Acid base and Salt Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Class-10 Solutions. Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Acid base and Salt by Dr Viraf and J Dalal for Class 10. Step by step Solutions of Acid base and Salt by Dr Viraf and J Dalal of Concept of Simplified Dalal ICSE Chemistry.
Acid base and Salt Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Class-10
Get Other Chapter Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Class-10 Solutions
How to Acid base and Salt Dalal Simplified Concept ICSE Chemistry Class-10
Note:– Before viewing Solutions of Acid base and Salt Dalal Simplified by Dr Viraf and J Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions . Read the Acid base and Salt Carefully to understand the concept in better way .After reading the Acid base and Salt solve all example of your text book with ICSE Specimen Sample Paper for Class-10 Exam of Council. Previous Year Solved Question Paper for ICSE Board
Additional Questions Acid base and Salt Dalal Simplified
Question 1.
Define the following as per ionic theory with examples and ionic equations wherever relevant
(1) acid
(2) base
(3) alkali
(4) neutralization
Answer:
(1) Acid — An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water yields – hydronium ions (H3O+ ) as the only positively charged ion.
![]()
(2) Base — A base is a compound which reacts with hydronium ions of an acid – to give salt and water
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
(3) Alkali — An alkali is a compound which when dissolved in water yields Hydroxyl ions (OH–) as they are negatively charged ions.
![]()
Alkali is a base soluble in water.
(4) Neutralization — | H+| ions of an acid completely or combine with |OH+| ions of a base to give salt and water only.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Question 2.
Differentiate between:
- Organic and inorganic acids
- Hydracids and oxyacids with examples.
Answer:
(1)
Organic acids – Those acids which are derived from plants, e.g., citric acid, acetic acid, tartaric acid Inorganic acids – Acids derived from minerals e.g. HCl2,h2SO4
(2)
Hydracids – Acids containing hydrogen and a non-metallic element other than oxygen, e.g. HCl, HBr, HI.
Oxyacids – Acids containing hydrogen, another element and oxygen, e.g. HNO3, H,SO4.
Question 3.
State on what basis does the strength of an acid and an alkali depend on.
Answer:
Strength of acids depends upon concentration of hydronium ion |H3O+| present in an aqueous solution
of an acid. Strength of alkali depends on the concentration of the hydroxyl ions |OH–| present in an aqueous solution of an alkali.
Question 4.
Differentiate between (1) strong and weak acid (2) strong and weak alkali with suitable examples and ionic equations.
Answer:
(1) Strong Acid – Is an acid which dissociates – almost completely in aqueous solution there by producing a – high concentration of hydrogen [H+] ions [or H3O+ions]
Examples: Hydrochloric, Sulphuric and Nitric acid.
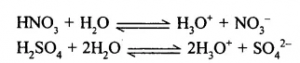
Weak Acid – Is an acid which dissociates – only partially in a aqueous solution thereby producing a – low concentration of hydrogen [H+] ions [or H3O+ ions].
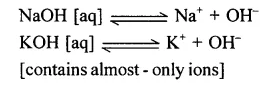
Examples: Lithium, Sodium and Potassium hydroxide
Weak alkali – Is an alkali which dissociates – only partially in aqueous solution thereby producing a – low concentration of hydroxyl [OH– ] ions.
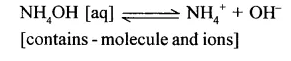
Examples: Ammonium hydroxide and Calcium hydroxide.
Question 5.
Name the ions formed when – HCl ; HNO3 ; H2SO4 ; CH3COOH ; NaOH and NH4OH ionise in aq. soln.
Answer:
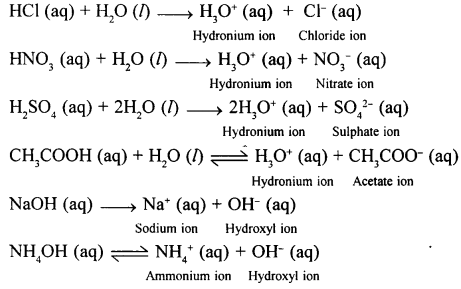
Question 6.
State giving reasons which is a stronger acid – dil. HCl or cone. H2CO3.
Answer:
Dil. HCl is a stronger acid than cone. H2CO3
Reason: HCl ionises almost completely in aqueous solution thereby producing a high concentration of Hp ions in aqueous solution. On the other hand, H2CO3 ionises to a very small extent producing a low
concentration of HO+ ions. More the concentration of H3O+ ions in solution, stronger is the acid. Hence dil. HCl is a stronger acid than cone. H2CO3.
Question 7.
State why the basicity of acetic acid is one and acidity of calcium hydroxide is two.
Answer:
Basicity of an acid is the number of hydrogen ions which can be produced from one molecule of the acids on complete dissociation. Acetic acid, CH.COOH gives one H+ per molecule the acid, hence acetic acid is monobasic i.e., its basicity is one.
![]()
Acidity of a base is the number of hydroxyl ions which can be produced from one molecule of the base on complete dissocation. Ca(OH)2 (calcium hydroxide) gives two hydroxyl ions per molecule of the base, hence calcium hydroxide is diacidic i.e., its acidity is two.
Question 8.
Give three reasons with equations wherever required, why sulphuric acid is a dibasic acid.
Answer:
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is a dibasic acid as explained below:
(1)
It ionises in aqueous solution to produce two hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid.
OR
It contains two replace all hydrogen ions per molecule of the acid.

Question 9.
State how acids are defined as per Arrhenius’s and Lowry – Bronsted’s theory.
Answer:
Arrhenius Theory –
Acids are substances which – dissociate in aqueous solution to give H+ ions.
Strong acids dissociate – almost completely, while weak acids dissociate partially.
Question 10.
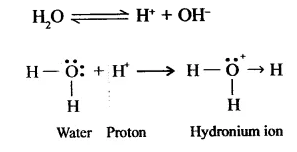
Oxygen atom in water has two Hone pair of electrons’. Explain the meaning of the term in italics. With the help of an electron dot diagram show the formation of hydronium ion and ammonium ion from a water molecule and an ammonia molecule respectively.
Answer:
A pair of electrons not shared with any other atom for bond formation is called a lone pair of electrons. In water, the central atom – oxygen has two lone pair of electrons as shown ahead:
Structure of water molecule
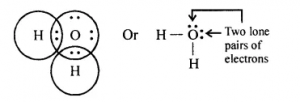
Formation of hydronium ion- (H3O+): When an acid is dissolved in water the proton (H+) released by the acid add onto the lone pair electrons of the oxygen atom of a water molecule. The proton (H+) accepts the lone pair of electrons forming a coordinate bond (shown by an arrow).
HCl → H+ + Cl–
Water Proton Hydronium ion
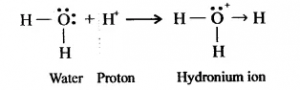
Formation of ammonium ion (NH4+): When ammonia gas is dissolved in water, the proton released by water adds onto the lone pair of electrons of the nitrogen atom of the ammonia molecule. The proton (H+) accepts the lone pair of electrons forming a coordinate bond (shown by an arrow).
Question 11.
State how you would obtain:
- Sulphuric acid from an acidic oxide
- KOH from a basic oxide.
Answer:
(1)
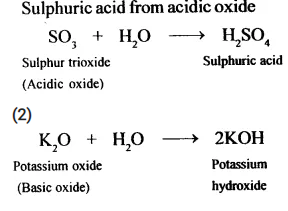
Question 12.
State two chemical properties each with equations of a solution containing
(1) H+ ions
(2) OH
Answer:
(1) Properties of a solution containing H+ ions: Acids when dissolved in water produce H2O+ or H ions. Typical chemical properties of aqueous solution of acids are:
(a) Neutralisation: H+ ions react with OH ions from alkalies to give water
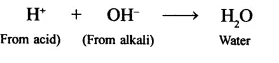
(b) Reaction with active metals: Active metals like Al, Zn, Fe, etc., react with dil. acids (HCl, H2SO4) to give hydrogen gas. In this reaction H+ is reduced to H, by the active metal. For example,
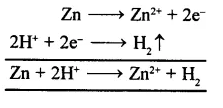
(2) Properties of solution containing OH– ions: Alkalies when dissolved in water produce OH” ions. Typical reaction of aqueous solution of alkalies are;
(a) Neutralisation: OH+ ions react with H+ ions from acids to give water.
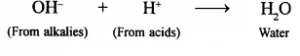
(b) Reaction with solutions of metallic salts: Hydroxides of metals other than Group 1 and 2 are generally insoluble in water. Such hydroxides are precipitated from their respective salt solutions by OH” ions. For example,
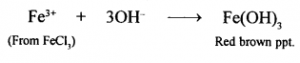
Question 13.
Give equations for the decomposition of a metallic
(1) chloride
(2) nitrate with cone. H2SO4.
Answer:
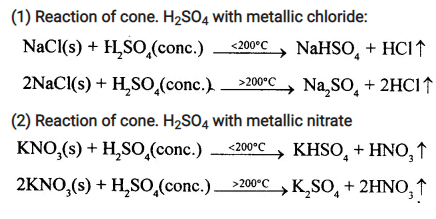
(1) Reaction of cone. H2SO4 with metallic chloride:
(2) Reaction of cone. H2SO4 with metallic nitrate
Question 14.
State in the above reactions a reason for the formation of the respective acids from cone. H2SO4.
Answer:
The reason for the formation of the respective acids from cone. H2SO4 is the volatility of the acid formed. At room temperature or above HCl is a gas while HNO3, which is a liquid at room temperature, volatileses at the reaction temperature (w 200°C).
Question 15.
Convert
(1) NaHCO3
(2) Na2CO3 to unstable carbonic acid by action with dil. H2SO4.
State the reason why ammonia is evolved when an ammonium salt and alkali are heated.
Answer:
- 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) → Na2SO4 + 2H2CO3
- Na2CO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) → Na2SO4 + H2CO3
Ammonia is evolved when an ammonium salt and alkali are heated.
![]()
This is because a non-volatile base, Ca(OH)2 displace a volatile base, NH4OH which decomposes to given NH3 and H2O.
Question 16.
Define pH value. What would you say about the pH of a solution in which (i) H+ ions = OH– ions
- evolves CO2when heated with Na2CO3
- OH” ions > H+ ions.
Answer:
pH value: The pH value of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm (to the bsise 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration expressed in mol L-1. Thus,
PH = -log10 [H+]
Where [H+] stands for hydrogen ion concentration in mol L-1.
- A solution in which [H+] = [OH–], is neutral with pH = 7.
- A solution which evolves CO2 with NaCO3 is acidic in nature with pH < 7.
- A solution in which [OH–] > [H+] is basic in nature with pH >7.
Question 17.
State whether litmus is a common acid-base indictor or a universal indicator.
Answer:
Litmus is a common acid-base indicator. It is not a universal indicator.
Question 18.
State the colour change in a neutral litmus in presence of
(1) acidic
(2) alkaline medium.
Answer:
Neutral litmus is purple in colour
- In acidic medium colour of neutral litmus changes from purple to red.
- In alkaline medium colour of neutral litmus changes from purple to blue.
Question 19.
State the colour change in a universal indicator e.g. pH paper on
- slightly acidic soil
- slightly alkaline soil
- dairy milk
- human blood tested for medical diagnosis.
Answer:
- In slightly acidic soil colour of universal indicator changes to yellow.
- In slightly alkaline soil colour of universal indicator changes to blue.
- In dairy milk colour of universal indicator change to green.
- In human blood colour of universal indicator changes to green (pH = 7.3).
Question 20.
Define
(1) salt
(2) normal salt
(3) acid salt – with relevant examples and equations.
Answer:
(1) Salts: A salt is a compound formed by partial or complete replacement of the replaceable hydrogen ions of an acid by a metallic ion or ammonium ion.
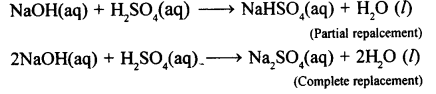
(2) Normal salt: The salt formed by complete replacement of the replaceable hydrogen ions present in a molecule of the acid by metallic or ammonium ion. For example,
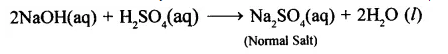
2NaOH(aq) + H2CO3(aq)→ Na2CO3(aq) + 2H2O (l)
NH4OH(aq) + HCl(aq)→ NH4Cl(aq) + H.O (l)
(3) Acid salt: The salt formed by partial replacement of the replaceable hydrogen ions present in a molecule of the acid by metallic or ammonium ion. For example,
NaOH(aq) + H3PO4(aq) → NaH2PO4(aq) + H2O(l)
2NaOH(aq) + H3PO4(aq)→Na2HPO4(aq) + 2H2O (l)
KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq)→ KHS04(aq) + H2O(l)
NH4OH(aq) + H2CO3(aq)→NH4HCO3(aq) + H.O (l)
Question 21.
State:
- the formation
- the components of – a basic salt.
State which of following salts is an – acid, normal or basic salt.
- bleaching powder
- potassium mercuric iodide
- sodium sulphite
- sodium hydrogen sulphite
- sodium silver cyanide
- basic lead nitrate
- potassium zincate
- alum
- calcium bicarbonate
- basic copper chloride
- trisodium phosphate.
Answer:
(1) Formation of a basic salt: A basic salt is formed by partial replacement of hydroxyl group of a diacidic or triacidic base with an acid radical (or an anion other than OH).
(2) Components of a basic salt: A basic salt contains a cation (other than H+ ion), a hydroxyl ion (OH– from base) and an anion (other than OH– ion). For example,
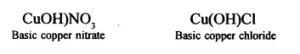
- Bleaching powder, CaOCl, (Normal salt/Mixed salt)
- Potassium mercuric iodide, K2(HgI4) .
(Normal salt/Complex salt) - Sodium sulphate, Na2SO4 (Normal salt)
- Sodium hydrogen sulphite, NaHSO3 (Acid salt)
- Sodium silver cyanide, Na[Ag(CN)2]
(Normal salt/Complex salt) - Basic lead nitrate, Pb(OH)NO3 (Basic salt)
- Potassium zincate, K2ZnO2 (Normal salt)
- Alum or potash alum, K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O
(Normal salt/Double salt) - Calcium bicarbonate, Ca(HCO3)2 (Acid salt)
- Basic copper chloride, Cu(OH)Cl (Basic salt)
- Trisodium phosphate, Na3PO4 (Normal salt)
Question 22.
Name three (1) sulphates (2) chlorides insoluble in water and – two (1) oxides (2) carbonates soluble in water.
Answer:
(1) Three sulphates insoluble in water
Lead sulphate (PbSO4), Calcium sulphate (CaSO4), and Barium sulphate (BaSO4).
(2) Three chloride insoluble in water
Silver chloride (AgCl), Lead chloride (PbCl2), and Mercury chloride (Hg2Cl2 or HgCl).
(1) Two oxides soluble in water
Sodium oxide (Na2O ), and Potassium oxide (K2O)
(2) Two carbonates soluble in water
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), and Ammonium carbonate [(Na4)2CO3]
Question 23.
State the method only, generally used for the preparation of the following salts
(1) Zn(NO3)2
(2) NH4Cl
(3) ZnSO4
(4) ZnS
(5) CaCO3
(6) FeCl3
(7) PbCl2
(8) Pb(NO3)2–
Answer:
| Salt | Method of preparation |
| 1. Zn(NO3)2 | Neutralisation of insoluble base by acid/Decomposition of insoluble carbonate by acid |
| 2. NH4Cl | Neutralisation (titration) of soluble base by acid/Decomposition of soluble carbonate by acid |
| 3. ZnSO4 | Neutralisation of insoluble base by acid/Decomposition of insoluble carbonate by acid |
| 4. ZnS | Direct combination (Synthesis)/Double decomposition (Precipitation) |
| 5. CaCO3 | Double decomposition (Precipitation) |
| 6. Fecl3 | Direct combination (Synthesis)/ |
| 7. pbCl2 | Double decomposition (Precipitation) |
| 8. Pb(NO3)2 | Neutralisation of insoluble base by acid/Decompostion of insoluble carbonate by acids |
Question 24.
Give balanced equations for the preparation of the following salts –
(a)
(1) CuSO4
(2) NaHSO4
(3) Na2SO4
(4) FeSO4
(5) BaSO4
(6) PbSO4 – using dil. H2SO4
(b)
(1) NaHSO4
(2) CuSO4 – using cone. H2SO4.
Answer:
(a) Using dil. H2SO4
- CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → CuSO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l)
- NaOH (aq) + H2SO4 (aq) → NaHSO4 (aq) + H2O(l)
- 2NaOH (aq) + H2SO4 (aq)→Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O(l)
- Fe (s) + H2SO4 (aq)→ FeSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
- BaCl2 (aq) + H2SO4 (aq)→ BaSO4 (s) + 2HCl (aq)
- Pb(NO3)2 + H2SO4 (aq)→ PbSO4 (s) + 2HNO3 (aq)
(b) Using cone. H2SO4

Question 25.
Starting from insoluble ZnO how would you obtain insoluble ZnCO3 by precipitation.
Answer:
ZnO (s) + 2HCl (aq)→ ZnCl2 (aq) + H2O(l)
ZnCl2 (aq) + Na2CO3 (aq)→ ZnCO3 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
Dissolve zinc oxide in minimum quantity of dil. HCl. Add to it a saturated solution ofNa2CO3 in water till
no more precipitation takes place. Filter and dry the ZnCO3 so obtained.
Question 26.
Give balanced equations for the action of a dilute acid on
(1) zinc carbonate,
(2) potassium bicarbonate for the preparation of the respective salt.
Answer:
- Zinc carbonate
ZnCO3 + 2HNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + H2O + CO
- Potassium bicarbonate
2KHCO3 + H2SO4 → K2S04 + 2H2O + 2CO2
Question 27.
Give balanced equations for the decomposition of
(1) calcium bicarbonate by dil. HCl,
(2) calcium carbonate by dil. HNO3,
(3) sodium sulphite by dil. H2SO4,
(4) zinc sulphide by dil. H2SO4.
Answer:
- Ca(HCO3)2 + 2HCl→ CaCl2 + 2H2O+ 2CO2
- CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO.)2 + H2O+ CO2
- Na2SO3 + H2SO4 (dil.) → Na2SO4 + H2O+ SO2
- ZnS + H2SO4 →ZnSO4 + H2S
Question 28.
State what will be the effect of each of the following solution on blue litmus –
(1) K2CO3 soln
(2) KCl soln.
(3) NH4NO3
Answer:
- K2CO3 is a salt of a strong base (KOH) and weak acid (H2CO3). Hence its aqueous solution will be basic in nature. It will have no effect on blue litmus solution.
- KCl is a salt of a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (KOH). Hence its aqueous solution will be neutral in nature. It will have no effect on blue litmus solution.
- NH4NO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and weak base (NH4OH). Hence its aqueous solution will be acidic in nature. It will turn blue litmus solution red.
Question 29.
Select the correct acid, base or salt from the list in bracket for each of the statements given below:
- An example of an acid derived from a mineral is……….. (citric acid / nitric acid / acetic acid)
Ans. Nitric acid
- An example of a base which is not a alkali is….. (caustic soda / zinc hydroxide / liquor ammonia / caustic potash)
Ans. Zinc hydroxide
- An example of a strong acid is dilute……… (acetic acid / sulphuric acid / tartaric acid / carbonic acid)
Ans. Sulphuric acid
- An example of a weak alkali is…. (potassium hydroxide / calcium hydroxide / sodium hydroxide) solution.
Ans. Calcium Hydroxide
- An acid having basicity 1 is……… (carbonic acid / acetic acid / sulphurous acid)
Ans. Acetic acid
- An acid obtained by dissolving sulphur trioxide in water is…. (sulphurous acid / sulphuric acid oleum)
Ans. Sulphuric acid
- A volatile acid obtained when nitre reacts with nonvolatile concentrated sulphuric acid on heating is (hydrochloric acid / sulphuric acid/ nitric acid)
Ans. Nitric acid
- A base obtained when lead nitrate undergoes thermal decomposition is……. (trilead tetroxide / lead (IV) oxide/ lead (II) oxide. .
Ans. Lead (II) oxide
- An acid obtained when concentrated nitric acid is heated with sulphur is…….. (sulphurous acid / sulphuric acid / nitrous acid)
Ans. Sulphuric acid
- The more volatile acid obtained when the less volatile acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate is……… (sulphuric acid / carbonic acid / nitric acid)
Ans. Carbonic acid
- The insoluble base obtained when sodium hydroxide reacts with iron (III) chloride is…. (iron (II) hydroxide / iron (III) hydroxide / iron (II) oxide)
Ans. Iron (III) hydroxide.
- A solution whose pH is above 7 is….. (vinegar / milk / liquor ammonia.
Ans. Liquor Ammonia
- The salt formed when sulphuric acid reacts with excess caustic soda solution is…… (sodium bisulphite / sodium sulphate / sodium sulphite / sodium bisulphate).
Ans. Sodium sulphate
- An example of an acid salt is……. [CH3COONa/NaNO3/ Na2HPO4/NaKCO3]
Ans. Na2HPO4
- An example of a soluble salt is ……… (AgCl / PbSO4 /CaSO4 / CaCl2)
Ans. CaCl2
- An example of an insoluble salt is….. (Na2CO3 \ K2CCl,/ MgCO3 / (NH4)2 CO3)
Ans. MgCO3
- A salt prepared by neutralization in which titration is involved is…….. (MgCl2 / CaCl2 / NH,Cl / CuCl2)
Ans. NH4Cl - An insoluble salt prepared by direct combination or synthesis is……. [FeCl3 / FeSO4 / FeS/Fe(NO3)2] Ans. FeS
- A salt prepared by precipitation i.e. by double decomposition of two salt solutions is………… (Na2SO4 /PbSO4 / ZnSO4 / CuSO4)
Ans. PbSO. - A salt prepared by simple displacement i.e. action of dilute acid on a metal is____ (PbCl2/ CuCL, / AlCl3 / HgCl)
Ans. AlCl3 - Decomposition of calcium hydrogen carbonate with…. [dil. HNO3 /dil. HCl/dil. H2SO4] results in formation of calcium chloride.
Ans. dil.HCl
- Action of dilute acid on a metallic sulphide results in evolution of____ [SO2/H2S/CO2] gas.
Ans. H2S
- A salt which on hydrolysis produces a neutral solution is……. (sodium chloride / ammonium chloride / sodium carbonate)
Ans. Sodium chloride
Part-B Analytical Chemistry
Question 1.
Salts of…………… (normal / transition) elements are generally coloured. From the ions K,+, Cr3+, Fe2+, Ca2+ So32-, Mno41-, No31- the ions generally coloured are
Answer:
Normal; Cr3+, Fe2+, Mno41
Question 2.
The hydroxide which is soluble in excess of NaOH is [Zn(OH)2 / Fe(OH)3 / Fe(OH)2]
Answer:
Zn(OH)2
Question 3.
The salt which will not react with NH4OH solution [ZnCl2/CuCl2/NH4 Cl/FeCl2]
Answer:
NH4Cl
Question 4.
The substance/s which react/s with hot cone. NaOH soln. and undergoes a neutralization reaction…………….. [Al203/Al/Al(OH)3]
Answer:
Al203
Question 5.
To distinguish soluble salts of zinc and lead, ……………….[NaOH/NH4OH] can be used.
Answer:
NaOH
Question 6.
Oxides and hydroxide of certain metals i.e………… (iron/ zinc/copper/aluminium/magnesium/Iead] are amphoteric and react with……………[acids/alkali/acids and alkalis].
Answer:
zinc, aluminium and lead; acids and alkalis
Complete the following equations:
- MgCl2 + NH4OH→ ……… +………..
- Zn + NaOH → ……… +…….
- ZnO + NaOH → ……… +…………
- Al(OH)3 + KOH → …….. +………..
- Zn(OH)2 + NaOH (excess) → ………. + ………..
- Pb(No3)2 + NH4OH → …… + ………..
- Al2 O3 + KOH → ……. +…………
- FeCl3 + NaOH → ………+ ……….
Answer:

–Try Also :–


Please try to give solution of GOYAL BROTHERS PRAKSHAN
uploaded soon