Srijan Class-9 Tissues ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-2. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check-1, 2, 3, 4 and 5,Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, Multiple Choice Type (including True False), Application /Skill (Figure Based ) Questions by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.

| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Srijan Publication |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | Veer Bala Rastogi |
| Book Name | …………. |
| Topics | Solutions of Concept Check-1, 2, 3, 4 and 5,Very Short Ans, Short Ans, Long Ans, MCQ, Application Skill Based Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Srijan Class-9 Tissues ICSE Biology Solutions Ch-2
–: Included Topics :–
Concept Check 1
Concept Check 2
Concept Check 3
Concept Check 4
Concept Check 5
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE,
B .SHORT ANSWER TYPE,
C .LONG ANSWER TYPE,
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE,
E. Application/Skill-based Questions
Note :- Before Viewing Srijan Solutions of Chapter-2 Tissues . Read the whole chapter carefully with figure. Chapter-2 Tissues is very important Chapter in ICSE Class 9th biology.
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Concept Check 1 (Page 25)
Answer the following questions.
Question 1:
What is a tissue ?
Answer :
Tissue is a group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit. A nonliving material, called the intercellular matrix, fills the spaces between the cells. This may be abundant in some tissues and minimal in others.
Question 2:
How are plant tissue broadly classified ?
Answer :
In plant anatomy, tissues are categorized broadly into three tissue systems: the epidermis, the ground tissue, and the vascular tissue
Question 3:
Where is apical meristem found ?
Answer :
Apical meristems, which are located at the tips of shoots and roots in all vascular plants, give rise to three types of primary meristems, which in turn produce the mature primary tissues of the plant
Question 4:
Which meristem is responsible for the increase in girth of a plant ?
Answer :
Apical meristems give rise to the primary plant body and are responsible for the extension of the roots and shoots. Lateral meristems are known as secondary meristems because they are responsible for secondary growth, or increase in stem girth and thickness.
Question 5:
Why are sclerenchyma cells so hard ?
Answer :
Cells of sclerenchyma have a tough protein called lignin in their cell walls this give structural strength to them all the cells of sclerenchyma tissues are dead this is the reason they are hard
Question 6:
Name the tissue that provides the up word movement of water and mineral salts in plant body.
Answer :
Xylem, plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support.
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Concept Check 2 (Page 28)
State whether the the following statements are true or false. If false, write the correct statements by changing the incorrect word/words only.
Question 1:
One surface of epithelial cells is always free.
Answer :
True
Question 2:
The intercellular matrix between epithelial cells is in plenty and gelatinous in nature.
Answer :
True
Question 3:
Sensory epithelium is found in the nasal passages.
Answer :
True
Question 4:
Epithelial layers are richly supplied with blood capillaries.
Answer :
False
correct- Connective tissue are richly supplied with blood capillaries.
Question 5:
Ciliated epithelium is modified columnar epithelium.
Answer :
True
Question 6:
The outer layers of stratified epithelium are formed of dead cells.
Answer :
True
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Concept Check 3 (Page 32)
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
Question 1:
…………………. tissue connects or binds cells, tissues and organs.
Answer :
Connective
Question 2:
……………………. cells secrete matrix of connective tissue.
Answer :
Mast
Question 3:
The wandering phagocytic cells found in connective tissue are called ……………….
Answer :
Fibrocytes
Question 4:
……………….. acts as heat insulator and shock absorber.
Answer :
Adipose tissue
Question 5:
Collagen fibres provide………………… strength to connective tissue.
Answer :
mechanical
Question 6:
……………………. fibres are abundant in tendon.
Answer :
White collagen
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Concept Check 4 (Page 34)
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
Question 1:
Striated muscle fibres are ………………….
Answer :
Voluntary muscles
Question 2:
…………………… is the special property of muscular tissue.
Answer:
Contraction
Question 3:
Skeletal muscles form nearly …………………… per cent of the entire body.
Answer :
50
Question 4:
The muscles found in the wall of urinary bladder or intestate are …………………… muscles.
Answer :
Nonstriated
Question 5:
The ………………………… muscles form sheets, whereas. ……………………… muscles form bundles
Answer :
Unstriped, Striped
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
Concept Check 5 (Page 28)
State whether the the following statements are true or false. If false, write the correct statements by changing the incorrect word/words only.
Question 1:
Nerve cells are also called cytons.
Answer :
False
correct- Nerve cells are also called newrons
Question 2:
A neuron is specialised to receive sensory stimuli.
Answer :
True
Question 3:
Neuron is the unit of nervous tissue.
Answer :
True
Question 4:
Nerve cells are the longest cells in the body.
Answer :
True
Question 5:
Nerve cells join to form nerve fibres,
Answer :
False
correct -Nerve cells join to form axon
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE, (Page 36)
Question 1:
Give one word for the following:
(a) Study of tissues.
(b) Group of cells performing specific functions.
(c) Protein that provides elasticity to yellow fibres
(d) Dividing cells at the tip of roots and stems.
(e) Tissue that transports organic food from the leaves
Answer :
(a) Histology
(b) Tissue
(c) Celestin
(d) Meristematic cell
(e) Phloem
Question 2:
Given below are the functions of epithelial tissue. Name the type of epithelium which performs each function:
(a) The epithelium that helps in secretion and absorption.
(b) The epithelium that helps in respiratory gas exchange
(c) The epithelium that helps in the movement of substances.
(d) The epithelium that protects against the entry of microbes into the body.
Answer :
(a) Cuboidal epithelium
(b) squamous epithelium
(c) Ciliated epithelium
(d) Squamous epithelium
Question 3:
State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) In monocot stems, intercalary meristem is located at the base of internode.
(b) The red blood corpuscles in man have a large nucleus.
(c) Fibres of flex and jute are sclerenchyma cells.
(d) Cell wall of tracheid’s is highly lignified.
(e) Muscle fibres can undergo cell division.
Answer :
(a) True
(b) True
(c) True
(d) True
(e) False
Question 4:
Match the columns.
Column A
(a) Axons and dendrites
(b) Adipose tissue
(C) Leucocytes
(d) Conducting tissue
(e) Muscle fibres
Column B
(i) Storage of fats
(ii) Vascular bundles
(iii) Neurons
(iv) Actin
(v) To engulf foreign particles
Answer :
(a) (iii) Neurons
(b) (i) Storage of fats
(c) (v) To engulf foreign particles
(d) (ii) Vascular bundles
(e) (iv) Actin
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
B. Short Answer Type Questions, (Page 36)
Question 1:
Give one function each of the following:
(a) Blood and lymph
Answer:
Both are two circulatory fluids of the body, Blood moves via blood vessels and lymph moves via lymphatic vessels. Blood transports gases, nutrients, and metabolic wastes. Lymph is draining of tissue fluid into the circulatory system. The major difference between blood and lymph is their function in the body.
(b) Tendon and ligament
Answer:
A tendon serves to move the bone or structure. A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue which attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable
(c) Cardiac muscle fibres
Answer:
Only present in hear, it contracts and allows the heart to pump blood into the body organs.
(d) Xylem
Answer:
Xylem, plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support. Xylem tissue consists of a variety of specialized, water-conducting cells known as tracheary elements.
(e) Meristem
Answer:
Meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in plants.
Question 2:
Give differences between the following :
(a) Chlorenchyma and aerenchym
Answer:
The main difference between chlorenchyma and paerenchyma is that chlorenchyma is a form of parenchyma, containing chloroplasts, but aerenchyma is another form of parenchyma, containing large air spaces. Generally, parenchyma is a form of ground tissue with living cells, having primary cell walls
(b) Tracheid and vessel
Answer:
Tracheids and vessels are the two water conducting elements found in the xylem. Tracheids are the major conducting element in ferns and gymnosperms. Vessels are only present in angiosperms. … The main difference between tracheids and vessels is their diameter and the efficiency in water
(c) Blood and lymph
Answer:
Blood has RBC’s, WBC’s, platelets and a fluid called plasma. Whereas lymph has WBC’s and watery fluid. They both have immune and also circulatory functions in them. One of the major differences between them is that blood flows through blood vessels and lymph through lymphatic vessels
(d) Bone and cartilage
Answer:
| Bones | Cartilage |
|---|---|
| The matrix is both organic and inorganic. | The matrix is completely organic. |
| Has deposits of calcium salts. | May or may not have deposition of calcium salts. |
| The bones have a rich blood supply. | Lacks blood supply (hence repair is slower) |
(e) Tendon and ligament
Answer
The most apparent difference between ligaments and tendons is that tendons join bone to a skeletal muscle and ligaments join bone to another bone. Tendons are strong and non-flexible while ligaments are flexible and elastic. Both play a vital role in joints and bones and are composed of living cells
(f) Meristematic and permanent tissues
Answer:
Meristematic tissue has cells small in size and isodiametric in shape. Permanent tissue has cells large in size and their shape varies. Cells are compactly arranged without having intercellular spaces. Cells are arranged loosely in the parenchyma and compactly in sclerenchyma
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
C .LONG ANSWER TYPE, (Page 36)
Question 1 :
Answer:
They are:
1. Parenchyma.
2. Collenchyma.
3. and Sclerenchyma.
Question 2 :
Describe the functions of different types of blood corpuscles.
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells carry the protein hemoglobin, which attaches to oxygen and delivers it to all of the body’s tissues.
WBC
Leukocyte cells work to keep the human body free of infection. These cells find and destroy microbes within the human body, responding to and treating infection.
Platelets
Platelets are tiny but important cell fragments in your blood that help your body control bleeding.
Question 3 :
Name the two types of fibres found in the connective tissue? Differentiate between the two.
Question 4 :
Answer:
Cardiac and skeletal muscle are both striated in appearance, while smooth muscle is not. Both cardiac and smooth muscle are involuntary while skeletal muscle is voluntary. .Cardiac muscle is also an involuntary muscle but is more akin in structure to skeletal muscle, and is found only in the heart.
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
D. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE, (Page 36)
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1 :
The simple tissue consisting of living cells which provide mechanical support is :
(d) Xylem
(b) Collenchyma
Question2 :
Aerenchyma occurs in
(a) Mesophytes
(b) Xerophytes
(c) Hydrophytes
(d) All the above
Question 3 :
Grit of pear is formed of
(a) Sclereids
(b) Tracheids
(c) Companion cells
(d) Sclerenchyma fibres
Question 4 :
Which of the following components of xylem is living
(a) Xylem parenchyma
(b) Trachea
(C)Tracheids
(d) Xylem fibres
Question 5 :
Which type of tissue forms the inner lining of a blood vessel?
(a) Epithelial
(b) Connective
(d) Muscle
(a) Epithelial
Question 6 :
Cardiac muscle fibres are
(a) Branched
(b) Striated
(d) All the above
(b) Striated
Question 7 :
Most abundant animal tissue is
(a) Epithelium
(b) Muscular
(d) Blood
(c) Connective
Question 8 :
Ligament connects a bone with
(b) Muscle
(d) Both (b) and (o)
(c) Bone
Tissues ICSE 9th Solutions Srijan Publishers
E. Application/Skill-based Questions (Page 36)
Question 1:
(a) Identify the figure given below. What function?
(b) Label x, Y, z.
(c) Z loses its nucleus in mature state. Still it remains alive. How?
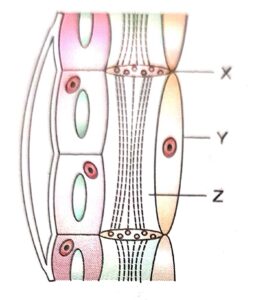
Answer :
(a) It is the living element of phloem.
Function : Its contains tubes for the transport of food product from green and storage organs to other organs of the plant.
(b)
X – Sieve plant
Y – Companion Cell
Z – Sieve tube cell
(c) The mature cell are without nucleus but with thin cell.
Question 2:
(b) Label the parts marked 1 to 3.
(c) Write the functions of parts marked 1l and 3.
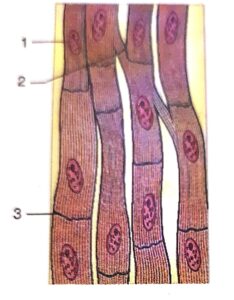
Question 3:
(b) Label the parts 1-3.
(c) Where is it located?
(d) Mention its function
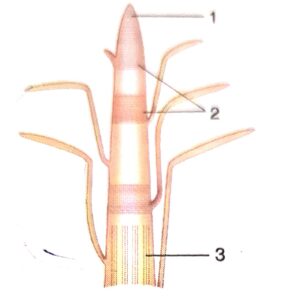
(a) Identify the figure given below.
(b) Label W, X Y and Z
(c) What is the chemical composition of material of figure?
(d) What is the function of X?
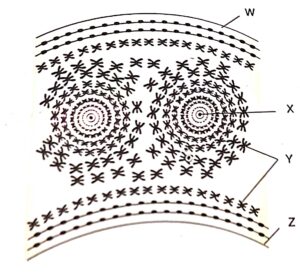



Thanks a lot
ok and keep in touch
Thank you icsehelp.com for solving all my problems related to biology