Circulatory System Class 10 Concise Descriptive Ans ICSE Biology Selina Solutions Ch-8. In this article you will get the solutions of Descriptive Type Questions as council latest syllabus. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10 Biology.
Circulatory System Class 10 Concise Descriptive Ans ICSE Biology Selina Solutions Ch-8
| Board | ICSE |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 10 |
| Book | Selina Concise |
| Chapter-8 | Circulatory System |
| Topics | Solutions of Descriptive Type Questions |
| Session | 2024-25 |
Descriptive Type Questions on Circulatory System
Que-1: Define the following terms:
(a) Circulatory system
(b) Blood
(c) Heart
(d) Diapedesis
(e) Phagocytosis
(f) Rh factor
Sol:
(a) Circulatory system — The circulatory system is a network consisting of blood, blood vessels and the heart. This network supplies tissues in the body with oxygen and other nutrients, transports hormones and removes unnecessary waste products.
(b) Blood — Blood is the circulating fluid contained in the heart and in the blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries of the circulatory system. Blood from the heart is pumped throughout the body using blood vessels.
(c) Heart — The heart is made of specialized cardiac muscle tissue that allows it to act as a pump within the circulatory system. Heart pushes the blood around the body and has different chambers such as right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle to prevent the mixing of oxygenated blood and carbon dioxide rich blood.
(d) Diapedesis — Diapedesis is the squeezing of leucocytes through the wall of capillaries into the tissues.
(e) Phagocytosis — Phagocytosis is the process in which most WBCs and particularly the neutrophils engulf particle-like solid substances, especially bacteria.
(f) Rh factor — Rh factor is an inherited antigen often found on the blood cells. Some individuals have these antigens and are thus Rh positive (Rh+) while others who do not have this antigen are Rh negative (Rh-)
Que-2: Distinguish between the following pairs on the basis of words indicated in the brackets ( ):
(a) Erythrocytes and Leukocytes (Nucleus)
(b) Leukocytes and Thrombocytes (Life-span)
(c) Arteries and Veins (Wall and lumen)
(d) Pulmonary and Systemic circulation (Kind of blood)
(e) Mitral valve and Tricuspid valve (Location)
Sol:
(a) Difference between Erythrocytes and Leukocytes (Nucleus):
| Character | Erythrocytes | Leukocytes |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
(b) Difference between Leukocytes and Thrombocytes (Life-span):
| Character | Leukocytes | Thrombocytes |
|---|---|---|
| Life span | Two weeks | 3-5 days |
(c) Difference between Arteries and Veins (Wall and lumen):
| Character | Arteries | Veins |
|---|---|---|
| Wall | Thick and muscular | Thin and less muscular |
| Lumen | Narrow | Wider |
(d) Difference between Pulmonary and Systemic circulation (Kind of blood):
| Character | Pulmonary circulation | Systemic circulation |
|---|---|---|
| Kind of blood | Pulmonary artery brings deoxygenated blood to lungs and pulmonary vein takes oxygenated blood from lungs to heart. | Oxygenated blood is transported to body parts from heart and deoxygenated blood is transported back to heart. |
(e) Difference between Mitral valve and Tricuspid valve (Location):
| Character | Mitral valve | Tricuspid valve |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Present between left atrium and left ventricle. | Present between right atrium and right ventricle. |
Que-3: Give reasons/explain:
(a) The left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
(b) The walls of right ventricle are thicker than those of the right auricle.
(c) Vitamin K is essential for the process of blood clotting.
(d) A mature mammalian Erythrocyte lacks nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
(e) People have a common belief that the heart is located on the left side of the chest.
Sol:
(a) The left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest points in the body such as the feet, the toes and the brain against the gravity while the right ventricle pumps the blood only up to the lungs. Therefore, the left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
(b) The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation whereas the right auricle receives the blood from venae cavae and passes it to the right ventricle. Therefore, walls of the right ventricle are thicker than those of the right auricle.
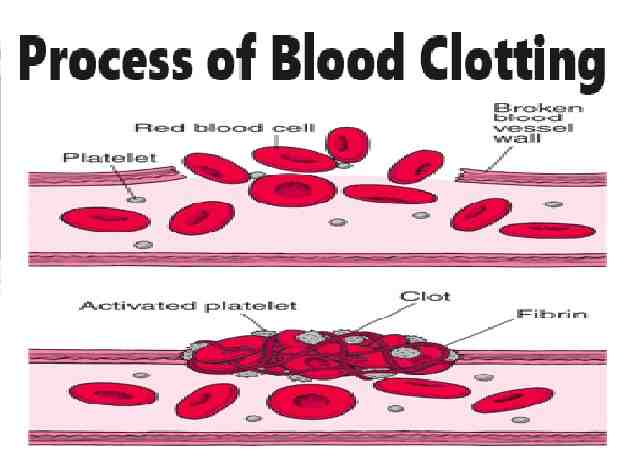
(c) Vitamin K acts as a catalyst that transforms some anti-clotting proteins, which are always present, into clotting proteins when there is a cut or wound to the body. The mechanism of blood clotting involves the presence of calcium and other clotting factors. Thrombokinase activates an enzyme called prothrombin activator. The enzyme prothrombin activator then converts plasma protein prothrombin into thrombin. Thrombin is the enzyme which in turn converts fibrinogen into fibrin. Polymerized fibrin together with platelets forms a clot at the wound site. The prothrombin is a plasma protein synthesized in the liver. Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of prothrombin. Hence, Vitamin K is essential for the process of blood clotting.
(d) Lack of nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum helps erythrocytes in the following way:
- Loss of nucleus makes the red cells biconcave, thus increasing their surface area to absorb more oxygen.
- Loss of mitochondria means that they cannot use the absorbed oxygen themselves.
- Absence of endoplasmic reticulum makes it flexible so that they can move through fine capillaries.
(e) The heart is right in the center between the two lungs and above the diaphragm. The narrow end of the roughly triangular heart is pointed to the left side and during working, the contraction of the heart is most powerful at this end giving a feeling that the heart is on the left side.
Que-4: Write important role/roles of the following:
(a) Tonsils
(b) Spleen
(c) Hepatic portal vein
(d) Basophils
(e) S.A.N.
Sol:
(a) Tonsils — Tonsils are lymph glands located on the sides of the neck. They tend to localize the infection and prevent it from spreading it in the body as a whole.
(b) Spleen — The spleen is a large lymphatic organ. The spleen acts as a blood reservoir in case of emergency such as haemorrhage, stress or poisoning. It produces lymphocytes and destroys worn out RBCs.
(c) Hepatic portal vein — The hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents.
(d) Basophils — Basophils are a type of white blood cells. They are the least common type of granulocyte which release chemicals called histamine for inflammation which dilate blood vessels.
(e) S.A.N. — The sinoatrial node (SAN) is a region of cardiac fibres located in the right atrium. The electrical wave of stimulation is initiated here and extends over the two atria, causing them to contract. It is often referred to as the pacemaker of the heart.
Que-5: What is meant by the term ‘Double circulation’? Distinguish between the two types of circulation in our body
Sol: Double circulation is a process during which blood passes twice through the heart during one complete cycle. The flow of blood in the heart consists of two phases —
- The short pulmonary (lung) circulation
- The long systemic (general body) circulation
Difference between pulmonary and systemic circulation —
| Pulmonary circulation | Systemic circulation |
|---|---|
| involves circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs. | involves circulation of blood between the heart and the body organs (except lungs). |
| It carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs to receive oxygen. | carries oxygenated blood to the body organs. |
| returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. | returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart |
Que-6: Write the main steps in coagulation of blood in their correct sequence?
Sol: Coagulation of blood (or clotting) occurs in a series of steps as follows:
- The injured tissue cells and the platelets which disintegrate at the site of the wound release a substance thrombokinase (also called thromboplastin).
- The thrombokinase acts as an enzyme and with the help of calcium ions present in the plasma, it converts a substance prothombin (inactive) of the plasma, into thrombin (active). Vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin is essential for the production of prothombin.
- Thrombin in the presence of calcium ions reacts with the soluble fibrinogen of the plasma to convert it into insoluble fibrin. Fibrin is a solid substance that forms threads. These microscopic threads of fibrin are sticky and form a mesh or network at the site of wound.
- Blood cells are trapped in the network of the fibrin; the network then shrinks and squeezes out the rest of the plasma which is in the form of a clear liquid, the serum. The solid mass which is left behind is called clot (or thrombus).
Que-7: Write the exact location of the following:
(a) Pulmonary semilunar valve
(b) Tonsils
(c) Heart
(d) Pacemaker
(e) Hepatic portal vein
Sol:
(a) Pulmonary artery
(b) Sides of neck
(c) Centre of chest, between the lungs and above diaphragm
(d) Upper right corner of the walls of the right atrium
(e) Between liver and stomach, intestine
–: End of Circulatory System Class 10 Concise Descriptive Ans ICSE Biology Selina Solutions :–
Return to : Concise Biology for ICSE Class 10 Selina Solutions
Please share with your Friends if helpful
thanks


