the digits of a number cannot be negative. So, x = 3.
Unit’s digit = 3
Ten’s digit = 9
Thus, the number is 93.
Question 15
Some school children went on an excursion by a bus to a picnic spot at a distance of 300 km. While returning, it was raining and the bus had to reduce its speed by 5 km/hr and it took two hours longer for returning. Find the time taken to return.
Answer 15

Question 16
Rs.480 is divided equally among ‘x’ children. If the number of children were 20 more, then each would have got Rs.12 less. Find ‘x’.
Answer 16
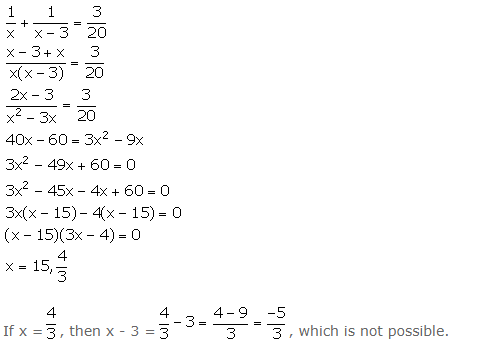
Question 17
A bus covers a distance of 240 km at a uniform speed. Due to heavy rain its speed gets reduced by 10km/h and as such it takes two hrs longer to cover the total distance. Assuming the uniform speed to be ‘x’ km/h, form an equation and solve it to evaluate ‘x’.
Answer 17
Time taken by bus to cover total distance with speed x km/h =
Time taken by bus to cover total distance with speed (x – 10) km/h =
According to the given condition, we have
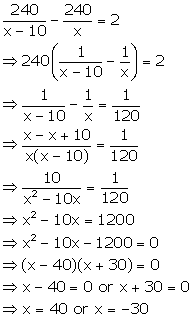
Since the speed cannot be negative, we have x = 40 km/h
Question 18
The sum of the ages of Vivek and his younger brother Amit is 47 years. The product of their ages in years is 550. Find their ages.
Answer 18
Given that he sum of the ages of Vivek and his younger brother Amit is 47 years.
Let the age of Vivek = x
⇒ the age of Amit = 47 – x
The product of their ages in years is 550 …. given
⇒ x(47 – x) = 550
⇒ 47x – x2 = 550
⇒ x2 – 47x + 550 = 0
⇒ x2 – 25x – 22x + 550 = 0
⇒ x(x – 25) – 22(x – 25) = 0
⇒ (x – 25) (x – 22) = 0
⇒ x = 25 or x = 22
Given that Vivek is an elder brother.
∴ x = 25 years = age of Vivek and
age of Amit = 47 – 25 = 22 years
End of Solving Simple Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Chapter-6
Return to :- Concise Selina Maths Solutions for ICSE Class-10
Thanks
Please share with your friends