Circulatory System ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Biology Chapter 8 . We Provide Step by Step Answer of Progress Check , MCQs, Very Short Answer Type, Short Answer Type, Long Answer Type Questions and Structured / Applications / Skill Type Questions of Exercise-8 Circulatory System ICSE Class-10 . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publishers PVT LTD |
| Subject | Concise Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | HS Vishnoi |
| Chapter-8 | Circulatory System |
| Topics | Solutions of MCQs, Very Short ,Descriptive, Structural/Skill Questions and Progress Check 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Circulatory System ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Biology
-: Select Topic :-
E. STRUCTURED / APPLICATION / SKILL TYPE
Progress Check 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
Circulatory System Chapter-8 Selina Biology Solution for ICSE Class-10
Page 109
Question 1
Non-granular WBCs are:
(a) lymphocytes and monocytes
(b) lymphocytes and basophils
(c) eosinophils and basophils
(d) eosinophils and monocytes
Answer 1
(a) lymphocytes and monocytes
Question 2
White blood cells engulf bacteria in a process called:
(a) diapedesis
(b) phagocytosis
(c) active transport
(d) passive transport
Answer 2
(b) phagocytosis
Question 3
The nearest organ to which the heart supplies oxygenated blood is
(a) Lung
(b) Stomach
(c) Intestine
(d) Heart itself
Answer 3
(d) Heart itself
Question 4
When a doctor is recording your pulse, he is pressing on your wrist exactly on a
(a) vein
(b) capillary
(c) artery
(d) arteriole
Answer 4
(c) artery
Question 5
The blood vessels supplying blood to the kidney is the
(a) renal vein
(b) renal artery
(c) dorsal aorta
(d) hepatic vein
Answer 5
(b) renal artery
Question 6
Angina Pectoris is due to
(a) defective nutrition
(b) chest pain due to inadequate supply of oxygen to the heart muscle
(c) defective functioning of mitral valve
(d) infection by a virus
Answer 6
(b) chest pain due to inadequate supply of oxygen to the heart muscle
Question 7
The chief function of lymph nodes is to
(a) produce WBCs
(b) produce hormones
(c) destroy old RBCs
(d) destroy pathogens
Answer 7
(d) destroy pathogens
Question 8
Heart sounds are produced due to
(a) closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves
(b) rushing of blood through valves producing turbulence
(c) closure of atrioventricular and semilunar valves
(d) entry of blood into auricles
Answer 8
(a) closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves
(b) rushing of blood through valves producing turbulence
(c) closure of atrioventricular and semilunar valves
B.VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Chapter – 8, Circulatory System ICSE Class-10 Selina Biology Solution
Page 109-110
Question 1
Given below are certain structures, write their chief functional activity.
(a) Blood platelets ——
(b) Neutrophils —–
(c) Erythrocytes —–
(d) Lymphocytes —–
(e) Bone marrow —–
Answer 1
(a) Blood platelets and blood coagulation
(b) Neutrophils and phagocytosis
(c) Erythrocytes and transportation of gases
(d) Lymphocytes and Produce antibodies
(e) Bone marrow and destruction of old and weak RBC’s/production of RBCs and WBCs.
Question 2
Name the following :
(a) The cells which transport oxygen to the different parts of the human body.
(b) The cells that initiate blood clotting.
Answer 2
(a) Red Blood Cells
(b) Blood Platelets
Question 3
Name the following :
(a) Any one vein which starts from an organ and ends in another organ besides the heart.
(b) The kind of blood vessels which have no muscular walls.
(c) Any artery which carries impure deoxygenated blood.
(d) The kind of blood cells which can squeeze out through the walls of one category of blood vessels.
(e) The smallest common blood vessels formed by the union of capillaries.
(f) The blood vessels which start from capillaries and end in capillaries.
(g) The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract.
(h) The valve present in between the chambers on the right side of the human heart.
(i) The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the ventricles get filled with blood from the atrium.
(j) The fluid found between the membranes of the heart.
Answer 3
(a) Hepatic portal vein
(b) Blood Capillaries
(c) Pulmonary artery
(d) White blood cells
(e) Venules
(f) Portal vein
(g) Atrial systole
(h) Tricuspid valve
(i) Atrial systole
(j) Pericardial fluid
Question 4
Complete the following statements by filling in the blanks from the choices given in the brackets.
(a) The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is the ______. (hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, hepatic vein)
(b) A blood vessel which has small lumen and thick wall is _______. (capillary, lymphatic duct, artery, venule)
(c) The valve which prevents the back flow of blood in the veins and lymph vessels ______.(mitral valve, tricuspid valve, semilunar valve)
(d) An anticoagulant present in the blood is _______.(heparin, hirudin, thromboplastin, calcium)
Answer 4
(a) The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is the hepatic portal vein.
(b) A blood vessel which has small lumen and thick wall is artery.
(c) The valve which prevents the back flow of blood in the veins and lymph vessels is semilunar valve.
(d) An anticoagulant present in the blood is heparin.
Question 5
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place:
(a) Lub : Atrioventricular valve : : Dup:_______
(b) Coronary artery: Heart : : Hepatic artery:______
Answer 5
(a) Lub : Atrioventricular valve : : Dup : Semilunar valves
(b) Coronary artery : Heart : : Hepatic artery : Liver
Question 6
Given reason, why a matured mammalian erythrocyte lacks nucleus and mitochondria?
Answer 6
A matured mammalian erythrocyte lacks a nucleus and mitochondria. The lack of a nucleus increases the surface area-volume ratio of RBCs, thus increasing the area for oxygen absorption. Also, the lack of a nucleus reduces the size of the cell, making it easy to flow through the blood vessels and more cells can be accommodated in a small area.
The lack of mitochondria implies that the cell does not use any oxygen absorbed for respiration, thus increasing the efficiency of the cell to transport oxygen as all the oxygen absorbed is transported without any loss.
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Circulatory System Chapter 8 Concise Biology Solution for ICSE Clas-10
Page 110
Question 1
Enumerate the structural differences between white blood cells and red blood cells.
Answer 1
Structural Differences between White Blood Cells and Red Blood Cells:
| White Blood Cells | Red Blood Cells |
| 1. White blood cells are amoeboid. | Red blood cells are minute biconcave disc-like structures. |
| 2. They are nucleated cells. | They anucleated cells. |
| 3. Haemoglobin is absent in red blood cells. | Haemoglobin is present in red blood cells. |
Question 2
Why is it necessary to know the blood groups before giving transfusion?
Answer 2
During blood transfusion it is necessary to know the blood groups before transfusion because it is important that the blood groups of the donor and the recipient are compatible. In case of an incompatible blood transfusion, the recipient develops antibodies that attack the antigens present on the RBCs of the donor causing the blood cells to clump together which may result in death.
Question 3
Differentiate between members of each of the following pairs with reference to phrases in brackets:
(a) Antibodies and Antibiotics (Source)
(c) Serum and Vaccine (Composition)
(d) Erythrocytes and leucocytes (function)
(g) Tricuspid and bicuspid valves (location)
Answer 3
(a)
Differences between antibodies and antibiotics based on their source:
| Antibodies | Antibiotics |
| They are produced by lymphocytes in response to the entry of pathogens in the bloodstream. | They are the medicines extracted from some bacteria and fungi. Antibiotics destroy or inhibit the growth of pathogens. |
(b)
Differences between serum and vaccine based on their composition:
| Serum | Vaccine |
| The plasma from which the protein fibrinogen has been removed is called serum. | Vaccine is killed or living weakened germs which are introduced in the body to stimulate the production of antibodies against pathogens for a particular disease. |
(c)
Differences between erythrocytes and leucocytes based on their function:
| Erythrocytes | Leucocytes |
| They function in the transport of oxygen throughout the body and in the removal of carbon dioxide from the body. | They help in the defense of the body against disease-causing pathogens. |
(d)
Differences between tricuspid valve and bicuspid valve based on their location:
| Tricuspid valve | Bicuspid valve |
| It is located between the right atrium and right ventricle of the heart. | It is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. |
Question 4
When are the sounds “LUBB” and “DUP” produced respectively during heart beat?
Answer 4
The first sound LUBB is produced when the atrio-ventricular valves i.e. tricuspid and bicuspid valves close at the start of ventricular systole.
The second sound DUP is produced at the beginning of ventricular diastole, when the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves close.
Question 5
Why do people have a common belief that the heart is located on the left side of the chest?
Answer 5
People have a common belief that the heart is located on the left side of the chest because the narrow end of the roughly triangular heart is pointed to the left side and during its working the contraction of the heart is more powerful on the left side which can be felt.
Question 6
Match the items in column A with those in column B. Rewrite the correct matching pair.
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) SA node | Plasma |
| (b) Defective haemoglobin in RBC | Serum |
| (c) Muscle fibres located in the heart | Pacemaker |
| (d) The liquid squeezed out of blood during clotting | Sickle cell anemia |
| (e) Never tires, keep on contracting and relaxing | Purkinje fibres |
| (f) Cardiac cycle | Cardiac muscles |
| (g) Liquid part of the blood without corpuscles | 0.85 sec |
Answer 6
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) SA node | Pacemaker |
| (b) Defective hemoglobin in RBC | Sickle cell anemia |
| (c) Muscle fibres located in the heart | Purkinje fibres |
| (d) The liquid squeezed out of blood during clotting | Serum |
| (e) Never tires, keep on contracting and relaxing | Cardiac muscles |
| (f) Cardiac cycle | 0.85 sec |
| (g) Liquid part of the blood without corpuscles | Plasma |
Question 7
The table below is designed to indicate the transport of certain substances in our body. Fill in the blanks with suitable answers.
| Substance | From | To |
| 1. —– | Lungs | Whole body |
| 2. Carbon dioxide | —– | —– |
| 3. Urea | —– | —– |
| 4. Digested carbohydrates | Intestines | —– |
| 5. —– | —– | Target organs |
Answer 7
| Substance | From | To |
| 1. Oxygen | Lungs | Whole body |
| 2. Carbon dioxide | Whole body | Lungs |
| 3. Urea | Whole body | Kidneys |
| 4. Digested carbohydrates | Intestine | Whole body |
| 5. Hormones | Endocrine glands | Target organs |
D. DESCRIPTIVE ANSWER TYPE
Selina Concise Biology Circulatory System Chapter 8
Page 110
Question 1
Define the following terms :
(a) Circulatory system
(b) Blood
(c) Heart
(d) Diapedesis
(e) Phagocytosis
(f) Rh factor
Answer 1
(a) Circulatory system : The system that contains the heart and the blood vessels and moves blood throughout the body. This system helps tissues get enough oxygen and nutrients, and it helps them get rid of waste products.
Question 2
Distinguish between the following pairs :
(a) Systole and Diastole
(b) Arteriole and Venule
(c) Universal donor and universal recipient
(d) Arteries and Veins
(e) Haemoglobin and Chlorophyll
Answer 3
(a) Systole and Diastole :
Diastole and systole are two phases of the cardiac cycle. They occur as the heart beats, pumping blood through a system of blood vessels that carry blood to every part of the body. Systole occurs when the heart contracts to pump blood out, and diastole occurs when the heart relaxes after contraction.
(b) Arteriole and Venule :
Arteries transport blood away from the heart and branch into smaller vessels, forming arterioles. Arterioles distribute blood to capillary beds, the sites of exchange with the body tissues. Capillaries lead back to small vessels known as venules that flow into the larger veins and eventually back to the heart.
(c) Universal donor and universal recipient :
The universal donor is O negative. i.e. group O, Rh D negative. The recipients blood will not have antibodies to this blood, the blood can be given to a patient with any blood group. The universal recipient is therefore AB positive, no matter which blood group is given, there should be no major reaction.
(d) Arteries and Veins :
Arteries are blood vessels responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart for reoxygenation.
(e) Haemoglobin and Chlorophyll :
| Haemoglobin | Chlorophyll |
| 1. It is a respiratory pigment that transports oxygen from the lungs across the body parts. | 1. It is a light-capturing pigment which facilitates light absorption during photosynthesis. |
| 2. It is red in colour. | 2. It is green in colour. |
| 3. The central ion is iron. | 3. The central ion is magnesium. |
| 4. It is found in human blood. | 4. It is found in green plants and algae. |
Question 3
Give reasons/explain:
(a) The left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
(b) The walls of right ventricle are thicker than those of the right auricle.
(c) Vitamin K is essential for the process of blood clotting.
Answer 3
(a) The left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest points in the body such as the feet, the toes and the brain against the gravity while the right ventricle pumps the blood only up to the lungs. Therefore, the left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
(b) The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation whereas the right auricle receives the blood from vena cavae and passes it to the right ventricle. Therefore, walls of the right ventricle are thicker than those of the right auricle.
(c) The mechanism of blood clotting involves the presence of calcium and other clotting factors. Thrombokinase activates an enzyme called prothrombin activator. The enzyme prothrombin activator then converts plasma protein prothrombin into thrombin. Thrombin is the enzyme which in turn converts fibrinogen into fibrin. Polymerized fibrin together with platelets forms a clot at the wound site. The prothrombin is a plasma protein synthesized in the liver. Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of prothrombin. Hence, Vitamin K is essential for the process of blood clotting.
Question 4
Write important role/roles of the following:
(a) Tonsils
(b) Spleen
(c) Hepatic portal vein
(d) Basophils
(e) S.A.N.
Answer 4
(a) Tonsils : Tonsils are lymph glands located on the sides of the neck. They tend to localize the infection and prevent it from spreading it in the body as a whole.
(b) Spleen : The spleen is a large lymphatic organ. The spleen acts as a blood reservoir in case of emergency such as haemorrhage, stress or poisoning. It produces lymphocytes and destroys worn out RBCs.
(c) Hepatic portal vein : The hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents.
(d) Basophils :They are a type of granular WBCs which release chemicals called histamine for inflammation which dilate blood vessels.
(e) S.A.N. : The sinoatrial node is a group of cells located in the wall of the right atrium of the heart. The action potential required for the rhythmic contractile activity of the heart is generated at the SA node. When the impulse is initiated, it results in the atrial systole.
Question 5
What is meant by the term ‘double circulation’ of blood in mammals? What is diastole?
Answer 5
Blood flows twice in the heart before it completes one full cycle. This process of blood circulation in the human body is called double circulation. The expansion or relaxation phase of the atria is called a diastole.
Question 6
What are the main steps in coagulation of blood in their correct sequence?
Answer 6
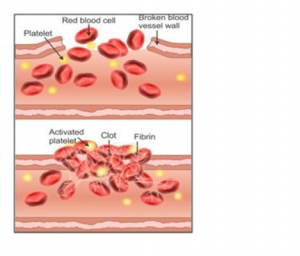
Blood clotting or coagulation occurs in a series of the following steps:
(a) The injured tissue cells and the platelets disintegrate at the site of wound to release thromboplastin.
(b) The thromboplastin with the help of calcium ions converts inactive prothrombin into active thrombin.
(c) Thrombin in the presence of calcium ions converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin which forms a mesh or network at the site of wound.
(d) The blood cells trapped in this network shrink and squeeze out the plasma to leave behind a solid mass known as the clot.
Question 7
What are the functions of blood plasma?
Answer 7
The functions of blood plasma are:
(a) Transports of digested food from the alimentary canal to tissues.
(b) Transports excretory materials from tissues to excretory organs.
(c) Distributes hormones from the glands to their target site.
(d) Distributes heat in the body to maintain the body temperature.
Question 8
What are the functions of blood plasma
Answer 8
The functions of blood plasma are:
(a) Transports of digested food from the alimentary canal to tissues.
(b) Transports excretory materials from tissues to excretory organs.
(c) Distributes hormones from the glands to their target site.
(d) Distributes heat in the body to maintain the body temperature.
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL/ TYPE
Circulatory System Chapter 8 Concise Biology Solution for ICSE Class-10
Page 111-112
Question 1
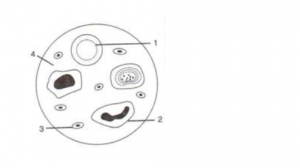
Given below is a diagram of a smear of human blood. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 indicated by guidelines.
(b) Mention two structural differences between the parts labeled 1 and 2.
(c) What is the main function of the parts labeled 1, 2 and 3 respectively?
(d) What is the life span of the part labeled “1”?
(e) Name a soluble protein found in “4” which helps in clotting of blood.
Answer 1
(a)
1 → Red Blood Cell (RBC),
2 → White Blood Cell (WBC),
3 → Blood Platelet
4 → Blood Plasma.
(b) The red blood cells are minute biconcave disc-like structures whereas the white blood cells are amoeboid.
(c) Function of part 1 (RBC): Transport of respiratory gases to the tissues and from the tissues, transport of nutrients from the alimentary canal to the tissues.
Function of part 2 (WBC): WBCs play major role in defense mechanism and immunity of the body.
Function of part 3 (Blood Platelet): Blood platelets are the initiator of blood clotting.
(d) The average life span of a red blood cell (RBC) is about 120 days.
(e) Thromboplastin
Question 2
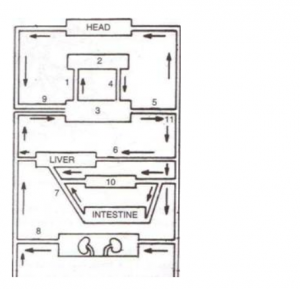
Given below is a highly schematic diagram of the human blood circulatory system.
(a) Which part (state the number) represents the heart? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Which numbers represent the following respectively?
Aorta
Hepatic portal vein
Pulmonary artery
Superior vena cava
Renal vein
Stomach
Answer 2
(a) The structure 3 represents the heart. It forms the centre of double circulation and is located between the liver and the head (as per the diagram). Also the blood circulation (indicated by 1) begins from heart to lungs.
(b)
| Aorta | 5 |
| Hepatic portal vein | 7 |
| Pulmonary artery | 1 |
| Superior vena cava | 9 |
| Renal vein | 8 |
| Stomach | 10 |
Question 3
The figures given below show diagrammatic cross-sections of three kinds of blood vessels.
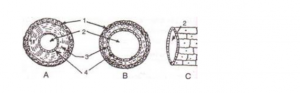
(a) Identify the blood vessels A, B and C.
(b) Name the parts labeled 1-4.
(c) Mention two structural differences between A and B.
(d) Name the kinds of blood that flow through A and through B respectively.
(e) In which one of the above vessels referred to in (a) above does the exchanges of gases actually take place?
Answer 3
(a) A- Artery, B-Vein, C-Capillary
(b) 1 – External layer made of connective tissue
2 – Lumen
3 – Middle layer of smooth muscles and elastic fibres
4 – Endothelium
(c) An artery has thick muscular walls and a narrow lumen. It does not have any valve. A vein on the other hand has thin muscular walls and a wider lumen. It has valves to prevent backflow of blood.
(d) A (Artery)- Oxygenated blood, B (Vein)- Deoxygenated blood
(e) At the capillary level the actual exchange of gases takes place.
Question 4
The diagram given below represents the human heart in one phase of its activity. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the phase
(b) Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
(c) Name the parts numbered 1 to 6.
(d) What type of blood flows through the parts marked ‘1’ and ‘2’?
(e) How many valves are closed in this phase?
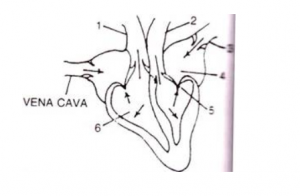
Answer 4
(a) Atrial Diastole and Ventricular Systole
(b) Ventricular muscles are contracting during this phase because the valves between the two ventricles and pulmonary artery and aorta are open while the atrio-ventricular valves are closed.
(c)
| 1 | Pulmonary Artery |
| 2 | Aorta |
| 3 | Pulmonary Vein |
| 4 | Left Atrium |
| 5 | Bicuspid Valve |
| 6 | Right Ventricle |
(d) Part 1 (Pulmonary artery) → Deoxygenated blood
Part 2 (Aorta) → Oxygenated Blood
(e) Two i.e., bicuspid and tricuspid valves are closed in this phase.
Question 5
Study the following diagram carefully and then answer the questions that follow:
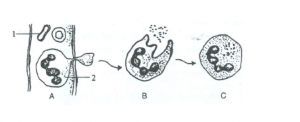
(a) Name the cell labelled 1.
(b) Identify the phenomenon occurring in A.
(c) Mention two structural differences between 1 and 2.
(d) Name the process occurring in B and C and state the importance of this process in the human body.
Answer 5
(a) 1 – Red blood cell
(b) Diapedesis
| RBC | WBC |
| They lack a nucleus. | It have a nucleus. |
| They are biconcave and disc-shaped. | It has a spherical and have different sizes. |
(d) The process which occurs in B and C is phagocytosis. In this process, the WBCs engulf the foreign particles and destroy them, thus preventing the occurrence of disease.
Question 6
Given below is a diagrammatic representation of certain types of blood vessels in human body.
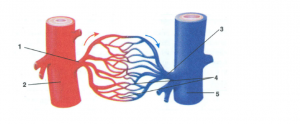
(a) Identify the types of blood vessels numbered 1 to 5.
(b) Where can such an arrangement be found as an example – in lungs or in heart walls?
Answer 6
(a)1 – Arteriole
2 – Artery
3 – Venule
4 – Capillaries
5 – Vein
(b) Such an arrangement can be observed in the lungs.
Question 7
The diagram below shows part of the capillary bed in an organ of the human body. Some of the blood arriving at the capillaries at points labeled A, moves out into the spaces between the tissue cells. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
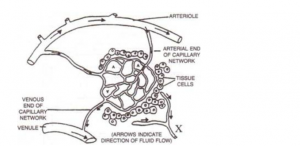
(a) When the liquid from the blood surrounds the cells, what is it called?
(b) Name any one important component of the blood which remains inside the capillaries and fails to move out into the spaces.
(c) Some of the liquid surrounding the cells does not pass directly back into the blood but eventually reaches it by another route through vessel X. name the fluid present in vessel X.
(d) State two important functions performed in our body by the fluid present in vessel X.
Answer 7
(a) Tissue Fluid
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Lymph
(d) The lymph supplies nutrition and oxygen to those parts where blood cannot reach. The lymph drains away excess tissue fluids and metabolites and returns proteins to the blood from tissue spaces.
Return to Concise Selina ICSE Biology Class-10
Thanks



Amazing answers
Can u give the answers for all the chapters
after lock down over in india genetics answer will be uploaded other chapter are available
yes your all chapter uploaded after lock down over in India
Amazing answers
Can u give the answers for all the chapters
https://icsehelp.com/concise-biology-icse-class-10-solutions-selina-publishers/
Thank u
keep in touch for any icse /isc related query