ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-16.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths APC Understanding Solutions. Solutions of Exe-16.1. This post is the Solutions of ML Aggarwal Chapter 16 – Mensuration for ICSE Maths Class-9. APC Understanding ML Aggarwal Solutions (APC) Avichal Publication Solutions of Chapter-16 Mensuration for ICSE Board Class-9. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-16.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Avichal Publishig Company (APC) |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-16 | Mensuration |
| Writer | ML Aggarwal |
| Book Name | Understanding |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-16.1 Questions |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Exe-16.1 Solutions of ML Aggarwal for ICSE Class-9 Ch-16, Mensuration
Note:- Before viewing Solutions of Chapter -16 Mensuration Class-9 of ML Aggarwal Solutions . Read the Chapter Carefully. Then solve all example given in Exercise-16.1, Exe-16.2, Exe-16.3, Exe-16.4, MCQs, Chapter Test.
Mensuration Exercise-16.1
ML Aggarwal Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page 353
Question 1. Find the area of a triangle whose base is 6 cm and corresponding height is 4 cm.
Answer :
Base of triangle = 6 cm
Height of triangle = 4 cm
We know that, Area of triangle = ½ × base × height
Substituting the values
= ½ × 6 × 4
By further calculation
= 6 × 2
= 12 cm2
Question 2. Find the area of a triangle whose sides are
(i) 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm
(ii) 29 cm, 20 cm and 21 cm
(iii) 12 cm, 9.6 cm and 7.2 cm
Answer :
(i) Consider a = 3 cm, b = 4 cm and c = 5 cm
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
= (3 + 4 + 5)/ 2
= 12/2
= 6 cm
Here,
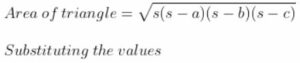
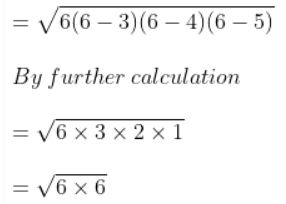
= 6 cm2
(ii) Consider a = 29 cm, b = 20 cm and c = 21 cm
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
= (29 + 20 + 21)/ 2
= 70/2
= 35 cm
Here,
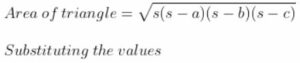

So we get
= 7 × 5 × 3 × 2
= 210 cm2
(iii) Consider a = 12 cm, b = 9.6 cm and c = 7.2 cm
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
= (12 + 9.6 + 7.2)/ 2
= 28.8/2
= 14.4 cm
Here
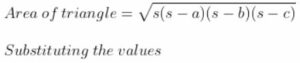

So we get
= 2.4 × 2.4 × 6
= 34.56 cm2
Question 3. Find the area of a triangle whose sides are 34 cm, 20 cm and 42 cm. Hence, find the length of the altitude corresponding to the shortest side.
Answer :
Consider 34 cm, 20 cm and 42 cm as the sides of triangle
a = 34 cm, b = 20 cm and c = 42 cm
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
= (34 + 20 + 42)/ 2
= 96/2
= 48 cm
Here,
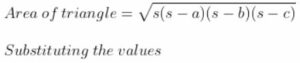
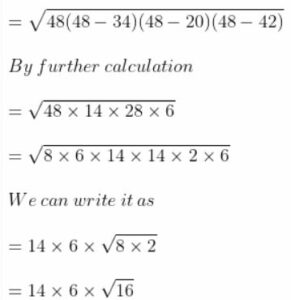
So ,
= 14 × 6 × 4
= 336 cm2
Here the shortest side of the triangle is 20 cm
Consider h cm as the corresponding altitude
Area of triangle = ½ × base × height
336 = ½ × 20 × h
By calculation
h = (336 × 2)/ 20
So ,
h = 336/10
h = 33.6 cm
Hence,
the required altitude of the triangle is 33.6 cm.
Question 4. The sides of a triangular field are 975m, 1050 m and 1125 m. If this field is sold at the rate of Rs. 1000 per hectare, find its selling price. [1 hectare = 10000 m²].
Answer :
Given that,
a = 975 m, b = 1050 m and c = 1125 m
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
= (975 + 1050 + 1125)/ 2
= 3150/2
= 1575 cm
Here,
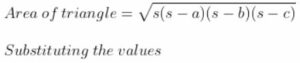

= 525 × 450 × 2
It is given that, 1 hectare = 10000 m2
= (525 × 900)/ 10000
By calculation
= (525 × 9)/ 100
= 4725/100
= 47.25 hectares
We know that, Selling price of 1 hectare field = Rs 1000
Selling price of 47.25 hectare field = 1000 × 47.25 = Rs 47250
Question 5. The base of a right angled triangle is 12 cm and its hypotenuse is 13 cm long. Find its area and the perimeter.
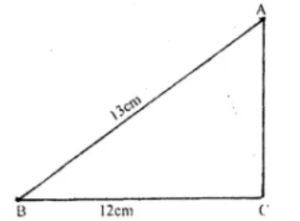
Answer :
Given that,
ABC is a right angled triangle
BC = 12 cm and AB = 13 cm
Use the Pythagoras theorem
AB2 = AC2 + BC2
132 = AC2 + 122
By calculation
AC2 = 132 – 122
So ,
AC2 = 169 – 144 = 25
AC = √25 = 5 cm
We know that, Area of triangle ABC = ½ × base × height
= ½ × 12 × 5
= 30 cm2
Similarly
Perimeter of triangle ABC = AB + BC + CA
= 13 + 12 + 5
= 30 cm
Question 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle whose side is 8 m. Given your answer correct to two decimal places.
Answer :
Given that,
Side of equilateral triangle = 8 m
We know that, Area of equilateral triangle = √3/4 (side)2
= √3/4 × 8 × 8
By calculation
= √3 × 2 × 8
= 1.73 × 16
= 27.71 m2
Question 7. If the area of an equilateral triangle is 81√3 cm² find its. perimeter.
Answer :
We know that, Area of equilateral triangle = √3/4 (side)2
81 √3 = √3/4 (side)2
By calculation
Side2 = (81 √3 × 4)/ √3
So,
(side)2 = 81 × 4
side = √(81 × 4)
side = 9 × 2 = 18 cm
So the perimeter of equilateral triangle = 3 × side
= 3 × 18
= 54 cm
(ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-16.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths )
Question 8. If the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 36 cm, calculate its area and height.
Answer :
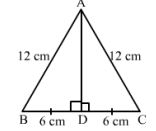
We know that, The perimeter of an equilateral triangle = 3 × side
36 = 3 × side
By calculation
side = 36/3 = 12 cm
So AB = BC = CA = 12 cm
Here,
Area of equilateral triangle = √3/4 (side)2
= √3/4 (12)2
By calculation
= √3/4 × 12 × 12
So ,
= √3 × 3 × 12
= 1.73 × 36
= 62.4 cm2
In triangle ABD
Using Pythagoras Theorem
AB2 = AD2 + BD2
Here BD = 12/2 = 6 cm
122 = AD2 + 62
By calculation
144 =AD2 + 36
AD2 = 144 – 36 = 108
So we get
AD = √108 = 10.4
Hence, the required height is 10.4 cm.
Question 9.
(i) If the length of the sides of a triangle are in the ratio 3:4:5 and its perimeter is 48 cm, find its area.
(ii) The sides of a triangular plot are in the ratio 3: 5:7 and its perimeter is 300 m. Find its area
Answer :
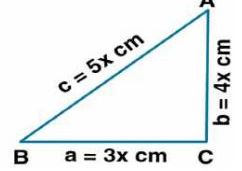
(i) Consider ABC as the triangle
Ratio of the sides are 3x, 4x and 5x
Take a = 3x cm, b = 4x cm and c = 5x cm
a + b + c = 48
3x + 4x + 5x = 48
12x = 48
So ,
x = 48/12 = 4
Here,
a = 3x = 3 × 4 = 12 cm
b = 4x = 4 × 4 = 16 cm
c = 5x = 5 × 4 = 20 cm
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
= (12 + 16 + 20)/ 2
= 48/2
= 24 cm
Here,
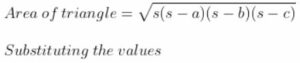
![]()

= 12 × 4 × 2
= 96 cm2
(ii) It is given that
Sides of a triangle are in the ratio = 3: 5: 7
Perimeter = 300 m
We know that, First side = (300 × 3)/ sum of ration
Substituting the values
= (300 × 3)/ (3 + 5 + 7)
By calculation
= (300 × 3)/ 15
= 60 m
Second side = (300 × 5)/ 15 = 100 m
Third side = (300 × 7)/ 15 = 140 m
Here,
S = perimeter/2 = 300/2 = 150 m
So ,
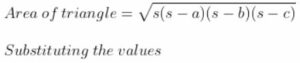

= 1500 × 1.732
= 2598 m2
Question 10. ABC is a triangle in which AB = AC = 4 cm and ∠ A = 90°. Calculate the area of ∆ABC. Also find the length of perpendicular from A to BC.
Answer :
AB = AC = 4 cm
Using the Pythagoras theorem
BC2 = AB2 + AC2
BC2 = 42 + 42
By calculation
BC2 = 16 + 16 = 32
BC = √32 = 4√2 cm
We know that, Area of △ABC = ½ × BC × h
Substituting the values
8 = ½ × 4√2 × h
By calculation
h = (8 × 2)/ 4√2
We can write,
h = (2 × 2)/ √2 × √2/√2
So ,
h = 4√2/2 = 2 × √2
h = 2 × 1.41 = 2.82 cm
Question 11. Find the area of an isosceles triangle whose equal sides are 12 cm each and the perimeter is 30 cm.
Answer :
The isosceles triangles is
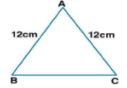
Here AB = AC = 12cm
Perimeter = 30 cm
So, BC = 30 – (12 + 12) = 30 – 24 = 6 cm
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/ 2
Substituting the values
= 30/ 2
= 15 cm
Here,
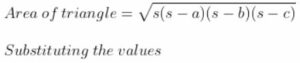
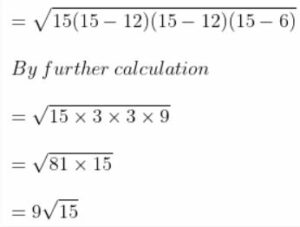
We can write
= 9 × 3.873
= 34.857
= 34.86 cm2
Question 12. Find the area of an isosceles triangle whose base is 6 cm and perimeter is 16 cm.
Answer :
in an isosceles triangle,
any two sides are equal
let each of the equal side be x
perimeter=16cm
base=6cm
therefore,
x+x+6=16
2x=16-6
2x=10
x = 10/2
x=5
area of triangle =½×base×height
since we need the height,
we draw a perpendicular from the base which will divide this triangle into two right angled triangles
with each base = to 6/2=3cm
hypotenuse is the side of isosceles triangle which is 5cm
let the height be x
Using Pythagoras theorem,
we have,
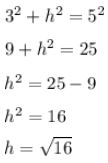
h=4
height is 4cm
area of triangle= ½×base×height
= ½ 6 x 4
= 12 cm²
is the area
(ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-16.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths )
Question 13. The sides of a right angled triangle containing the right angle are 5x cm and (3x – 1) cm. Calculate the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle if its area is 60 cm².
Answer :
Consider ABC as a right angled triangle
AB = 5x cm and BC = (3x – 1) cm
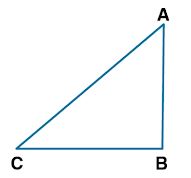
We know that, Area of △ABC = ½ × AB × BC
60 = ½ × 5x (3x – 1)
By calculation
120 = 5x (3x – 1)
⇒ 120 = 15x2 – 5x
It can be written ,
15x2 – 5x – 120 = 0
Taking out the common terms
5 (3x2 – x – 24) = 0
⇒ 3x2 – x – 24 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 9x + 8x – 24 = 0
Taking out the common terms
3x (x – 3) + 8 (x – 3) = 0
⇒ (3x + 8) (x – 3) = 0
Here,
3x + 8 = 0 or x – 3 = 0
We can write ,
3x = -8 or x = 3
⇒ x = -8/3 or x = 3
x = -8/3 is not possible
So x = 3
AB = 5 × 3 = 15 cm
BC = (3 × 3 – 1) = 9 – 1 = 8 cm
In right angled △ABC
Using Pythagoras theorem
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
AC2 = 152 + 82
By calculation
AC2 = 225 + 64 = 289
⇒ AC2 = 172
So, AC = 17 cm
Hence, the hypotenuse of the right angled triangle is 17 cm.
Question 14. In ∆ ABC, ∠B = 90°, AB = (2A + 1) cm and BC = (A + 1). cm. If the area of the ∆ ABC is 60 cm², find its perimeter.
Answer :
It is given that
AB = (2x + 1) cm
BC = (x + 1) cm
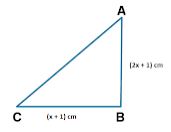
We know that, Area of △ABC = ½ × AB × BC
60 = ½ ×(2x + 1) (x + 1)
By cross multiplication
60 ×2 = (2x + 1) (x + 1)
By calculation
120 = 2x2 + 3x + 1
We can write ,
0 = 2x2 + 3x + 1 – 120
⇒ 0 = 2x2 + 3x – 119
So ,
2x2 + 3x – 119 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 17x – 14x – 119 = 0
Taking out the common terms
x (2x + 17) – 7 (2x + 17) = 0
⇒ (x – 7) (2x + 17) = 0
Here,
x – 7 = 0 or 2x + 17 = 0
⇒ x = 7 or 2x = – 17
⇒ x = 7 or x = -17/2
AB = (2x + 1) = 2 × 7 + 1
⇒ AB = 14 + 1 = 15 cm
⇒ BC = (x + 1) = 7 + 1 = 8 cm
In right angled △ABC
Using Pythagoras Theorem
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
AC2 = 152 + 82
⇒ AC2 = 225 + 64
⇒ AC2 = 289
So ,
AC = 17 cm
So the perimeter = AB + BC + AC
= 15 + 8 + 17
= 40 cm
(ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-16.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths )
Question 15. If the perimeter of a right angled triangle is 60 cm and its hypotenuse is 25 cm, find its area.
Answer :
We know that, Perimeter of a right angled triangle = 60 cm
Hypotenuse = 25 cm
Here, the sum of two sides = 60 – 25 = 35 cm
Consider base = x cm
Altitude = (35 – x) cm
Using the Pythagoras theorem
x2 + (35 – x)2 = 252
By calculation
x2 + 1225 + x2 – 70x = 625
⇒ 2x2 – 70x + 1225 – 625 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 70x + 600 = 0
Dividing by 2
x2 – 35x + 300 = 0
⇒ x2 – 15x – 20x + 300 = 0
Taking out the common terms
x (x – 15) – 20 (x – 15) = 0
⇒ (x – 15) (x – 20) = 0
Here,
x – 15 = 0
So,
x = 15
x – 20 = 0
So ,
x = 20 cm
So, 15 cm and 20 cm are the sides of the triangle
Area = ½ × base × altitude
= ½ × 15 × 20
= 150 cm2
Question 16. The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 40 cm. The base is two third of the sum of equal sides. Find the length of each side.
Answer :
Perimeter of an isosceles triangle = 40 cm
Consider x cm as each equal side
We know that, Base = 2/3 (2x) = 4/3 x
So according to the sum
2x + 4/3 x = 40
By further calculation
6x + 4x = 120
⇒ 10x = 120
By division
x = 120/10 = 12
Hence, the length of each equal side is 12 cm.
Question 17. If the area of an isosceles triangle is 60 cm2 and the length of each of its equal sides is 13 cm, find its base.
Answer :
Area of isosceles triangle = 60 cm2
Length of each equal side = 13 cm
Consider base BC = x cm
Construct AD perpendicular to BC which bisects BC at D
So BD = DC = x/2 cm
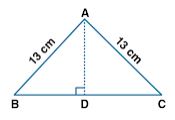
In right △ABD
AB2 = BD2 + AD2
132 = (x/2)2 + AD2
By calculation
169 = x2/4 + AD2
⇒ AD2 = 169 – x2/4 …(1)
We know that, Area = 60 cm2
AD = (area × 2)/base
AD = (60 × 2)/ x = 120/x …(2)
Using both the equations
169 – x2/4 = (120/x)2
By calculation
(676 – x2)/4 = 14400/x2
By cross multiplication
676x2 – x4 = 57600
We can write,
x4 – 676x2 + 57600 = 0
⇒ x4 – 576x2 – 100x2 + 57600 = 0
Taking out the common terms
x2 (x2 – 576) – 100 (x2 – 576) = 0
⇒ (x2 – 576) (x2 – 100) = 0
Here,
x2 – 576 = 0 where x2 = 576
So, x = 24
x2 – 100 = 0 where x2 = 100
So, x = 10
Therefore, the base is 10 cm or 24 cm.
Question 18. The base of a triangular field is 3 times its height If the cost of cultivating the field at the rate of ₹25 per 100m2 is ₹60000, find its base and height.
Answer :
Cost of cultivating the field at the rate of Rs 25 per 100 m2 = Rs 60000
Here the cost of cultivating the field of Rs 25 for 100 m2
So,
the cost of cultivating the field of Rs 1 = 100/25 m2
Cost of cultivating the field of Rs 60000 = 100/25 ×60000
= 4 ×60000
= 240000 m2
So,
the area of field = 240000 m2
½ × base × height = 240000 …(1)
Height of triangular field = h m2
Base of triangular field = 3h m2
Substituting the values in equation (1)
½ × 3h × h = 240000
By calculation
½ × 3h2 = 240000
⇒ h2 = (240000 × 2)/3
⇒ h2 = 80000 ×2
⇒ h2 = 160000
So ,
h = √160000 = 400
Here, the height of triangular field = 400 m
Base of triangular field = 3 ×400 = 1200 m2
Mensuration Exercise-16.1
ML Aggarwal Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions
Page 354
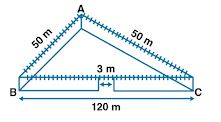
Question 19. A triangular park ABC? has sides 120 m, 80 m and 50 m (as shown in the given figure). A gardner Dhania has to put a fence around it and also plant grass inside. How much area does she need to plant? Find the cost of fencing it with barbed wire at the rate of ₹20 per metre leaving a space 3 m wide for a gate on one side.\
Answer :
ABC is a triangular park with sides 120 m, 80 m and 50 m.
Here the perimeter of triangle ABC = 120 + 80 + 50 = 250 m

Portion at which a gate is build = 3m
Remaining perimeter = 250 – 3 = 247 m
So the length of fence around it = 247 m
Rate of fencing = Rs 20 per m
Total cost of fencing = 20 × 247 = Rs 4940
We know that, S = Semi perimeter = (a + b + c)/2
= 250/2
= 125 cm
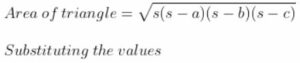

So,
= 375√15m²
Question 20. An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colours (shown in the given figure), each piece measuring 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm. How much cloth of each colour is required for the umbrella?
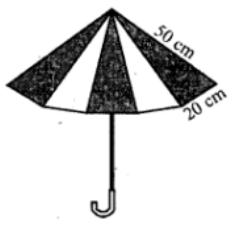
Answer:
An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colors
20 cm, 50 cm, 50 cm are the measurement of each triangle
So we get
s/2 = (20 + 50 + 50)/ 2
s/2 = 120/2 = 60
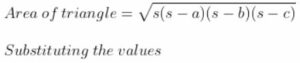
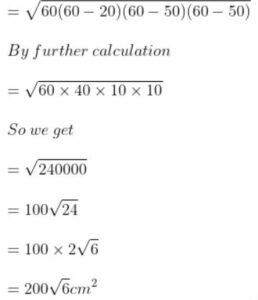
Question 21.
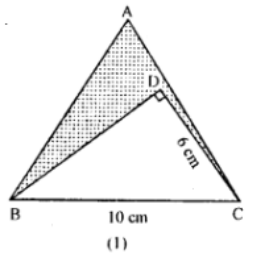
(a) In the figure (1) given below, ABC is an equilateral triangle with each side of length 10 cm. In ∆ BCD, ∠D = 90° and CD = 6 cm.
Find the area of the shaded region. Give your answer correct to one decimal place.
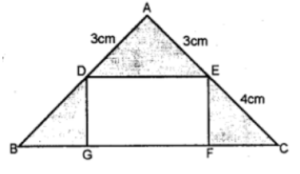
(b) In the figure(ii) given, ABC is an isosceles right angled triangle and DEFG is a rectangle. If AD = AE = 3 cm and DB = EC = 4 cm, find the area of the shaded region.
Answer :
(a) It is given that
ABC is an equilateral triangle of side = 10 cm
We know that, Area of equilateral triangle ABC = √3/4 × (side)2
= √3/4 × 102
= √3/4 × 100
So we get
= √3× 25
= 1.73 × 25
= 43.3 cm2
In right angled triangle BDC
∠D = 900
BC = 10 cm
CD = 6 cm
Using Pythagoras Theorem
BD2 + DC2 = BC2
BD2 + 62 = 102
BD2 + 36 = 100
So we get
BD2 = 100 – 36 = 64
BD = √64 = 8 cm
We know that, Area of triangle BDC = ½ × base × height
So we get
= ½ × BD × DC
= ½ × 8 × 6
= 4 × 6
= 24 cm2
Here the area of shaded portion = Area of triangle ABC – Area of triangle BDC
= 43.3 – 24
= 19.3 cm2
(b) It is given that
AD = AE = 3 cm
DB = EC = 4 cm
By addition we get
AD + DB = AE + EC = (3 + 4) cm
AB = AC = 7 cm
∠A = 900
We know that, Area of right triangle ADE = ½ × AD × AE
= ½ × 3 × 3
= 9/2 cm2
So triangle BDG is an isosceles right triangle
DG2 + BG2 = BD2
DG2 + DG2 = 42
By calculation
2DG2 = 16
DG2 = 16/2 = 8
DG = √8 cm
Area of triangle BDG = ½ × BG × DG
We can write,
= ½ × DG × DG
= ½ (√8)2
= ½ × 8
= 4 cm2
Area of isosceles right triangle EFC = 4 cm2
So the area of shaded portion = 9/2 + 4 + 4
Taking LCM
= (9 + 8 + 8)/ 2
= 25/2
= 12.5 cm2
— : End of ML Aggarwal Mensuration Exe-16.1 Class 9 ICSE Maths Solutions :–
Return to :- ML Aggarawal Maths Solutions for ICSE Class-9
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends