Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4E Descriptive Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Selina Publishers Solutions Chapter-4. Step By Step ICSE Selina Concise Solutions of Chapter-4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding with All Exercise including MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type, Numerical and Structured/Application Questions Solved . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4E Descriptive Answer Chemistry Class-9 ICSE Concise Selina Publishers
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publication |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-4 | Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding |
| Book Name | Concise |
| Topics | Solution of Exercise – 4E Descriptive Answer Type |
| Academic Session | 2023-2024 |
Exercise – 4E Descriptive Answer Type
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-81
Question 1.
Covalent bonds can be single, double or triple covalent bonds.
(a) How many electrons are shared in each?
(b) Give an example of each type.
Answer:
A single covalent bond is formed by sharing of one pair of electrons between atoms, each atom contributing one electron.
A double bond is formed by sharing of two pairs of electrons between two atoms.
A triple bond is formed by sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms.
Exercise – 4E Descriptive Answer Type
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Class-9 Chemistry Concise Solutions
Page-82
Question 2.
Taking MgCl2 as an electrovalent compound, CCl4 as a covalent compound, give four difference between electrovalent and covalent compounds.
Answer:
| MgCl2 – Electrovalent compound | CCl4 – Covalent compound |
| They are hard crystalline solids consisting of ions. | These are gases or liquids or soft solids. |
| They have high melting and boiling points. | They have low melting and boiling points. |
| They conduct electricity in the fused or aqueous state. | They do not conduct electricity in the solid, molten or aqueous state. |
| These are soluble in inorganic solvents but insoluble in organic solvents. | These are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents. |
Question 3.
Give orbital diagram of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Methane
(d) Hydrogen chloride
Answer:
Orbital Diagram:
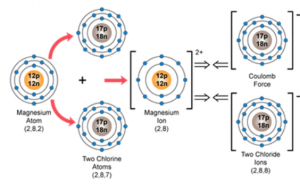
(a) orbital diagram of the Magnesium chloride
(b) orbital diagram of the Nitrogen

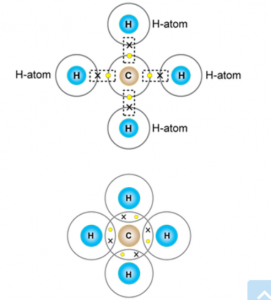
(c) orbital diagram of the Methane
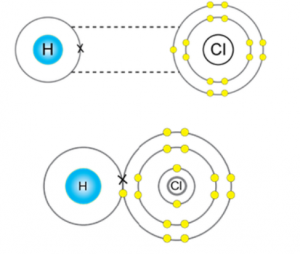
(d) orbital diagram of the Hydrogen chloride
Question 4.
Metal M forms a chloride with the formula MCl2. What type of bond is in MCl2? Write the formula of the compound when M combines with sulphur, oxygen and nitrogen.
Answer:
The bond formed between metal (M) and non-metal (chlorine) is ionic bond.
As M bonds with two chlorine atoms having electronic configuration [2,8,7], so we can say that M donates two electrons to two chlorine atoms to complete their octet and therefore, it has a valency of 2.
When metal (M) having +2 valency combines with sulphur [2,8,6] having -2 valency, M donates its two valence electrons to sulphur and formula of compound formed is MgS
When metal(M) having +2 valency combines with oxygen [2,6] having -2 valency, M donates its two valence electrons to oxygen and formula of compound formed is MgO
When metal (M) atoms having +2 valency combines with nitrogen [2,5] having -3 valency then an ionic bond is formed by the transfer of 6 electrons from 3 metal (M) atoms to 2 nitrogen atoms, hence the formula of the compound is Mg3N2.
Question 5.
Explain the following :
(a) Mass of an atom is concentrated inside the nucleus of the atom.
(b) Atoms combine by transfer and sharing of electron(s).
(c) An element has atoms with different mass number.
(d) Carbon-12 and carbon-14 both show similar chemical properties
Answer:
(a) Atom is made of primarily three sub-atomic particles namely electrons, protons and neutrons. An electron has negligible mass, and protons and neutron lie inside the nucleus, hence, mass of an atom is majorly present in the nucleus.
(b) Elements tend to combine with one another to attain the stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas. This is achieved either by gaining electrons or losing electrons or sharing of electrons with other atoms of the same element or another element to form a chemical compound.
(c) Isotopes are the elements having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
For example : 2412Mg and 2612Mg
Isotopes differ in the number of neutrons.
(d) Chemical properties are determined by the electronic configuration of an atom and electronic configuration of both isotopes of carbon is same, i.e., electronic configuration of C-12 is [2,4] and electronic configuration of C-14 is [2,4], hence they both have same chemical properties.
Question 6.
With the help of a diagram, state the number of bonds and the type of bonds in:
(a) ethene molecule
(b) ethyne molecule
Answer:
(a) Ethene molecule [C2H4] — It has one double covalent bond between the 2 Carbon atoms and four single covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms.

(b) Ethyne molecule [C2H2] — It has one triple covalent bond between the 2 Carbon atoms and 2 single covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms.
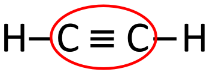
— : End of Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exe-4E Descriptive Answer Class-9 ICSE Chemistry Solutions :–
Return to Return to Concise Selina ICSE Chemistry Class-9
Thanks
Please share with your friends