Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-19 Solutions. We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-19 Symmetry for ICSE Class-7 RS Aggarwal Mathematics.
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-19 A, Exe-19 B and MCQs Exe-19 C with Mental Maths to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-7 Mathematics.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal brothers Prakshan |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 7th |
| Chapter-19 | Symmetry |
| Writer | RS Aggrawal |
| Book Name | Foundation |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-19 A, Exe-19 B and MCQs Exe-19 C with Mental Maths |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-19 Solutions
-: Select Topic :-
Basics of Symmetry
- Symmetry is a geometrical concept that is found in most cases including nature.
- Any geometric shape can be said to be symmetric or asymmetric
- A shape is said to be symmetric if there exists an imaginary line passing through that divides the shape into halves and that these halves overlap each other completely.
- In other words, fold the shape about the imaginary line to check if the two halves completely overlap each other or not. If they overlap each other completely the shape is symmetric, if not, then it is asymmetric.
- The imaginary line is called as the line of symmetry.
- The symmetry observed in the above example is called as a line or bilateral symmetry.
Reflection Symmetry
- There exists at least one line that divides a figure into two halves such that one-half is the mirror image of the other half.
- Reflection symmetry is a unique case of line symmetry as there exists lateral inversion in the two halves.
- Lateral inversion signifies that left side of one half is the right side of its mirror half.
Point Symmetry
- If a shape has point symmetry, then any point on the shape has a matching point which is exactly at the same distance from the point of symmetry but in the opposite direction
.Lines of symmetry for regular polygons
- Regular polygons are closed shapes that have equal sides and equal angles.
- Such polygons have multiple lines of symmetry.
Rotational Symmetry
- There exists another concept of symmetry that does not involve folding the figure to check if they coincide.
- Rotational symmetry is one where when a figure is rotated about a centre point, the figure looks exactly the same before rotation.
- The particular centre for which rotational symmetry is observed is called the centre of rotation.
- The angle of turning during rotation is called angle of rotation.
- The number of positions in which a figure can be rotated and still appears exactly like it did before the rotation is called order of symmetry.
Rotational symmetry:
A figure is rotated around a center point and it still appears exactly like it did before the rotation
Centre of rotation: Fixed point around which the rotation occurs
Angle of rotation: Angle of turning during rotation
Order of Symmetry: Number of positions in which a figure can be rotated and still appears exactly like it did before the rotation
Exe-19 A,
Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Page 209
Question 1:
Which of the following figures has only one line of symmetry ?
(a) A rectangle
(6) A parallelogram
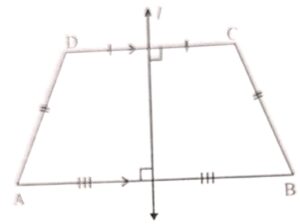
(c) An isosceles trapezium
(d) A circle
Answer :
(c) An isosceles trapezium has only one line of symmetry.
Question 2:
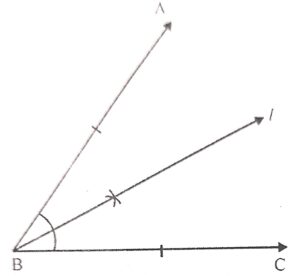
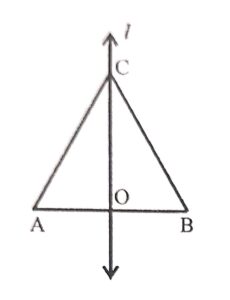
An angle having equal arms possesses how many Tines of symmetry ? Show all possible lines of symmetry in such an angle.
Answer :
An angle equal arms has one line of symmetry as shown in the figure l is the bisector of ABC in which AB = BC.
Question 3:
How many lines of Symmetry does a scalene triangle have ?
Answer :
In a scalene triangle, there is no line symmetry.
Question 4:
A square and a rectangle have :
(a) only one line of symmetry each
(b) two lines of symmetry each
(c) four lines of symmetry each
(d) an unequal number of lines of symmetry.
Answer :
(d) As a square has four lines of symmetry while a rectangle has two lines of symmetry.
Question 5:
A Rhombus has :
(a) one line of symmetry
(b) two lines of symmetry
(c) four lines of symmetry
(d) no line of symmetry
Answer :
(b) A rhombus has two lines of symmetry.
Question 6:
A parallelogram has :
(a) no lıne of symmetry
(b) one line of symmetry
(c) the same number of lines of symmetry as the rhombus
d) four lines of symmetry
Answer :
(a) A parallelogram has no line of symmetry
Question 7:
The capital letter “S” in the English alphabet has :
(a) no line of symmetry
(b) one line of symmetry
(c) two lines of symmetry
(d) infinite number of line of symmetry.
Answer :
The capital letter ‘S has no line of symmetry.
Question 8:
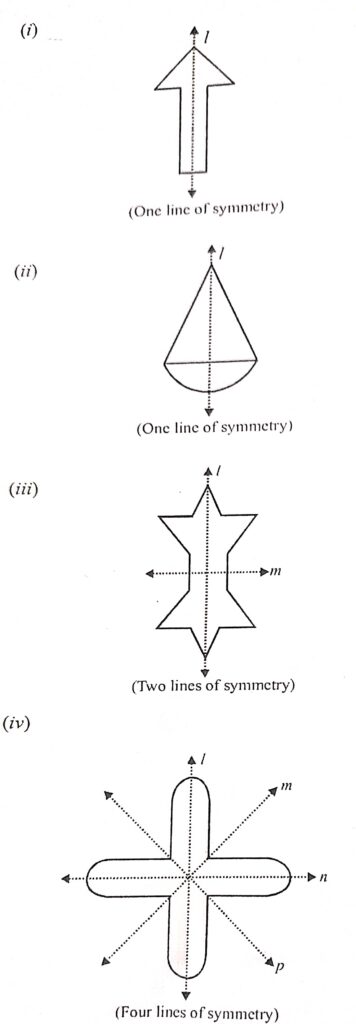
Draw all possible lines of symmetry in each of the following figures and state the number of lines of symmetry in each case:
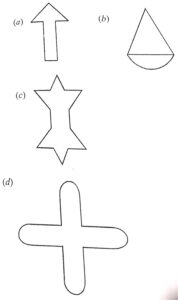
Answer :
The lines of symmetry in each of the given are drawn as given below :
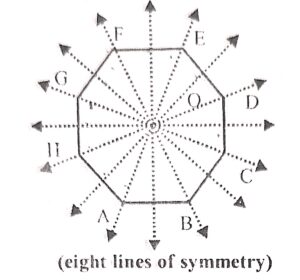
Question 9:
Draw a regular octagon and draw 3 possible lines of symmetry in it.
Answer :
In a regular octagon ABCDEFGH, there can be eight lines of symmetry as shown.
Question 10:
Draw all possible lines of symmetry in :
(a) a regular pentagon
(b) a regular hexagon
Answer :
(a) in a regular pentagon, there are five lines of symmetry.
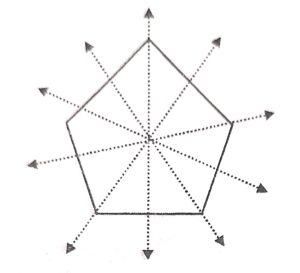
(b) In a regular hexagon, there are six lines of symmetry.
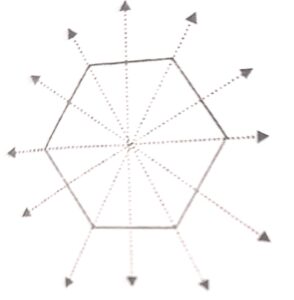
Question 11:
Construct a triangle ABC such that BC = 6.5 cm and ∠B = ∠C = 70°. Draw all possible lines of symmetry.
Answer :
Construction :
(a) Draw a line segment BC = 6.5 cm
(b) At B and C, draw rays making an angle of 70° each meeting each other at A
Then △ABC is the required triangle
(c) Draw the bisector of ZA which intersects BC.
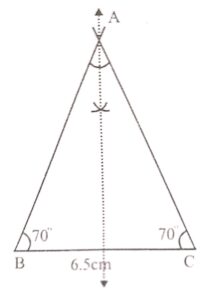
This is the required line of symmetry.
Question 12:
Construct a triangle ABC having BC = 5 cm, ∠B = 90° and ∠C = 45°. Draw all possible lines of symmetry.
Answer :
Construction:
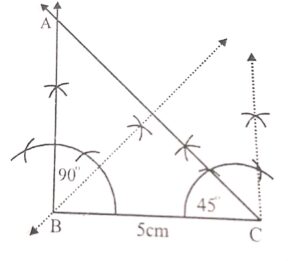
(a) Draw a line segment BC = 5 cm.
(b) At B, draw a ray making an angle of 90° and at C, an angle of 45° meeting each other at A.
Then △ABC is the required triangle whose A will be also 45°
(c) Draw the bisector of ∠B which bisect the side AC.
This is the only line of symmetry.
Question 13:
Construct a triangle PQR having PQ = 6 cm, ∠P= ∠R = 60° and draw all possible lines of symmetry.
Answer :
Construction :
∠P = ∠R = 60°
∠Q = 180° – (∠P+ ∠R)
= 180°- (60° + 60°)
=180° – 120° = 60°
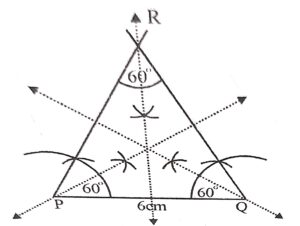
(a) Draw a line segment PQ = 6cm
(b) At P and Q, draw rays making an angle of 60° each meeting each other at R.
Then A PQR is the required triangle which is an equilateral.=
(c) Now draw the angle bisectors of ∠P, ∠Q and ∠R.
These are three lines of symmetry.
Question 14:
Construct a square having each side equal to 4 cm. Draw all possible lines of symmetry.
Answer :
Construction :
(a) Draw a line segment AB = 4cm
(b) At A and B, draw perpendiculars and cut of AD = BC = 4cm
(c) Join CD
Then ABCD is the required square.
(d) Join AC and BD.
(e) Draw perpendicular bisectors of sides AB and BC.
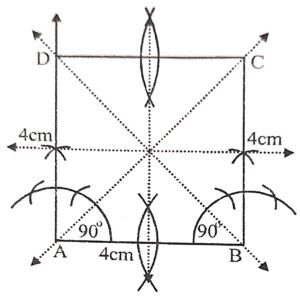
These are four lines of symmetry.
Question 15:
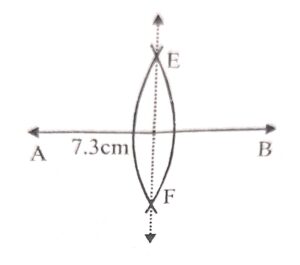
Construct a straight line AB = 7.3 cm. Draw its line of symmetry (using a pair of compasses).
Answer :
Construction:
(a) Draw a line segment AB = 7.3 cm
(b) With centers A and B and radius equal to a bit more than half of AB, draw arcs intersecting each other at E and F.
(c) Join EF and product it to both sides.
This is the line of symmetry.
Question 16:
State which of the following figures possess at least one line of symmetry :
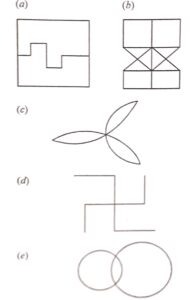
Answer :
Figure (b), (c) and (e) has one line of symmetry as shown in the given figure :
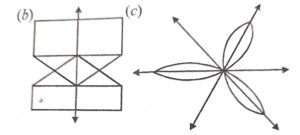
(e)
Exe-19 B,
Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Page 216
Question 1:
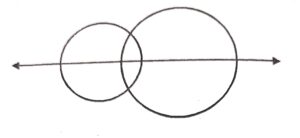
Which of the following geometrical figures has exactly one line of symmetry ?
(a) A rectangle
(b) A semicircle
(c) A regular pentagon
(d) A rhombus
Answer :
(b) A semicircle has one line of symmetry
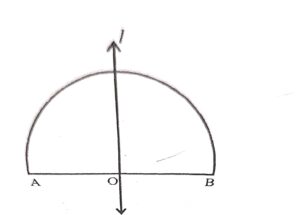
Question 2:
Which of the following geometrical figures has exactly two lines of symmetry ?
(a) A square
(b) A parallelogram
(c) An isosceles trapezium
(d) A rectangle
Answer :
(d) A rectangle has two lines of symmetry
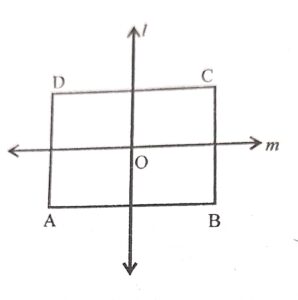
Question 3:
An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry, an isosceles triangle will have :
(a) No line of symmetry
(b) One line of symmetry
(c) Two lines of symmetry
(d) Three lines of symmetry
Answer :
(b) An isosceles triangle will have one line of symmetry.
Question 4:
State the type (S) of symmetry possessed by each of the following figures. Explain each type of symmetry for these figures:
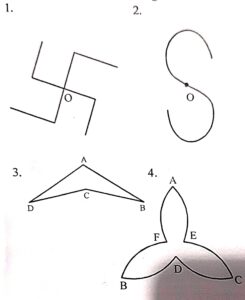
Answer :
1. Linear Symmetry : No
Point Symmetry : Point O is the centre of symmetry.
Rational Symmetry : Rational symmetry of order 4 about the point O.
2. Linear Symmetry : No
Point Symmetry : Point O is the centre of symmetry
Rotational Symmetry : Rotational symmetry of order 2 about the point O.
3. Linear Symmetry : A line of symmetry i.e., the line joining the points A and C.
Point Symmetry : No
Rotational Symmetry : No
4. Linear Symmetry : Three lines of symmetry i.e, the Lines AD, BE and CE
Point Symmetry : No
Rotational Symmetry : Rotational symmetry of order 3 about the point O of intersection of the lines AD, BE and CF
5. Linear Symmetry : A line of symmetry i.e. the line parallel to AB and passing through the point C.
Point Symmetry : No
Rotational Symmetry : No
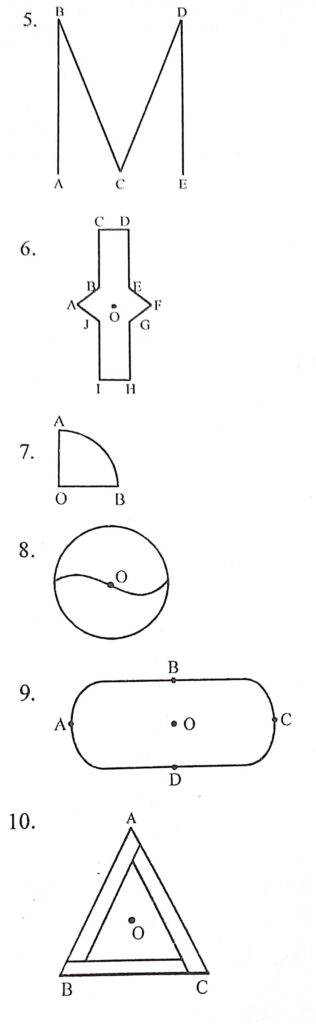
6. Linear Symmetry : Two lines of symmetry () the line joining the points A and F (ii) the line joining the mid-points of CD and IH.
Point Symmetry : The point O is the centre of symmetry.
Rotational Symmetry : Rotational symmetry of order 2 about the point O.
7. Linear Symmetry- A line of symmetry i.c., the bisector of the angle AOB.
Point Symmetry : No
Rotational Symmetry : No
8. Linear Symmetry : No
Point Symmetry : The point O is the centre of symmetry.
Rotational Symmetry-Rotational symmetry of order 2 about the point O.
9. Linear Symmetry : Two lines of symmetry () the line joining the points A and C (ii) the line joining the points B and D.
Point Symmetry : The point O of intersection of the lines AC and BD is the centre of symmetry.
Rotational Symmetry : Rotational symmetry of order 2 about the point O.
10. Linear Symmetry : No.
Point Symmetry : No.
Rotational Symmetry : Rotational symmetry of order 3 about the point O. Ans
MCQs Exe-19 C,
Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Page 216-217
Choose the correct option in each of the following :
Question 1:
A line segment 1s symmetrical about
(a) any line perpendicular to it.
(b) any line passing through its mid-point
(c) any line parallel to it.
(d) its perpendicular bisector.
Answer :
A line segment is symmetrical above to its perpendicular bisector.
Question 2:
A scalene triangle has
(a) no line of symmetry
(b) one line of symmetry
(c) two lines of symmetry
(d) three lines of symmetry
Answer :
A scalene triangle has no line of symmetry.
Question 3:
The lines of symmetry of a rhombus are
(a) perpendicular bisector of each of its sides
(b) its two diagonals
(c) the lines joining the mid points of its opposite sides
(d) its sides
Answer :
The line of symmetry of a rhombus are its two diagonals.
Question 4:
A circle has
(a) no line of symmetry
(b) one line of symmetry
(c) two lines of symmetry
(d) an unlimited number of lines of symmetry
Answer :
A circle has an unlimited number of lines of symmetry
Question 5:
The line of symmetry of a rectangle are
(a) its four sides
(b) its two diagonals
(c) the bisectors of its four interior angles
(d) the lines joining the midpoints of its opposite sides.
Answer :
The line of symmetry of a rectangle are the lines joining he midpoints of its opposite sides.
Question 6:
ABCD is a kite in which AB = AD and CB = CD. The kite is symmetrical about
(a) the diagonal AC
(b) the diagonal BD
(c) both the diagonals AC and BD
(d) the lines joining the mid-points of its opposite sides.
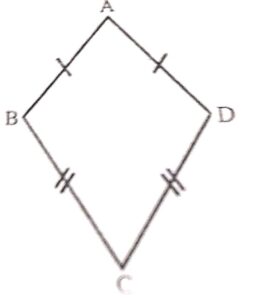
Answer :
In kite ABCD, AB AD and CB CD. It is symmetrical about diagonal AC.
Question 7:
In △ABC, AB = AC and AD ⊥ BC, BE ⊥ CA and CF ⊥ AB. Then, △ABC is symmetrical about
(a) AD
(b) BE
(c) CF
(d) BC
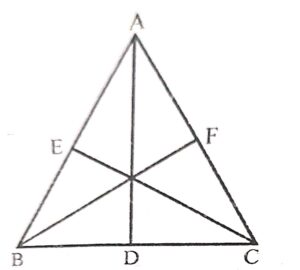
Answer :
In △ABC, AB = AC, AD ⊥ BC, BE ⊥ CA and CF ⊥ AB.
Then △ABC is symmetrical about AD. (AB = AD)
Question 8:
Which amongst the following letters has the highest number of lines of symmetry ?
(a) A
(b) K
(c) X
(d) N
Answer :
Letter X has two lines of symmetry. A, K has one and N has no line of symmetry.
Question 9:
Which of the following letters of thee English alphabet does not possess a point symmetry ?
(a) C
(b) N
(c) S
(d) X
Answer :
C has no point of symmetry.
Question 10:
An equilateral triangle has a rotational symmetry of the order
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer :
An equilateral triangle has three rotational symmetry of the order.
Question 11:
An isosceles triangle possesses
(a) linear symmetry
(b) point symmetry
(c) rotational symmetry
(d) all of these
Answer :
An isosceles triangle has posses a linear symmetry
Question 12:
A regular pentagon does not possess
(a) linear symmetry
(b) point symmetry
(c) rotational symmetry
(d) all of these
Answer :
A regular pentagon does not possess point
Question 13:
A parallelogram does not possess
(a) linear symmetry
(b) point symmetry
(c) rotational symmetry
(d) all of these
Answer :
A parallelogram does not possess a linear symmetry.
Question 14:
An equilateral triangle does not possess
(a) linear symmetry
(b) point symmetry
(c) rotational symmetry
(d) none of these
Answer :
An equilateral triangle does not posses point symmetry.
Question 15:
Which of the following letters off English alphabet has a rotational symmetry ?
(a) C
(b) K
(c) N
(d) T
Answer :
N has a rotational symmetry
Mental Maths
Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Page 218
Question 1:
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A circle has .. .. lines of symmetry.
(ii) The letter S does not possess ,………….. symmetry.
(iii) A semi-circle is symmetrical about the ………….. of its diameter.
(iv) The letter H has .. …..line(s) of symmetry.
(v) A quadrilateral having 4 lines of symmetry as well as rotational symmetry of order 4 is ……….
Answer :
(i) A circle has infinite lines of symmetry.
(ii) The letter S does not possess linear symmetry.
(iii) A semi-circle is symmetrical about the perpendicular bisector of its diameter.
(iv) The letter H has two line(s) of symmetry.
(v) A quadrilateral having 4 lines of symmetry as well as rotational symmetry of order 4 is square.
Question 2:
Write true (T) or false (F):
(i) A Kite possesses a linear symmetry but no rotational symmetry.
(ii) The order of rotational symmetry of a regular hexagon is 6
(iii) A parallelogram does not have any line of symmetry.
(iv) A square has a point symmetry but rhombus does not.
(v) The letter N does not possess a rotational symmetry.
Answer :
(i) A Kite possesses a linear symmetry but no rotational symmetry. True
(ii) The order of rotational symmetry of a regular hexagon is 6 True
(iii) A parallelogram does not have any line of symmetry. True
(iv) A square has a point symmetry but rhombus does not. False
(v) The letter N does not possess a rotational symmetry. False
(Letter N possess a rotational symmetry about the point marked).
–: End of Symmetry RS Aggarwal Class-7 Solutions :–
Return to- RS Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-7 Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Thanks