Srijan Class-9 Dentition ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-10. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type ( including True False), Application / Skill ( Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Solutions of Srijan Class-9 Dentition ICSE Biology Ch-10
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-10 | Dentition |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Ch-10 Dentition Srijan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
Concept Check 1 (Page 117)
Fill in the blanks.
1. Each tooth consists of root neck and crown.
2 Dentine is the yellowing bone-like tissue that lies inside the enamel.
3. In human child Premolars teeth are not found.
4. Premolars and molars are also called check teeth.
5. The molars that appear only after the age of 24 years in human is called ………….. teeth.
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 118)
Ch-10 Dentition ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
Question 1: Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) The visible part of a tooth, which is projected beyond the gum, is the …………
(b) Last molar on either side in each jaw of man is called ……………..
(c) The hardest material in the body of mammals is ……………. of teeth.
(d) ………………. teeth are used for biting and cutting food.
Answer :
(a) Crown
(b) Wisdom teeth
(c) Enamel
(d) Incisors
Question 2: Write the following parts:
(a) The part of tooth enclosed in the gum.
(b) The part of tooth embedded in the socket of jaw bone
(c) The layer that forms bulk of the tooth.
(d) The hardest material that forms white cover on the crown of tooth.
Answer :
(a) Neck
(b) Root
(c) Plup
(d) Enamel
B. Short Answer Type Questions (Page118)
Ch-10 Dentition ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
Question 1: Answer the following questions briefly:
(a) What are thecodont teeth?
(b) Write down the dental formula of an adult man.
(c) Write one main function of molars, canines and incisors.
Answer :
(a) Thecodont dentition is a morphological arrangement in which the base of the tooth is completely enclosed in a deep socket of bone
(b) The dental formula is used to represent the arrangement of the teeth in upper and the lower row. The dental formula for the adult human beings is 2123/2123. There are 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars and 3 molars in one row. There are total 32 teeth in the adult human being
(c)
Incisors
The incisors are the most visible of all the teeth. Also, they are also the fastest to develop. The permanent teeth contain four incisors on the upper jaw and four incisors on the lower jaw. The eight incisors have the primary function of biting food as a result of their sharpness.
Canines
The canines are the next to develop after the canines. They are sharper than the canine and meant for ripping and tearing food. There are two canines on the upper jaw and two canines in the lower jaw. For the milk teeth, the upper canines appear before the lower canines (a four months difference) while for the permanent teeth, the lower canines appear two years before the upper canines.
Molars
Molars develop in a child as part of the milk teeth between a year and 1.5 years. Later on, as the child develops, the milk teeth molars are replaced by the premolars. The permanent molars develop two on the upper jaw and two on the lower jaw before the premolars replace the primary ones while two others develop after the premolars have replaced the primary molars. In a fully formed adult, there are four molars on either side of the mouth.
Question 2: Differentiate between the following:
(a) Premolar and molar
(b) Milk teeth and permanent teeth
(c) Enamel and dentine
Answer :
(a) Premolar and molar–
As noun the difference between molar and premolar is that molar is a back tooth having a broad surface used for grinding one’s food while premolar is a tooth situated in front of the molar teeth; especially a tooth in humans with two cusps which is between the canines and the molars
(b) Milk teeth and permanent teeth—Primary teeth are smaller and look whiter than permanent teeth because they have thinner enamel. Their roots are also shorter and thinner. Primary teeth are usually just 20, while there are 32 permanent adult teeth. Permanent teeth will start to appear when a child is around six years old, and the jaw is large enough
(c) Enamel and dentine–While enamel is approximately 85% mineral, combined with a small amount of collagen, organic material and water, dentin is highly organic. Dentin is comprised of about 45% mineral, with the remainder a combination of organic matter and water
C. Long Answer Type Questions (Page 118)
Ch-10 Dentition ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
Question 1: Name different parts of tooth with their functions as seen in the longitudinal section of a tooth.
Answer :
Root :– The root is the part of the tooth that extends into the bone and holds the tooth in place. It makes up approximately two-thirds of the tooth.
- Root canal. The root canal is a passageway that contains pulp.
- Cementum. Also called cement, this bone-like material covers the tooth’s root. It’s connected to the periodontal ligament.
- Periodontal ligament. The periodontal ligament is made of connective tissue and collagen fiber. It contains both nerves and blood vessels. Along with the cementum, the periodontal ligament connects the teeth to the tooth sockets.
- Nerves and blood vessels. Blood vessels supply the periodontal ligament with nutrients, while nerves help control the amount of force used when you chew.
- Jaw bone. The jaw bone, also called the alveolar bone, is the bone that contains the tooth sockets and surrounds the teeth’s roots; it holds the teeth in place.
Neck :–The neck, also called the dental cervix, sits between the crown and root. It forms the line where the cementum (that covers the root) meets the enamel.
- Gums. Gums, also called gingiva, are the fleshy, pink connective tissue that’s attached to the neck of the tooth and the cementum.
- Pulp. Pulp is the innermost portion of the tooth. It’s made of tiny blood vessels and nerve tissue.
- Pulp cavity. The pulp cavity, sometimes called the pulp chamber, is the space inside the crown that contains the pulp.
Crown:–The crown of a tooth is the portion of the tooth that’s visible.
- Anatomical crown. This is the top portion of a tooth. It’s usually the only part of a tooth that you can see.
- Enamel. This is the outermost layer of a tooth. As the hardest tissue in your body, it helps to protect teeth from bacteria. It also provides strength so your teeth can withstand pressure from chewing.
- Dentin. Dentin is a layer of mineralized tissue just below the enamel. It extends from the crown down through the neck and root. It protects teeth from heat and cold.
Question 2: Describe four types of human teeth with their diagrams
Answer : four types of human teeth
Incisors
Incisors are present at the front of the mouth. These teeth have sharp edges and are adapted for cutting food into small, chewable pieces. Humans have eight incisors, four incisors in the upper jaw and four in the lower jaw.
Canines
Canines are also called cuspids. They are situated at the ‘corners’ of the dental arches. They are characteristically sharp, elongated and pointy surface. Their primary function is to grip and tear food (tough food such as meat). Humans have four canines, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower jaw.
Premolars
Premolars are also called bicuspids and are located behind the canines. These teeth have a flat surface with ridges, which is adapted for crushing and grinding food into smaller portions. Humans have eight premolars, two on each side of the jaws.
Molars
Molars are the largest and strongest teeth. It has a large and flat biting surface, which is well-adapted for grinding food. Humans have 12 molars, six in each jaw. Four of those are wisdom teeth, which is also called the third molar, which come in between the ages of 17 to 25.
D. Multiple Choice Questions (Page 118)
Ch-10 Dentition ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
Question 1: Which one of the following pairs of types of teeth perform one common function as stated against it?
(a) Molars, Incisor -Grinding
(b) Premolars, Molars-Grinding
(c) Canines, Premolars Biting
(d) Incisors, Canines-Holding
Answer : (b) Premolars, Molars-Grinding
Question 2: These teeth are not found in milk teeth
(a) Molars
(b) Premolars
(c) Incisors
(d) Canines
Answer : (b) Premolars
E Application/Skil1-based Questions (Page 118)
Ch-10 Dentition ICSE Class-9th Srijan Publishers Biology Solutions
The diagram given below represents the dentition man:
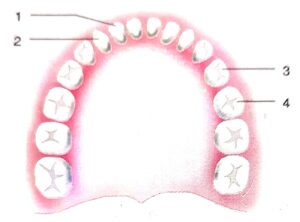
(a) Label the parts numbered as 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) State the function of canines and molars.
(c) State whether the diagram is of milk teeth or permanent teeth.
(d) Write down the dental formula on the basis of given diagram.
Answer : (a)
1. Incisor
2. Canines
3. Premolars
4. Molars
(b)
Canines : Canines are four in number Canines are long and conical. Canines are specialised for holding and taring food.
Molars : Molars have 3 (tricuspids), 4 or 5 asp. Molar usally have three roots.
(c) The diagram is of permanent teeth.
(d) Dentist Formula : (No. of teeth in one half of of upper jaw /No. of teeth in one half of lower jaw) x 2
Thanks



All diagrams are not in a site
call 8957797189 if problems