Economics Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B Solved for ICSE Class-10. Step by step solutions as council prescribe guideline of model sample question paper. Student can achieve their goal in next upcoming exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10..
Solutions of ICSE Class 10 Economics Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B
| Board | ICSE |
| Class | 10th (x) |
| Subject | Economics |
| Topic | Specimen Paper Solved |
| Syllabus | Revised Syllabus |
| Session | 2022-23 |
| Sec-B | Descriptive |
ICSE Economics Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Question 5:
(i) Explain five important features of perfect competition market.
(ii) (a) What do you mean by law of demand? (b) Discuss any three exceptions to law of demand.
Answer:
(i) There are five characteristics that have to exist in order for a market to be considered perfectly competitive. The characteristics are homogeneous products, no barriers to entry and exit, sellers are price takers, there is product transparency, and no seller has influence over the prices in the market.
(ii) (a) The law of demand states that other factors being constant (cetris peribus), price and quantity demand of any good and service are inversely related to each other. When the price of a product increases, the demand for the same product will fall.
(b) The three exceptions to the law of Demand are
Giffen goods: A Giffen good is a low-income, non-luxury product for which demand increases as the price increases and vice versa. A Giffen good has an upward-sloping demand curve which is contrary to the fundamental laws of demand which are based on a downward sloping demand curve.
Veblen effect: Abnormal market behavior where consumers purchase the higher-priced goods whereas similar low-priced (but not identical) substitutes are available.
income change: Changes in real income can result from nominal income changes, price changes, or currency fluctuations. When nominal income increases without any change to prices, this means consumers can purchase more goods at the same price, and for most goods, consumers will demand more.
Question 6:
(i) Explain any five rights of a consumer.
(ii) (a) Define capital formation. (b) Explain any three characteristics of capital.
Answer: (i) five rights of a consumer.
- Right to be informed: An important component of consumer protection is the right to be informed. Adequate and accurate information about quality, quantity, purity, standard and the price of goods and services must be provided to consumers. This information helps consumers in their buying decision and use of the product.
- Right to seek redressal: Consumers have been given the right to redress their grievances relating to the performance, grade, quality etc. of goods and services. In case of any defect, the product must be repaired or replaced by the seller. The Consumer Protection Act has duly provided for a fair settlement of genuine grievances of consumers. It has also set up a proper mechanism for their redressal at the district, state and national levels.
- Right to safety: Every consumer has the right to be safeguarded against those goods and services which can be hazardous to life, health or property.
- Right to choose: Consumers have the right to choose from a variety of goods and services at competitive prices as per their own wishes, tastes and preferences.
- Right to be heard: A consumer has the right to seek redressal and compensation in case of any exploitation.
(ii) (a) Capital formation is a concept used in macroeconomics, national accounts and financial economics. Occasionally it is also used in corporate accounts.
(b) three characteristics of capital.
1. Capital is a Passive Factor: Capital is a passive factor of production. This is so because capital is ineffective without the cooperation of labor.
2. Capital is Man-Made : Capital is a man-made thing. Its production and supply is controlled by the efforts of man.
John Stuart Mill says, capital is the “accumulated product of past labor destined for the production of future wealth”. This means that capital is generated when human labor is applied to natural resources.
3. Capital is not Indispensable: Capital is not an indispensable factor of production like labor and land. This would mean that production can be possible even without capital.
Question 7:
(i) Explain any five determinants of individual demand.
(ii) Differentiate between increase in supply and decrease in supply.
Answer: (i) The five determinants of demand are:
- The price of the good or service
- The income of buyers
- The prices of related goods or services—either complementary and purchased along with a particular item, or substitutes bought instead of a product
- The tastes or preferences of consumers will drive demand
- Consumer expectations about whether prices for the product will rise or fall in the future
(ii) When more quantity of a commodity is supplied at the same price it is called increase in supply. When less quantity of a commodity is supplied at the same price it is called decrease in supply.
Question 8:
(i) Mention five points of difference between direct and indirect taxes.
(ii) Explain any five economic causes for the growth of public expenditure in India in recent time.
Answer: (i) difference between direct and indirect taxes.
- Direct tax is levied and paid for by individuals, Hindu undivided Families (HUF), firms, companies etc. whereas indirect tax is ultimately paid for by the end-consumer of goods and services.
- The burden of tax cannot be shifted in case of direct taxes while burden can be shifted for indirect taxes.
- Lack of administration in collection of direct taxes can make tax evasion possible, while indirect taxes cannot be evaded as the taxes are charged on goods and services.
- Direct tax can help in reducing inflation, whereas indirect tax may enhance inflation.
- Direct taxes have better allocative effects than indirect taxes as direct taxes put lesser burden over the collection of amount than indirect taxes, where collection is scattered across parties and consumers’ preferences of goods is distorted from the price variations due to indirect taxes.
(ii) There is a continuous growth in public expenditure in developing countries like India due to various reasons as follows:
- Increase in the Activities of the Government: These functions include the spread of education, public health, public works, public recreation, social welfare schemes etc. It is observed that new functions are continuously being undertaken and old functions are being performed more efficiently on a large scale by the government. This leads to an increase in public expenditure.
- Growing Urbanization: Rapid spread of urbanization is a global phenomenon of the day. This leads to an increase in the government expenditure on water supply, roads, energy, schools and colleges, public transport, sanitation etc.
- Increasing Defense Expenditure: In modern times, the defence expenditure of the government is increasing even in peacetime due to unstable and hostile international relationships.
- Spread of Democracy: Majority of the countries in the world are democratic in nature. A democratic form of government is expensive due to regular elections and other such activities. It results in an increase in the total expenditure of the government.
- Disaster Management: Many natural and man-made calamities like earthquakes, floods, cyclones, social unrest etc. are occurring more frequently. The government has to spend a huge amount on disaster management which increases total expenditure. Modern governments are working for ‘welfare state’. Hence, there is a continuous increase in public expenditure.
Question 9:
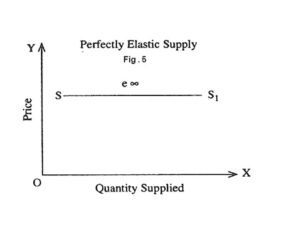
(i) Draw a graphical figure showing perfectly elastic supply.
(ii) (a) Define a commercial bank. (b) Explain any two types of deposits accepted by commercial banks.
Answer: a graphical figure showing perfectly elastic supply.
(ii) (a) A commercial bank is a financial institution which accepts deposits from the public and gives loans for the purposes of consumption and investment to make profit.
(b) Current Account: A current account, also known as financial account is a type of deposit account maintained by individuals who carry out significantly higher number of transactions with banks on a regular basis.
Recurring Deposits: A Recurring Deposit, commonly known as RD, is a unique term-deposit that is offered by Indian Banks.
Question 10:
(i) Explain any two quantitative method of controlling money supply of a central bank.
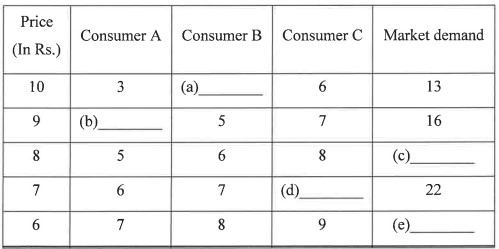
(ii) Fill in the following market demand table:
Answer:
(i) two quantitative method of controlling money supply of a central bank.
Bank Rate: Bank rate, also known as discount rate in American English, is the rate of interest which a central bank charges on its loans and advances to a commercial bank.
(b) Open Market Operations (OMOs): The purchase and sale of securities in the open market by a central bank–are a key tool used by the Federal Reserve in the implementation of monetary policy.
(ii) update soon
–: End of Economics Specimen Paper 2023 Sec-B Solved for ICSE Class-10 :—
Return to : ICSE Specimen Paper 2023 Solved
–: visit also :–
- ICSE Class-10 Textbook Solutions Syllabus Solved Paper Notes
- School will be closed on These Dates in August, Check Total Holidays
- High Salary Top Courses After 12th Science for Boys / Girls
- Which School Board is Better for IIT JEE and NEET Preparation?
- Which Entrance Exam Is Easier To Crack – NEET, IIT, JEE?.
- CISCE 2023 Exam: Clue of Board Paper Standard
- ICSE Board Paper Class-10 Solved Previous Year Question
Thanks