Class-6 Dalal Matter ICSE New Simplified Chemistry SolutionsDr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Allied Publishers Solutions. Chapter-3. We Provide Step by Step Solutions of Exercise/Lesson -3 Elements Compound and Mixtures with Objective Type Questions, Fill in the blanks and Give reason , Match the following of Dr Viraf J Dalal Middle School Chemistry Allied Publishers. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6.
Class-6 Dalal Matter ICSE New Simplified Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3
EXERCISE-3
Question 1.
Explain the term ‘matter’. One kind of matter can be distinguished from another by its physical properties and chemical properties. State the main physical properties of matter.
Answer 1:
A substance which has mass and occupy space and velocity can not be equal light is called matter
Physical properties include state, shape, colour odour, density, etc.
Chemical properties include reactions of different materials with others.
Main Physical Properties of Matter
- Colour : All matter an be distinguished by their varied – colours.
- Smell– different Matter has different Smell
- Solubility : different Matter has different Solubility
- Melting & Boiling Points : different Matter has different Melting & Boiling Point
Question 2.
The three main states of matter are solids, liquids and gases. Compare the three states with reference to the following characteristics of matter –
(a) volume
(b) shape
(c) compressibility
(d) diffusion.
Answer -2:
| Characteristics | Solids | Liquids | Gases |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Volume | Definite volume | Definite volume | Not definite volume |
| (b) Shape | Definite shape | Not fix | Not fix |
| (c)Compressibility | not compressed | less compressible | Highly compressible |
| (d) Diffusion | not diffuse | Shows diffusion | Fast diffusion |
Question 3.
Matter in any state is composed of particles. Compare the three states of matter i.e. solids, liquids and gases with reference to :
(a) intermolecular space
(b) intermolecular force of attraction
(c) movement of particles
Answer 3:
| Characteristics | Solids | Liquids | Gases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermolecular spaces | Minimum | More than solids | Maximum |
| Intermolecular force of attraction | Strong | Less strong | Least |
| Movement of particles | from mean position | In continuous motion | Freely, in any direction |
Question 4.
Describe simple experiments to prove that – solids
(a) occupy space
(b) have mass
(c) have a definite volume
Answer 4:
(a) Solids occupy space:
A measuring cylinder is filled with water and and water level is marked ‘A’
A piece of wooden block is immersed in the measuring cylinder, the water level rises up and it is marked ‘B’
Now, the wooden block is removed the water level falls back to ‘A’
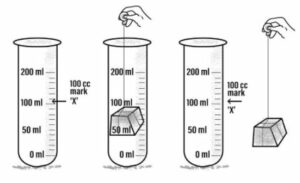
This experiment show that the wooden block pushes water upwards and occupies its space. Hence, solids occupy space.
(b) Solids have mass:
Every solid has mass and can be proved by weigh with the help of simple scale
(c) Have a definite volume :
A piece of wooden block is immersed in a container filled with water, the water level rises up. The wooden block displaces water and retains its volume.
Hence, solids have a definite volume.
Question 5.
Describe simple experiments to prove that – liquids
(a) have mass
(b) have a definite volume
(c) have no definite shape
Answer 5:
(a) Have definite mass
A container filled with a liquid is placed on one side of a simple scale, and the scale tilts towards one side. which confirm that liquid has fix mass
(b) have a definite volume —
A liquid is poured from a measuring cylinder to a container and the volume of liquid in the container is same as the liquid in the measuring cylinder which confirm that liquid has fix volume
(c) have no definite shape —
Liquid occupy the shape of container which confirm that liquid has no fix shape
Question -6.
Describe simple experiments to prove that – gases
(a) occupy space
(b) have mass
(c) have no definite volume or shape
Answer- 6:
(a) occupy space —
When we pump the wheal of cycle it take space in tube which confirm that gas has occupy space —
(b) Have mass —
scale inflated balloon on one side of a simple scale and normal on other side thus the scale tilts towards one side. confirm The balloon has mass which makes the scale tilt.
(c) Have no definite volume or shape —
A gas takes up the volume of any container or enclosed space they enter into.
They also take up the shape of the container.
Question 7.
Explain the term ‘Interconversion of matter’. With reference to ice, water and water vapour show diagrammatically the change of state of matter from solid to liquid to gaseous and back to original state.
Answer 7:
‘Interconversion of matter:- “Change of ,state of matter from one state to another state and back to its original state is called inter – conversion of matter.”
The diagram showing the Change of State of Matter :
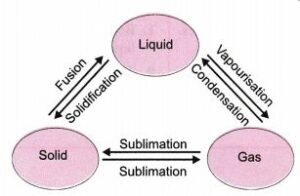
- Ice to water – Melting
- Water to water vapour – evaporation
- Water vapour to water – condensation
- Water to ice – Freezing
Question 8.
Explain the terms
(a) melting
(b) vaporization
(c) condensation
(d) freezing
(e) melting point
(f) boiling point.
Answer 8:
Matter can change from solid to liquid to gaseous state and back to solid state. This is called change of state of matter.
(a) Melting – The conversion of a solid to its liquid state is melting.
(b) Vaporisation – The conversion of a liquid to its gaseous state i.e. vapours by heating is vaporisation.
(c) Condensation – The conversion of vapor in gaseous state to its liquid state by cooling is condensation.
(d) Freezing – The conversion of a liquid to its solid state is freezing.
(e) Melting point – The temperature at which solid melts into liquid is melting point.
(f) Boiling point – The temperature at which water boils and turns into vapour.
Question 9.
State what would you observe if
(a) sugar is added to pebbles take in a plastic beaker
(b) sand is added to glass balls in a beaker. What would you conclude from this imaginative demonstration.
Answer 9:
When sugar is added to pebbles and sand is added to glass balls in a beaker.
It can be seen that sugar and sand take spaces between pebbles and glass balls. This demonstration concludes that intermolecular spaces can be occupied easily.
Question 10.
With the help of a simple diagram how would you show that – solids expand on heating.
Answer 10:
Solids expand on heating can be shown by two different experiments. The experiments are :
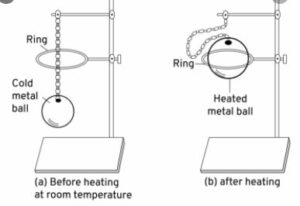
Question 11.
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Solids have a definite shape and are highly rigid while gases have to definite shape and are least rigid.
(b) Sugar can be distinguished from talcum powder using water.
(c) Water on freezing turns into ice.
(d) A bottle of perfume on opening evolves an odour which can be sensed over a long distance.
Answer 11:
(a) In solids, the intermolecular spaces are negligible and the atoms move about in their own position which gives solids a definite shape and makes them rigid while in gases, the intermolecular spaces are large which allows the atoms to move around freely and hence, they are least rigid and have no definite shape.
(b) Sugar dissolves in water while talcum powder does not dissolve.
(c) Water has a fixed melting and boiling point.
(d) A bottle of perfume on opening evolves an odour, because gases diffuse into the air very easily and can be sensed over a long distance.
Question 12.
Complete the statements given below by selecting the correct word/s.
(a) Solids and liquids have a definite ______ but gases do not. ( mass, shape, volume )
(b) The space between atoms in gases is maximum while in ______ is minimum. ( solids, liquids, gases)
(c) Conversation of a vapour into a liquid is called ______ . (vaporization , condensation, freezing )
(d) ______ is an example of a crystalline substance. (wax, sugar, tea)
Answer-12
(a) Volume
(b) Solids
(c) condensation
(d) Wax
Question 13.
State which of the following statements are false. If false write the correct statement.
(a) Solids are highly compressible and rigid.
(b) Atoms/molecules in gases move only about their own positions.
(c) The conversion of water to ice is called freezing.
Answer-13
(a) True
(b) False, Atoms of gases move around freely.
(c) True
Objective Type Questions
Class-6 Dalal Matter ICSE New Simplified Chemistry Solutions Chapter-3
Question-.1.
Fill in the blanks with the correct word/s from the bracket.
- From the three states of matter, _________ expand the least.
- Brownian movement is maximum in _________ .
- Cohesive forces are negligible in _________ .
- Matter can change from one state to another by change in _________ .
- The space between atoms(molecules) of solid is _________ .
- Intermingling of molecules is called _________ .
- Ice on absorption of heat converts to ‘X’ a procee called _________ . ‘X’ changes to water vapour on _________ . Water vapour changes back to ‘X’ on _________ . The constant temperature at which ice changes into ‘X’ is called its _________ .
Answer-1
- From the three states of matter, solids expand the least.
- Brownian movement is maximum in gases.
- Cohesive forces are negligible in gases.
- Matter can change from one state to another by change in temperature or pressure.
- The space between atoms [molecules] of solids is minimum.
- Intermingling of molecules is called diffusion.
- Ice on absorption of heat converts to ‘X’ a process called melting. ‘X’ changes to water vapour on heating. Water vapour changes back to ‘X’ on condensation. The constant temperature at which ice changes into ‘X’ is called its fusion point.
Question-.2.
State which of the following are physical properties of a substance.
- Chlorine gas has a – strong irritating odour.
- Sodium nitrate is soluble in water, but calcium carbonate is not.
- Magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, liberating hydrogen gas.
- Manganese dioxide, a catalyst which alters the rate of a chemical reaction is black in colour.
- The melting point of ice is 0°C
- Lead chloride reacts with barium sulphate to give a white precipitate of lead sulphate.
- Water acidified with dilute sulphuric acid is a good conductor of electricity.
- Naphthalene on heating directly turns into vapour.
- Hydrogen sulphide gas has a strong rotten egg odour.
- Sulphur is a yellow amorphous powder insoluble in water.
Answer-2
- Physical
- Physical
- Chemical
- Chemical
- Physical
- Chemical
- Physical
- Chemical
- Physical
- Physical
Question-.3.
Match the characteristics of the three states of matter in List I with their correct answer from List II.
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Are highly rigid and have a definite shape | A : Solids and gases only |
| 2. Have no definite shape | B : solids only |
| 3. Have a definite volume but no definite shape | C : Liquids and gases only |
| 4. Are highly compressible and least rigid | D : Gases only |
| 5. Have no definite volume | E : Solids, liquids and gases |
| 6. Have no definite shape and volume | F : Liquids only |
| 7. Occupy space | G : Solids and liquids only |
| 8. Are not compressible | |
| 9. Are slightly compressible | |
| 10. Have mass |
Answer-3:
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Are highly rigid and have a definite shape | B : solids only |
| 2. Have no definite shape | C : Liquids and gases only |
| 3. Have a definite volume but no definite shape | F : Liquids only |
| 4. Are highly compressible and least rigid | D : Gases only |
| 5. Have no definite volume | D : Gases only |
| 6. Have no definite shape and volume | D : Gases only |
| 7. Occupy space | E : Solids, liquids and gases |
| 8. Are not compressible | B : solids only |
| 9. Are slightly compressible | F : Liquids only |
| 10. Have mass | E : Solids, liquids and gases |
Question-.4.
Match the arrangement of atoms in the three states of matter in List I with the correct state in List II.
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Arrangement of atoms is far apart | A : Solids |
| 2. Force of attraction between atoms is very strong | B : liquids |
| 3. Movement of atoms is in any random direction | C : Gases |
| 4. Particles diffuse very easily | |
| 5. Particles show movement about their own position |
Answer-4:
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Arrangement of atoms is far apart | C : Gases |
| 2. Force of attraction between atoms is very strong | A : Solids |
| 3. Movement of atoms is in any random direction | C : Gases |
| 4. Particles diffuse very easily | C : Gases |
| 5. Particles show movement about their own position | A : Solids |
Question-.5.
State the correct term from A, B, C, D, E or F in List II which represents the change of state of matter or its relevant property from List I.
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Solid ‘X’ to liquid ‘Y’ | A : Condensation |
| 2. Liquid ‘Y’ to its vapour ‘Z’ | B : Vaporization |
| 3. ‘Z’ to ‘Y’ | C : Melting |
| 4. ‘Y’ to ‘X’ | D : Freezing |
| 5. The temperature at which ‘Y’ changes to ‘Z’ | E : Melting point |
| F : Boiling point |
Answer-5:
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| 1. Solid ‘X’ to liquid ‘Y’ | C : Melting |
| 2. Liquid ‘Y’ to its vapour ‘Z’ | B : Vaporization |
| 3. ‘Z’ to ‘Y’ | A : Condensation |
| 4. ‘Y’ to ‘X’ | D : Freezing |
| 5. The temperature at which ‘Y’ changes to ‘Z’ | F : Boiling point |
.– : End of Class-6 Matter Dalal Simplified Solutions :–
Return to – Dalal Simplified Chemistry for ICSE Class-6 Solutions
Thanks
Share with your friends.