Srijan Class-9 Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-4. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check-1, and 2,Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type (including True False), Application /Skill (Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Srijan Class-9 ICSE Biology Chapter-4 Pollination and Fertilisation
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Chapter-4 | Pollination and Fertilisation |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check-1, and 2, Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
ICSE Biology Solutions Srijan Class-9 Pollination and Fertilisation Ch-4
–: Included Topics :–
Concept Check 1
Concept Check 2
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE,
B .SHORT ANSWER TYPE,
C .LONG ANSWER TYPE,
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE,
E. Application/Skill-based Questions
Note :- Before Viewing Srijan Solutions of Chapter-4 Pollination and Fertilisation Read the whole chapter carefully with figure. Chapter-4 Pollination and Fertilisation is very important Chapter in ICSE Class 9th biology.
Concept Check 1 (Page 50)
Srijan Class-9 Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-4
State whether the the following statements are true or false. If false, write the correct statements by changing the incorrect word/words only.
Question 1:
Cross pollination is a wasteful process in comparison to self pollination.
Answer :
True
Question 2:
Cleistogamy is a device to ensure cross pollination.
Answer :
False
Question 3:
Anemophily means pollination by insects.
Answer :
False
Question 4:
In maize wind pollination occurs.
Answer :
True
Question 5:
Unisexuality is an adaptation for self-pollination.
Answer :
False
Concept Check 2 (Page 53)
Srijan Publication ICSE Class-9 Biology Ch-4 Pollination and Fertilisation
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
1. The process of fusion of male gamete with the egg is called Syngamy.
2. Ovule is contained with in the Ovary.
3. Secondary nucleus gives rise to Endosperm.
4. Outer integument of ovary forms Testa after fertilisation.
5. The zygote divides repeatedly to form the Embryo.
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 53)
Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Question 1:
Give the proper term for each of the following
(a) The condition in which anther and stigma of a bisexual flower mature at the same time.
(b) Fusion of one male gamete with the egg nucleus.
(c) Pollination brought about by the agency of air.
(d) A type of pollination in which pollen grains are transferred from the anthers of a flower to the stigma of a flower present on a separate plant.
Answer :
(a) Homogamy
(b) Syngamy
(c) Anemophily
(d) Cross-Pollination
Question 2:
Give one example for each of the following:
(a) A wind-pollinated flower.
(b) An insect-pollinated flower.
(c) A water-pollinated flower.
(d) A flower which is pollinated by elephant.
Answer :
(a) Sugarcane
(b) Rose
(c) Hydrilla
(d) Rafflesia
Question 3:
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) In homogamy pollination, the anther and stigma mature at the same time.
(b) In cross-pollination there is much wastage of pollen grain.
(c) For Entomophily the flowers must be showy and scented.
(d) When anthers of the flower mature earlier than the stigma, it is called protandry.
(e) Fruit is a mature ripened ovary.
Question 4:
Complete the following statements by choosing the correct alternatives from those given within brackets:
(a) Pollen grains of insect-pollinated flowers are (heavy, large, dry, spiny-walled)
(b)The condition unfavourable for cross pollination includes (unisexuality, cleistogamy, heterostyly, herkogamy).
Answer :
(a) Large
(b) Cleistogamy
Question 5:
Match the columns.
Column A
(a) Maize
(b) Endosperm
(c) Autogamy
(d) Exine
(e) Cleistogamy
(f) Entomophily
Column B
(i) Self-pollination
(ii) Camelina
(iii) Pollination by insect
(iv) Pollination by wind
(v) The triploid tissue
(vi) Outer coat of pollen
Answer :
(a) (iv) Pollination by wind
(b) (v) The triploid tissue
(c) (i) Self-pollination
(d) (vi) Outer coat of pollen
(e) (ii) Camelina
(f) (iii) Pollination by insect
Question 6:
State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) Fertilisation is fusion of anther with the ovary.
(b) Generative nucleus in the pollen tube divides to form two male gametes.
(c) Pollen tube enters the ovule through micropyle.
Answer :
(a) False
(b) True
(c) False
Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
B. Short Answer Type Questions, (Page 54)
Question 1:
What happens to the following after fertilisation?
(a) Ovary
(b) Ovule
(c) Egg cell
(d) Secondary nucleus
Answer :
(a) Ovary into fruit
(b) Ovule into Seed
(c) Egg cell into seed cover
(d) Secondary nucleus into endosperm
Question 2:
Differentiate between the following :
(a) Self pollination and Cross pollination
(b) Seed and Fruit
(c) Anemophily and Entomophily
Answer :
(a) Self pollination and Cross pollination
Cross-Pollination
The cross-pollination is defined as the deposition of pollen grains from a flower to the stigma of another flower. Commonly, the process is done by insects and wind. By insects, the process takes place in several plants like strawberries, grapes, raspberries, tulips, apples, plums, pears, daffodils, and more. Pollination by the wind is observed in different grasses, maples trees, dandelions and catkins.
Self Pollination
In this process, the pollen grains transfer from the stigma of the same or genetically similar flower. Self-pollination can be observed in legumes such as orchids, sunflowers, peas, peanuts, oats, peaches, potatoes, wheat, and others
(b) Seed and Fruit
Difference Between Fruit and Seed. The key difference between fruit and seed is that fruit is the developed ovary of angiosperms after fertilization while seed is a fertilized ovule of plants. After the fertilization, the ovule becomes the seed, and the ovary becomes the fruit
(c) Anemophily and Entomophily
Question 3:
Answer the following questions briefly:
(a) Mention two ways in flowers which favour cross pollination.
(b) List some advantages of self pollination.
(c) What are disadvantages of cross pollination?
Answer :
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another or the same flower.
Anemophily are those flowers in which pollination is carried out by wind.
Entomophily are those flowers in which pollination is carried out by insects.
C .LONG ANSWER TYPE, (Page 54)
Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Question 1:
What is pollination? Mention its types and two advantages of each type of pollination.
Answer :
Advantages of Self Pollination:
1. It maintains the parental characters or purity of the race indefinitely
3. The plant does not need to produce large number of pollen grains.
4. Flowers do not develop devices for attracting insect pollinators.
5. It ensures seed production. Rather it is used as fail safe device for cross-pollinated flowers.
Question 2:
How does cross pollination form a better progeny?
Answer :
Cross pollination forms a better progeny because it allows for diversity in the species, as the genetic information of different plants are combined. However, it relies on the existence of pollinators that will travel from plant to plant
Question 3:
What events lead to fertilisation in a flower?
Answer :
Fertilization in flowering plants happens through a process called pollination. Pollination occurs when pollen grains from the anther land on a stigma. After pollen grains land on the stigma, a pollen tube grows from the pollen grain, through the style, and into the ovary.
Question 4:
Give four differences between insect-pollinated and wind-pollinated flowers.
Answer :
| Wind pollinated flowers | Insect pollinated flowers |
| Pollinating Agent | |
| The pollinating agent is wind. | The pollinating agents are an insect. |
| Morphological features of a Flower | |
| The wind-pollinated flowers comprise light coloured petals, without a pleasant strong smell. | The insect-pollinated flowers comprise brightly coloured petals with a pleasant strong smell. |
| Pollen Grains | |
| In wind-pollinated flowers, the produced pollen grains are smaller and lighter in weight, which can be carried by the wind easily. | In insect-pollinated flowers, the produced pollen grains are larger in size, sticky and spiny which helps the insect to carry the pollen grains. |
| Stigma | |
| Stigma is feathery or sticky and found hanging out of petals. | Stigma is small and is situated deep inside the petals. |
| Stamens | |
| The stamens are long and visible out of petals. | Stamens may be small and hidden inside petals. |
| Anther | |
| The anthers are often seen being supported outside the flower | The anthers are found deep inside the flower. |
| Filaments | |
| The filaments found in these flowers are slender and long. | The filaments found in these flowers are strong and short. |
| Production of Nectar | |
| These flowers do not produce nectars. | These flowers produce a lot of nectars. |
| Wastages | |
| There is a lot of wastage as more number of pollen grains are produced. | There is no wastage as less number of pollen grains are produced. |
| Type of Flowers | |
| Plants bear only unisexual flowers. | Plants bear bisexual flowers. |
Question 5:
What are the advantages of the following in the flowers to the plant concerned?
(a) Bright and coloured petals
(b) Minute and light pollen
(c) Fragrance and nectar
(d) Long and feathery stigma
Answer :
a) Bright and coloured petals- Attract insect for pollination
(b) Minute and light pollen–favour air pollination
(c) Fragrance and nectar–Attract insect for pollination
(d) Long and feathery stigma- favour air pollination to long distance
Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE, (Page 54)
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1:
Exine and intine are the parts of
(a) Pollen grain
(b) Seed
(c) Stigma
(d) Embryo sac
Answer :
(a) Pollen grain
Question 2:
Which one of the following processes describes fertilisation in flowering plants?
(a) Pollen grains landing on the stigma.
(b) Pollen released from the anther.
(c) Pollen tube growing down the style.
(d) Pollen tube releasing a male nucleus to fuse with an egg nucleus.
Answer :
(d) Pollen tube releasing a male nucleus to fuse with an egg nucleus.
Question 3:
In a typical complete, bisexual and hypogynous flower, the arrangement of floral whorls on the thalamus from the outermost to the innermost is
(a) Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium
(b) Calyx, Corolla, Gynoecium and Androecium
(c) Gynoecium, Androecium, Corolla and Calyx
(d) Androecium, Gynoecium, Corolla and Calyx
Answer :
(a) Calyx, Corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium
Question 4:
Which one of the following is one of the characteristics of self pollinated flowers?
(a) Flowers are large and showy.
(b) Flowers are scented.
(c) Stigma and anthers mature at the same time.
(d) Pollen is produced in very large quantities.
Answer :
(c) Stigma and anthers mature at the same time.
Question 5:
In nature cleistogamous flowers are
(a) Wind-pollinated
(b) Bird-pollinated
(c) Self-pollinated
(d) Insect pollinated
Answer :
(c) Self-pollinated
Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
E. Application/Skill-based Questions (Page 54)
Question 1:
Draw a labelled diagram of ovule as seen in longitudinal section.
Answer :
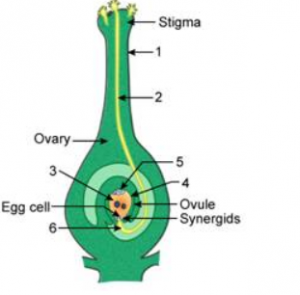
Question 2:
Given alongside is the longitudinal section of pistil.
(a) Label the parts marked 1-7.
(b) What is the function of stigma?
(c) What is the function of a pollen tube?
Answer :
(a)
1. Pollen tube
2. Style
3. Ovary
4. Embryo sac
5. Micropyle
6. Female gametes
7. Male gametes
(b) Stigma : It is the terminal knob-like part of the carpel. It is sticky or feathery, adapted to receive the pollen grains.
(c) Pollen tube : It contain a generative nucleus.
–: End of Srijan Class-9 Pollination and Fertilisation ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-4 :–
Return to :- Srijan Publication ICSE Biology Class-9
Thanks



Please while giving answers to from the next try to ensure that you are giving the false statement… Means in true false questions when an answer is false plz give the statement why it is false…
thanks for your precious suggestion