Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B Solved for ICSE Class-10. Step by step solutions as council prescribe guideline of model sample question paper. During solutions of Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B we explain with Labelled Figure , Graph, Table , Reaction and Structure whenever necessary so that student can achieve their goal in next upcoming exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
Solutions of ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 10th (x) |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Topic | Specimen Paper Solved |
| Syllabus | Revised Syllabus |
| Session | 2022-23 |
| Section-B | Descriptive Type |
| Max mark | 80 |
Warning :- before viewing solution view Question Paper. Also visit that How CISCE Change Same Question in Different Pattern and ask again in exam which feel a new one question while it was previous year question . Therefore a question arise into the mind of student if CISCE Ask Repeated Question in Board Exam..?.
ICSE 2023 EXAMINATION SPECIMEN QUESTION PAPER
Chemistry
(SCIENCE PAPER – 2)
Maximum Marks: 80
- Time allowed: Two hours
- Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
- You will not be allowed to write during first 15 minutes.
- This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
- The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
- Section A is compulsory. Attempt any four questions from Section B.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
ICSE Biology Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B Solved for Class-10
(Attempt any four questions.)
Question 3:
(i) Identify the Anion present in each of the following compounds.
(a) When Barium Chloride Solution is added to a solution of compound B, a white precipitate insoluble in dilute Hydrochloric acid is formed.
(b) When dilute Sulphuric acid is added to compound D, a gas is produced which tums lime water milky but has no effect on acidified potassium dichromat solution.
Answer :
(a) When Barium Chloride Solution is added to a solution of compound B, a white precipitate insoluble in dilute Hydrochloric acid is formed Sulphate ion
(b) When dilute Sulphuric acid is added to compound D, a gas is produced which tums lime water milky but has no effect on acidified potassium dichromat solution Carbonate ion.
(ii) Write the products and balance the equation.
(a) S + Conc HNO3 >
(b) ZnS + HCl >
Answer :
(a) S+6HNO3→H2SO4+6NO2+2H2O.
(b) ZnS+2 HCl→ZnCl2+H2S
(iii) Arrange the following as per the instruction given in the brackets:
(a) Na, K, Cl, Si, S. (increasing order of electro negativity)
(b) Be, Li, F,C,B,N,O (increasing order of metallic character)
(c) Br, F,I, Cl (increasing order of atomic size)
Answer :
(a) K, Na, Si, S, Cl
(b) F, O, N, C, B, Be, Li
(c) F, Cl. Br, I
(iv) Fill in the blanks selecting the appropriate word from the given choice:
(a) In a covalent compound the bond is formed due to ……….. of electrons (sharing / transfer)
(b) A molecule which has a single lone pair of electrons …….. (NH3 / H20)
(c) Electrovalent compounds do not conduct electricity in their ……. state. (molten / solid)
Answer :
(a) sharing
(b) NH3
(c) solid
Question 4:
(i) For each of the substances given below, what is the role played in the extraction of Aluminum.
(a) Cryolite
(b) Graphite
Answer :
(a) Cryolite plays an important role in the refining of aluminium. The melting point of aluminium oxide is very high (more than 2000∘C) and so melting it would be a very expensive process. Hence we use cryolite to decrease the melting point of aluminium oxide from 2000 – 2500∘C to 900 – 1000∘C.
(b) Thus the role of graphite in electrometallurgy of aluminium is to prevent the liberation of oxygen so that the aluminium is not oxidized by oxygen.
(ii) Calculate:
(a) A gas cylinder is filled with hydrogen and it holds 5 gms of gas. The same cylinder holds 85 gms of gas X under same temperature and pressure. Calculate the vapour density of gas X.
(b) Give the empirical formula of CH3COOH.
Answer :
(a) V.D. of gas ‘X’ = (wt of 1 gas cylinder of gas ‘X’)/ wt. of 1 gas cylinder of H2
= 85/5
= 17
(b) Empirical formula shows the least number of whole number elements in a compound. CH3COOH can also be written as C2H4O2. Now dividing the molecular formula by 2 we get the empirical formula of acetic acid as CH2O.
(iii) The following questions are pertaining to the laboratory preparation of Hydrogen chloride gas.
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation for its preparation mentioning the condition required.
(b) Why is concentrated Nitric Acid not used in the preparation of Hydrogen Chloride gas?
(c) How is Hydrogen Chloride gas collected?
Answer :
(a)
(b) Conc. HNO3 is Volatile
(c) Upward displacement of air.
(iv) Explain the following:
(a) Concentrated Nitric acid appears yellow when it is left standing in a glass bottle.
(b) An inverted Funnel is used to dissolve Hydrogen Chloride gas in water.
(c) All apparatus made of glass is used in the laboratory preparation of Nitric acid.
Answer :
(a) The pure nitric acid is colourless conc nitric acid undergoes decomposition as it is very unstable to heat. On decomposition they form reddish brown nitrogen dioxide gas which when dissolved in the acid appears yellow in colour.
(b) An inverted funnel connected to the HCI gas supply is placed in a beaker in such a way that the rim of the funnel just touches the surface of water in the beaker. HCI gas coming through delivery tube fills the mouth of the funnel and then dissolves in water. By this way we get hydrochloric acid in the beaker.
(c) Because Nitric acid vapors attack rubber and corck
Question 5:
(i) (a) State one property of Ammonia demonstrated in the Fountain Experiment.
(b) Give the ionic equation when Ammonium Hydroxide is dissolved in water.
Answer :
(a) By fountain experiment, we demonstrate the high solubility of ammonia gas in water.
(b) NH4OH(aq) → NH3(g) + H2O(l) (that ammonia hydroxide does not dissociate because it is a weak acid)
(ii) Name a probable Cation present based on the following Observations:
(a) Reddish brown precipitate insoluble in Ammonium Hydroxide.
(b) Blue coloured sulphate solution.
Answer :
(a) Ferric ion (Fe3+)
(b) Cupric Ion (Cu2+)
(iii) Give balanced chemical equation for the following:
(a) Laboratory Preparation of Methane from Sodium Acetate.
(b) Preparation of Ethyne from 1, 2 dibromoethane.
(c) Ethene reacting with Chlorine.
Answer :
(a) Sodium acetate is heated with soda lime: Dry sodium acetate on heating with dry soda lime (NaOH + CaO), gives methane.
(b) When 1,2 -dibromoethane is boiled with alcoholic potassium hydroxide, ethyne is formed.
CH2Br−CH2Br+KOHBoiling−−−−→CH≡CH+2KBr+2H2O
(c) CH2=CH2+Cl2→CH2Cl−CH2Cl.
(iv) State one relevant observation for each of the following reactions:
(a) When excess Ammonia is passed through an aqueous solution of Lead Nitrate.
(b) Copper Sulphate solution is electrolysed using Copper electrodes.
(c) Ammonium hydroxide is added to Ferrous Sulphate solution.
Answer :
(a) A white precipitate of Pb(OH)2 is formed which is soluble in NH3
(b) When copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes, reddish pink deposit of copper metal takes place on cathode.
(c) When Ammonium Hydroxide is added to ferrous sulphate solution a dirty green precipitate of Fe(OH)2 is formed.
Question 6:
(i) Define:
(a) Gay Lussac’s law of combining volume.
(b) Vapour Density
Answer :
(a) It states that the chemical reaction in which the gaseous reactants combine together to form one or more gaseous products, the ratio of the volumes of reactants and products will be in the whole number ratio. Example: H2+Cl2⟶2HCl.
(b) Vapour density is the density of a vapour in relation to that of hydrogen. It may be defined as mass of a certain volume of a substance divided by mass of same volume of hydrogen. vapour density = mass of n molecules of gas / mass of n molecules of hydrogen.
(ii) Solve:
1250cc of oxygen was burnt with 300cc of ethane (C2H6). Calculate the volume of the unused oxygen.and the volume of the carbon dioxide formed.
2C2H6 + 702 –> 4CO2 + 6H20
Answer :
2C2H6 + 702 –> 4CO2 + 6H20
From the equation , 2V of ethane reacts with 7V oxygen.
So, 300 cc of ethane reacts with (300×7)/2 = 1050 cc
Hence, unused O2 = 1250 – 1050 = 200 cc
From 2V of ethane, 4V of CO2 is produced.
So, 300 cc of ethane will produce (300×4)/2 = 600 cc of CO2
(iii) State the conditions required for the following reactions:
(a) Conversion of Sulphur dioxide to Sulphur trioxide.
(b) Conversion of Ammonia to Nitric acid
(c) Conversion of Nitrogen to Ammonia
Answer :
(a) Favourable conditions for the conversion of SO2 to SO3 are as follows: Exothermic reactions are favoured at low temperature, and the yield is maximum at about 410–450°C. Pressure of about 1–2 atmosphere is used. Excess of oxygen increases the production of sulphur dioxide.
(b) Catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide. Conditions for catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide : Platinum catalyst and 800°C temperature.
(c)
(iv) Choose the role played by concentrated Sulphuric acid as A, B, C which is responsible for the reactions 1 to 3.
A. Oxidizing agent
B. Non Volatile Acid
C. Dehydrating agent
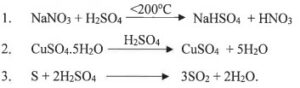
Answer :
(1) B. Non Volatile Acid
(2) C. Dehydrating agent
(3) A. Oxidizing agent
Question 7:
(i) Find the empirical formula and molecular formula of an organic compound from the data given below:
C= 75.92% H = 6.32%, N = 17.76% its vapour density is 39.5
(At.wt: C=12, H=1, N=14)
Answer :
(ii) Identify the functional group in the following organic compounds:
(a) HCHO
(b) C2HsCOOH
Answer :
(a) Aldehyde
(b) Carboxylic Acid
(iii) During the Electrolysis of Copper II Sulphate solution using platinum as cathode and graphite as anode.
(a) State what you observe at the cathode.
(b) State the change noticed in the electrolyte.
(c) Write the reaction at the cathode.
Answer :
(a)
(b) Blue Color of cu2+ ions in the electrolytes solutions in the fade.
(c) Cu2+ + 2e- –> Cu
(iv) Choose the answer from the list which fits the description.
[CaO, CO2, NaOH, Fe(OH)3, CO]
(a) A basic oxide.
(b) An oxide which is acidic.
(c) An Alkali.
Answer :
(a) CaO
(b) CO2
(c) NaOH
Question 8:
(i) Draw the electron dot structure for the following.
(a) H3O+
(b) CH4
Answer :
(a) 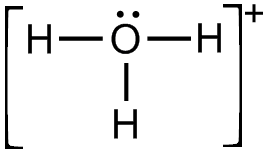
(b) 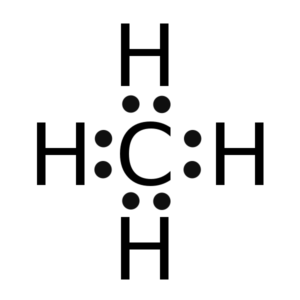
(ii) Distinguish between the following as directed:
(a) Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Sulphate by using dilute HCl
(b) Ammonium Sulphate and Sodium Sulphate by using Calcium hydroxide.
Answer :
(a) Sodium carbonate on treating with dil. HCl results in the formation of sodium chloride with the liberation of carbon dioxide gas. Sodium sulphite on treating with dil. HCl results in the formation of sodium chloride with the liberation of sulphur dioxide gas
(b)
Ammonia prepared by treating ammonium sulphate with calcium hydroxide is completely used by NiCl2. 6H2O to form a stable coordination compound
Ca(OH)2 + Na2SO4 = CaSO4 + NaOH
(iii) Name the particles present in:
(a) Strong Electrolyte
(b) Weak Electrolyte
(c) Non Electrolyte
Answer :
(a) Ions
(b) Ions and molecules
(c) Molecules
(iv) An element X has atomic number 17. Answer the following questions.
(a) State the period & group to which it belongs:
(b) Is it a Metal or Non Metal?
(c) Write the formula between X and Hydrogen.
Answer :
(a) Period = 3
Group = 17 (Halogen)
(b) Non Metal
(c) HX
— End of ICSE Chemistry Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B Solution :–
Return to : ICSE Specimen Paper 2023 Solved
–: visit also :–
- ICSE Class-10 Textbook Solutions Syllabus Solved Paper Notes
- School will be closed on These Dates in August, Check Total Holidays
- High Salary Top Courses After 12th Science for Boys / Girls
- Which School Board is Better for IIT JEE and NEET Preparation?
- Which Entrance Exam Is Easier To Crack – NEET, IIT, JEE?.
- CISCE 2023 Exam: Clue of Board Paper Standard
- ICSE Board Paper Class-10 Solved Previous Year Question
Thanks