Srijan Publications Cell Cycle and Cell division Textbook Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-1. We Provide Solutions of Concept Check , MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type Questions and Structured / Applications / Skill Type Questions of Exercise-1 Cell Cycle and Cell division. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
Srijan Publications Cell Cycle and Cell division Textbook Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-1
-: Select Topics :-
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
LONG ANSWER TYPE
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
Concept Check 1 (page-12)
Srijan Publications Cell Cycle and Cell division Textbook Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-1
Answer the following questions :
1. Name the types of cell divisions.
Answer :
There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Most of the time when people refer to “cell division,” they mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells
2. Which cells of human body do not divide after maturation?
Answer :
Neurons, fat cells, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, mature bone cells, retinal receptor cells, and most mature blood cells are the cells of human body which do not divide after maturation
3. Why was interphase named as resting phase?
Answer :
Originally this phase of the cell cycle was called the “resting stage“, since light microscopy could not detect any activities taking place within the cells.
4. What is karyokinesis?
Answer :
Karyokinesis: During cell division, the process of partition of a cell’s nucleus into the daughter cells. See also: Cytokinesis; Mitosis
5. During which phases of the cell cycle does each chromosome consist of two chromatids ?
Answer :
Because each chromosome was duplicated during S phase, it now consists of two identical copies called sister chromatids that are attached at a common center point called the centromere
6. Give one difference between the cell division in a plant cell and an animal cell.
Answer :
Cell division varies between animals and plants, but there are many steps in common. The differences have largely to do with specialized structures in each type of cell. Plants have both a cell membrane and a cell wall, whereas animal cells have no cell wall. Animals also have cell centrioles, but higher plants don’t
Concept Check 2 (page-14)
Srijan Publications Cell Cycle and Cell division Textbook Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-1
Answer the following questions.
1. Which cells undergo meiosis?
Answer :
Whereas somatic cells undergo mitosis to proliferate, the germ cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes (the sperm and the egg). The development of a new progeny organism is then initiated by the fusion of these gametes at fertilization
2. Give one basic difference between meiosis I and meiosis II.
Answer :
Meiosis is the production of four genetically diverse haploid daughter cells from one diploid parent cell. In meiosis II, these chromosomes are further separated into sister chromatids. Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not
3. What is the meaning of diploid chromosome number?
Answer :
Diploid is the term that refers to the number of each type of chromosome that an organism has. And diploid specifically means every cell in that organism has two copies of each type of chromosome
4. Why is the first meiotic division called reduction division?
Answer :
The process of meiosis involves two divisions of the genetic material. The first division is called the reduction division – or meiosis I – because it reduces the number of chromosomes from 46 chromosomes or 2n to 23 chromosomes or n (n describes a single chromosome set
5. Gametes for sexual reproduction must be produced by meiosis. Why?
Answer :
Gametes must be produced by meiosis for sexual reproduction because the numbers of chromosomes are reduced to half during meiosis and then the normal diploid numbers of chromosomes are regained during the process of fertilization.
Srijan Publications Cell Cycle and Cell division Textbook Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-1
page-22
A. Very Short Answer 1ype Questions
1. Give one word tor the following:
(a) Structure that initiates cell division.
(b) Chromosomes appear thread like.
(c) The type of cell divisive which Occurs in the cells of the reproductive organs.
(d) The stage of mitosis during which nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappears.
(e) A membrane that disappears during late prophase.
Answer:
a) Structure that initiates cell division.–Nucleus
(b) Chromosomes appear thread like.- Chromatin fibre
(c) The type of cell divisive which Occurs in the cells of the reproductive organs-Meosis
(d) The stage of mitosis during which nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappears-Telophase
(e) A membrane that disappears during late prophase.-nuclear membrane
2. State whether the following statements are true or false.
If false, rewrite the correct form of statements.
(a) During cell divisions, cytoplasm divides first which is followed by nuclear division.
(b) Mitosis occur in reproductive cells.
(c) Crossing over takes place between chromatids.
(d) Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm.
(e) Meiosis occurs in the cells of root tip.
(f) In meiosis, the first meiotic division is the reduction division but the second division is simply mitosis.
(g) Mitosis is the type of cell division occurring in the cells of injured parts of the body.
(h) Resting stage in mitosis is called metaphase.
Answer:
(a) False-
correct statement- During cell divisions, Nucleus divides first which is followed by cytoplasm.
(b) False
correct statement- Meosis occur in reproductive cells.
(c) This statement is false.
correct statement– Crossing over involves the exchange of segments of DNA between homologous chromosomes during mitosis.
(d) true-Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm.
(e) false
Mitosis occurs in the cells of root tip.
(f) False
correct statement- In meiosis, the first meiotic division is the mitotic division but the second division is meiosis.
(g) true-Mitosis is the type of cell division occurring in the cells of injured parts of the body.
(h) false-Resting stage in mitosis is called interphase.
3. Match the columns.
Column A Column B
(a) Chromosome become (i) Anaphase
arranged in a horizontal
plane at the equator
(b) Daughter chromosomes (ii) Prophase
move to opposite poles of
the spindle.
(c) Chromosomes become (iii) Telophase
visible as fine, long threads.
(d) Chromosomes lose their (iv) Metaphase
distinctiveness and gradually
become transformed into
chromatin network.
Answer:
| a | (ii) prophase |
| b | (i) anaphase |
| c | (iv) metaphase |
| d | (iii) Telophase |
4. Given below are sets of certain terms. Without changing the first term, rearrange the remaining terms so as to be in logical sequence as per the direction given in
brackets.
(a) G1 Phase, G2 Phase, Prophase, S Phase (sequence in cell cycle)
(b) Interphase, Anaphase, Prophase, Telophase, Metaphase (sequential stages in karyokinetic)
Answer:
(a) G1 Phase, S Phase , G2 Phase, Prophase, (sequence in cell cycle)
(b) Interphase,, Prophase, Metaphase , anaphase , telophase (sequential stages in karyokinetic)
B Short Answer 1ype Questions.
Srijan Publications Cell Cycle and Cell division Textbook Solutions ICSE Class-10 Ch-1
1. Give differences between the Following:
(a) Metaphase and anaphase.
(b) Cytokines and karyokinetic
(c) Haploid and diploid cells
(d) Mitosis and Meiosis
(e) Metaphase and anaphase chromosomes
Answer:-
(a) Metaphase and anaphase.-During metaphase,: chromosomes are arranged in the equatorial plane, whereas during anaphase, daughter chromosomes move towards the Opposite poles of the spindle
(b) Cytokines and karyokinetic-Karyokinesis is defined as the division of the nucleus during the M phase of the cell cycle. The daughter chromosome is separated into two daughter nuclei. Cytokinesis, on the other hand, is defined as the division of the cytoplasm during the M phase of the cell cycle.
(c) Haploid and diploid cells-Diploid is a cell or organism that has paired or two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. Haploid or monoploid is a cell or organism that has just a single copy of each chromosome. These cells are formed after mitotic cell division
(d) Mitosis and Meiosis-Cells divide and reproduce in two ways, mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results in four sex cells
(e) Metaphase and anaphase chromosomes–In metaphase (a), the microtubules of the spindle (white) have attached and the chromosomes have lined up on the metaphase plate. During anaphase (b), the sister chromatids are pulled apart and move toward opposite poles of the cell
2. With reference to cell division, explain the following terms:
(a) Chromatid
(b) Gene
(c) Haploid
(d) Centrosome
(e) Homologous chromosomes
(f) Centromere
Answer:
(a) Chromatid—A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome. During cell division, the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes
(b) Gene—a specific sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that is located usually on a chromosome and that is the functional unit of inheritance
(c) Haploid—Haploid is the quality of a cell or organism having a single set of chromosomes. Organisms that reproduce asexually are haploid. Sexually reproducing organisms are diploid (having two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent). In humans, only their egg and sperm cells are haploid
(d) Centrosome—A centrosome is a cellular structure involved in the process of cell division. … Proteins called microtubules assemble into a spindle between the two centrosomes and help separate the replicated chromosomes into the daughter cells.
(e) Homologous chromosomes—Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism’s mother; the other is inherited from the organism’s father.
(f) Centromere—A centromere is a constricted region of a chromosome that separates it into a short arm (p) and a long arm (q). During cell division, the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes
C. Long Answer Type Questions
1. How does mitosis differ in animal and plant cells?
Answer
The most important and observable difference in the plant animal cells mitosis is the cytokinesis. In plants a new cell plate is formed between the daughter cells for the future cell wall, while in animal cells the cell membrane constricts to separates the parent cell into daughter cells
2. What is meant by cell cycle? Discuss its various stages.
Answer:
Phases of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a 4-stage process consisting of Gap 1 (G1), Synthesis, Gap 2 (G2) and mitosis. An active eukaryotic cell will undergo these steps as it grows and divides. After completing the cycle, the cell either starts the process again from G1 or exits the cycle through G0. From G0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation.
The stages in the cell cycle between one mitosis and the next, which include G1, S and G2, are known collectively as the interphase.
G1 phase
- Cell increases in size
- Cellular contents duplicated
S phase
- DNA replication
- Each of the 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) is replicated by the cell
G2 phase
- Cell grows more
- Organelles and proteins develop in preparation for cell division
M phase
- Mitosis followed by cytokinesis (cell separation)
- Formation of two identical daughter cells
3. Discuss the significance of mitosis and meiosis.
Answer:
Mitosis and meiosis are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes. The purpose of mitosis is cell regeneration, growth, and asexual reproduction,while the purpose of meiosis is the production of gametes for sexual reproduction. Mitosis is a single nuclear division that results in two nuclei that are usually partitioned into two new daughter cells. The nuclei resulting from a mitotic division are genetically identical to the original nucleus. They have the same number of sets of chromosomes, one set in the case of haploid cells and two sets in the case of diploid cells. In most plants and all animal species, it is typically diploid cells that undergo mitosis to form new diploid cells. In contrast, meiosis consists of two nuclear divisions resulting in four nuclei that are usually partitioned into four new haploid daughter cells. The nuclei resulting from meiosis are not genetically identical and they contain one chromosome set only. This is half the number of chromosome sets in the original cell, which is diploid.
D. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
1. The point where two sister chromatids of a chromosome are attached is known as
(a) Chiasmata
(b) Chromatid
(c) Chromomere
(d) Centromere
Answer-(d) Centromere
2. Which of the following is reduction division?
(a) Meiosis-I
(b) Meiosis-II
(c) Mitosis
(d) Interphase
Answer- (a) Meiosis-I
E. Application/Skill-based Questions
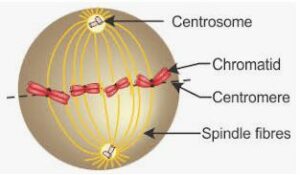
1 Draw a diagram of the nucleus of a cell, having chromosome number 6, as it would appear in the Metaphase stage of Mitosis and label the following parts in the diagram.
(a) Aster
(b) Achromatic spindle
(c) Chromatid
(d) Centromere
Answer:-
2 Given here is a a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division in an animal cell.
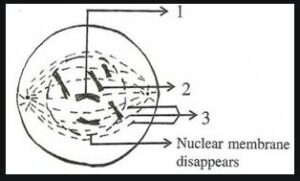
(a) Identify the stage. Give a reason to support your answer.
(b) Name the cell organelle that forms the aster.
(C) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
(d) Name the stage that follows this stage of mitosis How can this stage be identified?
(e) Mention two points of difference between mitosis aa meiosis with regard to :
(i) the number of daughter cells formed
(ii)the chromosome number in the daughter cell.
Answer:
(a) Late prophase. Because the nuclear membrane and nucleolus have disappeared.
(b) Centrioles.
(c) 1 – Centromere
2 – Chromatids.
3 – Spindle fibre.
(d) Metaphase. The centromeres of chromosomes are drawn to the equator by equal pull of two chromosomal spindle fibres that connects each centromere to the opposite poles, forming a metaphasic plate.
(e)
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| (i) Two daughter cells are produced. | (i) Four daughter cells are produced. |
| (ii) It is equational division i.e. the number of chromosome in the daughter cells or parent cells remains the same. | (ii) It is reductional division i.e. the number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the daughter cells. |
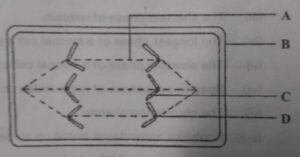
(a) Identify the stage of cell division.
(b) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(c) What is the unique feature observed in this stage?
(d) Where does this type of cell division usually occur?
(e) How many daughter cells are formed from this type of cell division?
(f) Is the dividing cell shown a plant cell or an animal cell? Give a reason to support your answer.
(b) the parts labelled
(c) the unique feature observed in this stage- Chromosome assume V, J or L shape
(d) this type of cell division usually occur at growth part
(e) Four daughter cells are formed from this type of cell division
(f) an animal cell because astral ray formation by centrosome
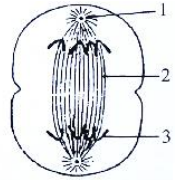
(b) Identify the above stage and give a reason to Support your answer.
(c) Mention where in the body this type of cell division Occur.
(d) Name the stage prior to this stage and draw a diagram to represent the Same stage during mitotic division
Answer:
(a) the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
1 – Centromere
2 – Spindle fibres
3 – Chromatids
(b)
The stage described in the diagram is the late anaphase of mitosis in an animal cell. The stage can be identified by the presence of separated chromatids which are found at the two poles of the cell. The appearance of the furrow in the cell membrane classifies the stage as the late anaphase.
(c)
The division is mitotic division and this kind of cell division occurs in all the cells of the body except for the reproductive cells.
(d) The stage before anaphase is metaphase
5. The given diagram snows a Stage during mitotic Division in an animal cell:
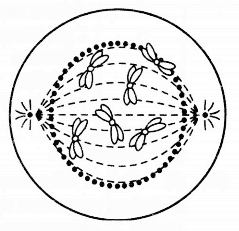
(b) Draws neat labeled diagram of the cell as it would appear in the next stage.
(C) In what two ways is mitotic division in an animal cell different from the mitotic division in a plant cell?
(d) Name the type of cell diV1s1on that occurs during :
(i) Growth of a shoot
(ii) Formation of Pollen grains.
(i) Late prophase. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
(ii)

(iii)
| No | Mitosis in Plant Cell | Mitosis in Animal Cell |
| 1 | Asters are not formed. | Asters are formed. |
| 2 | Occurs at the growing tips. | Occurs throughout the body. |
(iv)
A. Mitosis
B: Meiosis
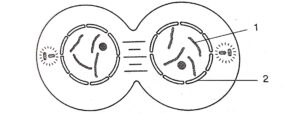 (a) Identity the stage giving suitable reasons.
(a) Identity the stage giving suitable reasons.(b) Name the parts numbered I and 2.
(c) What is the technical term for the division of nucleus?
(d) Mention the stage that comes before the stage shown in the diagram. Draw a neat labelled diagram of the stage mentioned.
(e) Which is the cell division that results in half the number of chromosomes in daughter cells?
(i) Telophase
(ii) 1 – Daughter chromosome, 2 – Nuclear membrane
(iii) Karyokinesis is the technical term for the division of a nucleus.
(iv) Anaphase
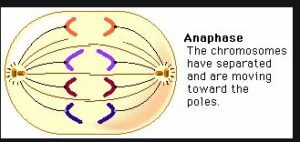
(v) Meiosis
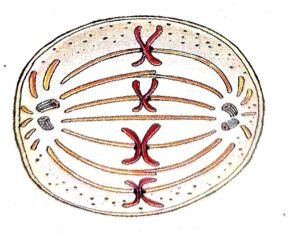
(a) Identify whether it is a plant cell or an animal cell. Give a reason in support of your answer.
(b) Name the stage depicted in the diagram. What is the unique feature observed in this stage?
(c) Name the type of cell division that Occur during:
(i) Replacement of old leaves by new ones.
(ii) Formation of gametes.
(d) What is the stage that comes before the stage Show in the diagram?
(e) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of the stage mentioned in (d) above keeping the chromosome number Constant.
a) Animals cell. Because it lacks cell-wall.
b) Metaphase. Chromosomes lined up in one plane at the equator
c)
i). Mitotic cell division
ii)Meiosis (Reductional) cell division
d) Prophase comes before metaphase
e)


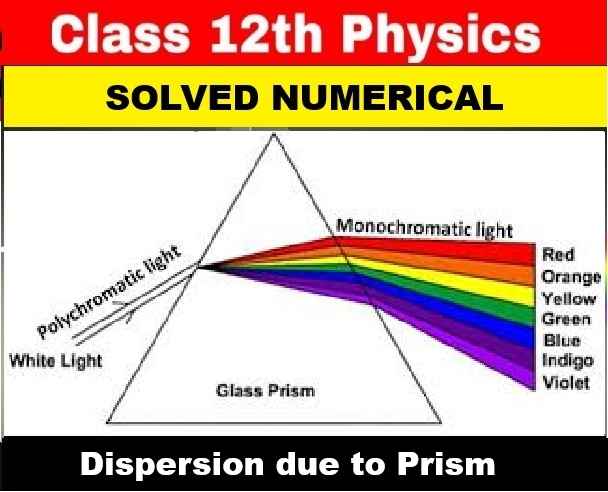
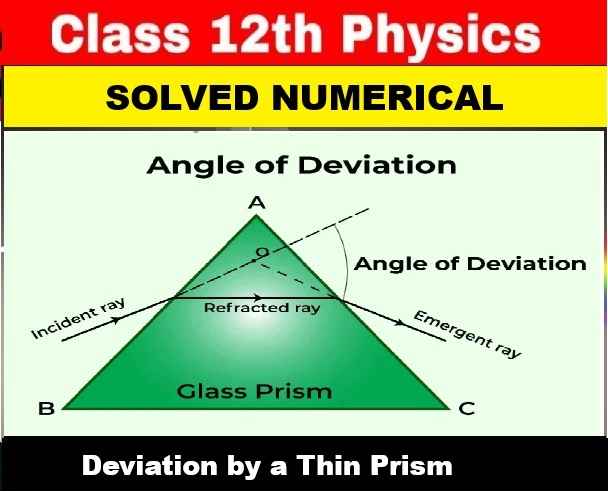
Can I get printout
No , printing allow in pdf format . due to updating time to time pdf format not practical use