Air and Atmosphere MCQs Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5, Air and Atmosphere Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-5. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -5 Match the following, Complete statements, Name the following, Give word of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6.
Air and Atmosphere MCQs Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 6th |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Book Name | Dalal New Simplified |
| Chapter-5 | Air and Atmosphere |
| Unit-1 | Air and Atmosphere |
| Topic | Solution of exercise MCQs |
| Session | 2023-24 |
Objective Types Questions
Air and Atmosphere MCQs Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5
Question: 1. Match the statements in List I with the correct answers in List II.
| List – I | List – II |
| 1. An impurity in air | A: Water vapour |
| 2. The component of air which supports combustion | B: Respiration |
| 3. The inert component in air, slightly soluble in water | C: Rare gases |
| 4. The component of air which minimizes the rate of evaporation | D: Sulphur dioxide |
| 5. The process which involves oxidation of food substance in living organisms | E: Helium |
| 6. The component of air which finds application in observation balloons | F: Carbon dioxide |
| 7. The process which involves oxidation of substance, liberating heat and light energy | G: Combustion |
| 8. The component of air which is heavier than air and fairly soluble in water | H: Nitrogen |
| 9. The process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants resulting in formation of carbohydrates | I: Photosynthesis |
| 10. The component of air, which is lighter than air and less than 1% in air | J: Oxygen |
Answer:
| List – I | List – II |
| 1. An impurity in air | A: Sulphur dioxide |
| 2. The component of air which supports combustion | B: Oxygen |
| 3. The inert component in air, slightly soluble in water | C: Nitrogen |
| 4. The component of air which minimizes the rate of evaporation | D: Water vapour |
| 5. The process which involves oxidation of food substance in living organisms | E: Respiration |
| 6. The component of air which finds application in observation balloons | F: Helium |
| 7. The process which involves oxidation of substance, liberating heat and light energy | G: Combustion |
| 8. The component of air which is heavier than air and fairly soluble in water | H: Carbon dioxide |
| 9. The process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants resulting in formation of carbohydrates | I: Photosynthesis |
| 10. The component of air, which is lighter than air and less than 1% in air | J: Rare gases |
Question: 2. The diagrams below represents an experiment to show the presence of a – component of air:
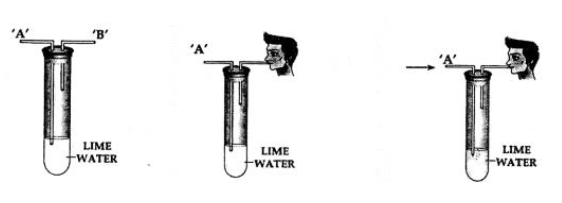
Question: 1. State why air is sucked from – outlet ‘B’ and not from outlet ‘A’.
Answer: Because if we suck from ‘A’, lime water will be sucked out.
Question: 2. State why the air is sucked ‘slowly’ from – the outlet ‘B’.
Answer: Because if air is sucked fast, lime water will also be sucked out.
Question: 3. State the observation seen after completion of the experiment.
Answer: Lime water turns milky.
Question: 4. State the reason for the above observation seen.
Answer: The reason is the formation of CO2.
Question: 5. Name another component which if present in air as pollutant – would have given a similar observation.
Answer: Sulphur dioxide.
Question: 3. Complete the statements given below by filling in the blanks with the correct word/s from the word/s in bracket:
1. The …stratosphere… [atmosphere/troposphere/stratosphere] is a layer which extends upto about 10-50 kms. above the earth.
2. …hydrogen sulphide… [helium/hydrogen sulphide] is and example of a pollutant present in air.
3. The component of air used in photosynthesis is …carbon dioxide… and the product of photosynthesis is …oxygen… [oxygen/carbon dioxide/nitrogen].
4. The product formed which is common to both combustion and respiration is …nitrogen dioxide… [oxygen/carbon dioxide/nitrogen dioxide].
5. The component of air which is variable in air above sea level & in air in general …water vapour… [oxygen/nitrogen/water vapour].
Question: 4. Name the following:
Question: 1. The product formed when phosphorus burns in oxygen.
Answer: Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5).
Question: 2. The layer of atmosphere which contains the ozone layer.
Answer: Stratosphere
Question: 3. The active component of air which supports combustion and is used up in burning.
Answer: Oxygen
Question: 4. The main, rare [inert] gas present in air.
Answer: Argon
Question: 5. The component of air which is present more in industrial areas.
Answer: Carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide, dust particles.
Question: 6. The type of bacteria which directly absorb nitrogen from the air and converted to soluble nitrates in the soil.
Answer: Symbiotic bacteria.
Question: 7. The product of respiration released in exhaled air, other than carbon dioxide.
Answer: Water vapour and energy.
Question: 8. An inert gas which has a low boiling point and is used for producing very low temperatures.
Answer: Helium
Question: 9. A process which removes carbon dioxide from the air.
Answer: Photosynthesis
Question: 10. The component of air which does not support combustion.
Answer: Nitrogen
Question: 5. State whether the following statements are ‘True’ or ‘False’. If false write the correct statement:
| Statements | True/False |
| 1. The mesosphere in the atmosphere, contains most of the air, fit for respiration. | F |
| 2. The percentage of carbon dioxide in the air is – between 0.2 to 0.4%. | T |
| 3. Carbon dioxide, water vapour and energy in the form of heat are evolved during respiration. | T |
| 4. Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight & chlorophyll. | T |
| 5. Air is a mixture and not a compound since the components of air – cannot be separated by physical methods. | F |
Question: 6. Give word equations for the following conversions:
Question: 1. Nitrogen of the air to nitric oxide.
Answer: Nitrogen + Oxygen ⇌ Nitric oxide
The nitric oxide reacts with oxygen to give nitrogen dioxide.
Question: 2. Nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide.
Answer: Nitric oxide + Oxygen → Nitrogen dioxide
The nitrogen dioxide further reacts with oxygen and water vapour of the air to give nitric acid.
Question: 3. Nitrogen dioxide to nitric acid.
Answer: Nitric oxide + Oxygen → Nitrogen dioxide
The nitrogen dioxide further reacts with oxygen and water vapour of the air to give nitric acid.
Question: 4. Nitric acid to soluble nitrates in the soil.
Answer: Calcium carbonate + Nitric acid → Calcium nitrate + water + carbon dioxide
The water soluble calcium nitrates are absorbed by the plants and converted to plant proteins.
Question: 5. Carbon dioxide in air to carbohydrates in plants.
Answer:

Carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll is changed into carbohydrates and oxygen is released out.
—: End of Air and Atmosphere MCQs Class-6 Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry Solutions Chapter-5 :—
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-6 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.