Tissues Goyal Brother Solutions ICSE Class-9 Biology Ch-3. We Provide Solutions of Exercise-3 The Tissues Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Ch-3. The solution contain All Type exercise question such as name the following, odd one, MCQs and figure based. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
ICSE Class-9 Biology Ch-3 The Tissues Goyal Brother Prakashan Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal Brother Prakashan |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 9th |
| Writer | Dr. S.K. Aggarwal |
| Chapter-3 | The Tissues |
| Topics | Solutions of Exercises-3 |
| Edition | for 2022-2023 Academic Session |
Ch-3 The Tissues Goyal Brother Prakashan ICSE Class-9 Biology Solutions
(Page-37-38)
Questions 1. Name the following :
(i) Thick-walled isodiametric dead cells—Sclerenchyma
(ii) Two simple tissues which provide mechanical support to plants-collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
(iii) Different types of permanent tissues in plants.–parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
(iv) Growing regions which cause increase in girth of the plant body–Lateral meristem‘
(v) Growing regions which produce growth in length–Apical meristems
(vi) Components of xylem.—xylem tracheids, xylem vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
(vii) Components of phloem —Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibers.
(viii) Different types of animal tissues—epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissues.
(ix) Different types of connective tissue–dense regular connective tissue, cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood, and hematopoietic tissue
(x) Components of blood—plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Questions 2. Mention the regions of the plant body where following tissues are found:
(i) Parenchyma— Leaves, fruits, and flowers
(ii) Collenchyma–primary growth in stems and leaves.
(iii) Phloem—Primary phloem originates from the procambial regions in meristems, while secondary phloem originates from the vascular cambium
(iv) Protective tissues—usually in contact with the environment.
(v) Areolar tissue—deep under the epidermis
Questions 3. Define the following:
(i) Meristematic tissue–The meristematic tissue is usually found in the apices of the root systems and the shoots and is in a continuous state of division.
(ii) Aerenchyma— modified parenchymatous tissue having large intracellular air spaces that is found especially in aquatic plants where it facilitates gaseous exchange and maintains buoyancy.
(iii) Chlorenchyma—A type of parenchymatous tissue that contains chlorophyll is known as chlorenchyma. It assists plants in performing their photosynthetic function. It can be found below the epidermis on the leaf stalks.
(iv) Vascular tissues—Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. They typically occur together in vascular bundles in all plant organs, traversing roots, stems, and leaves. Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the plant.
Questions 4. Give examples of the type of epithelium which respectively:
(i) bear cilia—Ciliated Epithelium
(ii) protect the body from mechanical injury–Squamous Epithelium
(iii) help in absorption–Columnar Epithelium
(iv) occur where there is wear and tear–squamous epithelium
Questions 5. Which kind of muscle is involved in the following processes?
(i) Movement of the arm—Voluntary muscle is striated muscle
(ii) Contraction of blood vessels–smooth muscle
(iii) Movement of food along the alimentary canal–Peristalsis Is the Contraction of Muscle Tissue That Helps Move and Break Down Foodstuffs
Questions 6. Give differences between the following:
(i) Simple and Complex tissues
| Simple tissue | Complex tissue |
|---|---|
| 1. Simple tissues are made up of single type of cells. | Complex tissues are made up of different type of cells. |
| 2. Simple tissue consists of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclernchyma. | Complex tissue consists of xylem and phloem. |
| 3. It occurs in all parts of plant. | It occurs only in vascular region. |
(ii) Parenchyma and Sclerenchyma
| Parenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
|---|---|
| Cells are usually loosely packed with large intercellular spaces. | There are no intercellular spaces between the cells. |
| Stores nutrients and water in stems and roots | Provides strength to the parts of the plant. |
(iii) Blood and Lymph–Lymph consists of only white blood cells, proteins, salts, glucose, fats, and water whereas blood consists of RBC’s, WBC’s and platelets and other substances such as glucose, amino acids etc.
(v) Bone and Cartilage–Bones are the hard, inelastic and a tough organ that forms part of the vertebral skeleton. Cartilage is a soft, elastic and flexible connective tissue that protects the bone from rubbing against each other
(vi) Striated and Unstriated muscles–Striated muscles are the cylindrical, non-branched, multinucleated muscles with alternative light and dark bands while non-striated muscles are long, non-branched, uninucleated muscles without alternative light and dark bands
Questions 7. How is it advantageous for an organism to be made of different kinds of cells instead of only one kind?
Answer : It is advantageous for an organism to be made of different kind of cells instead of one because different kinds of cells can do different jobs at a single time. Eg. – red blood works as a transportation medium. On the other hand white blood cells do different work at the same time.
Questions 8. Mention five important characteristics and functions of
(i) meristematic tissues
- Cells are small and usually cubical.
- Cell walls are thin and Nuclei are large.
- Vacuoles are almost absent.
- Cells tightly packed with almost intercellular spaces.
- The new cell produced is transformed into mature permanent tissues.
Its main function is to begin growth of new cells in young seedlings at the tips of roots and shoots
(ii) permanent tissues.
- Cells of these tissues have no power of division.
- Cells are well developed and properly shaped.
- Cell wall is comparatively thick.
- Nucleus of the cells are bigger and cytoplasm is dense.
- Usually there are vacuoles in the cell.
- There may have intercellular spaces in between cells
The permanent tissue in plants mainly helps in providing support, protection as well as in photosynthesis and conduction of water, minerals, and nutrients. Permanent tissue cells may be living or dead
Questions 9. Mention the characteristic features of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma
Answer :
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
|---|---|---|
| Comprises a thin cell wall and made up of cellulose. | It comprises an uneven cell wall and is made up of pectin and hemicellulose. | It comprises a hard and thick cell wall and is made up of lignin. |
Questions 10. Which components of xylem tissue are living and which ones are dead?
Answer : Tracheids, vessel elements and xylem fibers are dead cells of the xylem. The only living cells of xylem are parenchyma cells. Either tracheids or vessel elements are found in one xylem tissue. Living component of xylem is Xylem parenchyma
Questions 11. Which components of phloem tissue are living and which ones are dead?
Answer : Sieve tubes have peripheral cytoplasm and large vacuole but lack a nucleus. Phloem companion cells are parenchymatous and these have a nucleus. These are also the living cells of phloem. Phloem fibers are dead
Questions 12. Write in brief, about (i) Epidermis, (ii) Cork.
Answer :
(i) Epidermis : epidermis is the outermost layer of skin on your body. It protects your body from harm, keeps your body hydrated, produces new skin cells and contains melanin, which determines the color of your skin
(ii) Cork–Cork is the outer protective layer of bark of a tree. The cork cells are dead and compactly packed with no intercellular space. Their cell walls are coated with a waxy substance, suberin, which do not allow water and gases to pass through
Questions 13. Mention the characteristic features and functions of:
(i) Epithelial tissue—Epithelial tissues are widespread throughout the body. They form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
(ii) Connective tissue–Major functions of connective tissue include: 1) binding and supporting, 2) protecting, 3) insulating, 4) storing reserve fuel, and 5) transporting substances within the body. Connective tissues can have various levels of vascularity. Cartilage is avascular, while dense connective tissue is poorly vascularized.
(iii)Muscular tissue— Muscle tissue is characterized by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they can shorten and generate a pulling force. When attached between two movable objects, such as two bones, contraction of the muscles cause the bones to move
(iv) Nervous tissue—Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities. It stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning
Questions 14. Describe the functions of:
(i) Lymph—Lymph is a colourless fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system. The main role of the lymphatic system is to act as a filter against microbes, organic wastes, toxins and other debris. It carries lymphocytes throughout the body that fight against infections.
(ii) Cardiac muscle tissue–Cardiac muscle tissue forms the muscle surrounding the heart. With the function of the muscle being to cause the mechanical motion of pumping blood throughout the rest of the body, unlike skeletal muscles, the movement is involuntary as to sustain life
(iii) Ligament–A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
(iv) Tendon–A tendon is a cord of strong, flexible tissue, similar to a rope. Tendons connect your muscles to your bones. Tendons let us move our limbs. They also help prevent muscle injury by absorbing some of the impact your muscles take when you run, jump or do other movements.
(v) Cartilage–Cartilage has many functions, including the ability to resist compressive forces, enhance bone resilience, and provide support on bony areas where there is a need for flexibility. The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte, which resides within the lacunae
Questions 15. How does cardiac muscle differ from both voluntary muscle and smooth muscle in its structure and its function?
Answer : Both cardiac and smooth muscle are involuntary while skeletal muscle is voluntary. … Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is not under conscious control. Cardiac muscle is also an involuntary muscle but is more akin in structure to skeletal muscle, and is found only in the heart
Questions 16. If you are provided with three slides, each containing one type of muscle fibre, how will you identify them?
Answer :
SMOOTH MUSCLES : These muscle fibers are smooth in nature because they do not have any striations. They do not contain any dark and light bands occurring repeatedly.
SKELETAL MUSCLE :These muscles have stripes in it. Unlike smooth muscles, in this skeletal muscle there occurs alternating dark and light bands occurring repeatedly.
CARDIAC MUSCLE :These muscle fibers are branched. Cardiac muscle fiber has a very distinct characteristics from the two other muscle fibers that is they have intercalated disc present in them.
So, by observing all these character on the slides through microscope, we can distinguish which slide contains what type of muscle fibers
Questions 17. Draw and describe the structure of a neuron.
Answer : 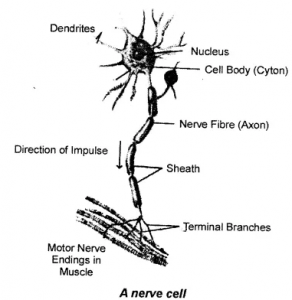
Questions 18. Observe the given figure and answer the following:
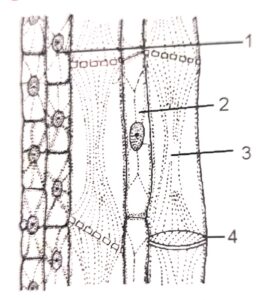
(i) What does the figure show?
(ii) Label the parts numbered 1-4.
(iii) Give the function of part 3.
Answer :
(i) phloem tissue
(ii) 1.plasmodesma, 2. companian, 3. cell sieve tube 4.sieve plate
(iii) conduct food
Questions 19. Observe the figure given below and answer the following:
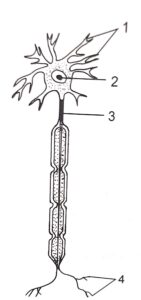
(i) Name the cell shown in the figure
(ii) Label the parts numbered 1-4.
(iii) Give the function of the structure seen in the figure.
Answer :
(i) neuron
(ii) 1. dendrite,2nucleus,3 axon,. 4.nerve ending
(iii) carry impulse
–: End of The Tissue Goyal Brother Solutions ICSE Class-9 Biology :–
Return to:- ICSE Biology for Class 9 Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions
thanks


