Genetics Biology ICSE Class-10th Concise Selina Solutions- Some Basic Fundamental Chapter-3. .Step by Step Selina Solutions of Progress Check 1, 2, 3, 4 ,MCQ ,Very Short , Descriptive Type and Structural /Skill Type Questions . Selina Publications series Books are most popular among ICSE student. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publishers PVT LTD |
| Subject | Concise Biology |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | HS Vishnoi |
| Chapter-3 | Genetics (Some Basic Fundamental ) |
| Topics | Solutions of MCQs, Very Short ,Descriptive and Structural/Skill Questions and Progress Check |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Genetics Biology ICSE Class-10th Concise Selina Solutions- Some Basic Fundamental Chapter-3
-: Select Topics :-
A-MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE
D. LONG ANSWER TYPE
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
A. Multiple Choice Type, Genetics Biology ICSE Class-10th Concise Selina Solutions- Some Basic Fundamental Chapter-3
(Page 34)
Question 1
Which one of the following is the phenotypic monohybrid ratio in F2 generation?
a) 3 : 1
b) 1 : 2 : 1
c) 2 : 2
d) 1 : 3
Answer :
a) 3 : 1
Question 2
If a pure tall plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant, then offspring will be
(a) all tall
(b) all dwarf
(c) 3 tall 1 dwarf
(d) 50% tall 50% dwarf
Answer
(a) all tall
Question 3
The 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 dihybrid ratio is due to
(a) segregation
(b) crossing over
(c) independent assortment
(d) homologous pairing
Answer
(c) independent assortment
Question 4
A plant with green pods and smooth seeds with genotype Ggss will give rise to the following gametes:
(a) Gg and Ss
(b) Gs and ss
(c) Gs and gs
(d) Gg and gs
Answer
(c) Gs and gs
Genetics Biology ICSE Class-10th Concise Selina Solutions- Some Basic Fundamental , B. Very Short Answer Type
(Page 34-35)
Question 1
Match the terms in column I with their the explanations in column II
| Column I
(Term) |
Column II
(Explanation) |
|
| a | Genetics | (i) Chromosomes similar in size and shape |
| b | Autosomes | (ii) The alternative forms of a gene |
| c | Recessive gene | (iii) Study of laws of inheritance of characters |
| d | Allele | (iv) A gene that can express when only in a similar pair |
| e | Homologous chromosomes | (v) Chromosomes other than the pair of sex chromosomes |
Answer
(a) – (iii) Study of laws of inheritance of characters
(b) – (v) Chromosomes other than the pair of sex chromosomes
(c) – (iv) A gene that can express when only in a similar pair
(d) – (ii) The alternative forms of a gene
(e) – (i) Chromosomes similar in size and shape
Question 2
Name any two genetic diseases in humans.
Answer
Colour-blindness, Thalassaemia, Sickle cell anaemia and Haemophilia (Any two)
Question 3
Which one of the following genotypes is homozygous dominant and which one homozygous recessive in regard to tongue rolling:
Rr, rr, RR?
Answer
Homozygous dominant – RR
Homozygous recessive – rr
Genetics – Some Basic Fundamental, Biology ICSE Class-10th Concise Selina Solutions C. Short Answer Type
(Page 35)
Question 1 :
Differentiate between:
(a) Genotype and Phenotype
(b) Character and Trait
(c) monohybrid and dihybrid cross (phenotypic ratio in F2 generation).
Answer :
(a)
| Phenotype | Genotype |
| The observable characteristic which is genetically controlled is called phenotype. | The set of genes present in the cells of an organism is called its genotype. |
(b)
| Character | Trait |
| Any heritable feature is called a character. | The alternative form of a character is called trait. |
(b)
| Monohybrid cross | Dihybrid cross |
| Phenotypic ratio – 3:1 | Phenotypic ratio- 9:3:3:1 |
Question 2 :
Among lion, tiger and domestic cat, all the three have the same number of 38 chromosomes, yet they have different appearances. How do you account for such differences?
Answer :
The characteristics of a species such as physical appearance, body functions and behavior are not only the outcome of chromosome number, but these depend on the genotype of every organism. That means the set of genes present in the organisms may very and therefore lion, tiger and domestic cat have the same number of 38 chromosomes, their characteristics (like different appearances) are the result of the genes located on the chromosomes.
Question 3 :
List any three features of garden pea with their dominant and recessive traits.
Answer :
Features of garden pea :
| Character | Dominant trait | Recessive trait |
| Flower Colour | Purple | White |
| Seed Colour | Yellow | Green |
| Seed Shape | Round | Wrinkled |
| Pod Shape | Inflated | Constricted |
| Flower Position | Axial | Terminal |
Question 4 :
Explain why generally only the male child suffers from colour blindness and not the female?
Answer :
Colour-blindness is caused due to recessive genes which occur on the X chromosome.
Males have only one X chromosome. If there is recessive gene present on X chromosome, then the male will suffer from colour-blindness.
Females have two X chromosomes. It is highly impossible that both the X chromosomes carry abnormal gene. Hence, if one gene is abnormal and since it is recessive, its expression will be masked by the normal gene present on the other X chromosome. Females are unlikely to suffer from colour-blindness.
D. Descriptive Type,
Genetics – Some Basic Fundamental, Biology ICSE Class-10th Concise Selina Solutions
(Page 53 )
Question 1 :
Define the following terms :
(a) Pedigree chart
(b) Variation
(c) Mutation
Answer :
(a) Pedigree Chart: A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance or phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors from one generation to the next. In the pedigree chart, males are shown by squares and females by circles.
(b) Variation : Any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or by the effect of environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials (phenotypic variation).
(c) Mutation : Mutation occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. A Mutagen is an agent of substance that can bring about a permanent alteration to the physical composition of a DNA gene such that the genetic message is changed.
Question 2 :
State the three Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
Answer :
Mendel’s laws of inheritance are:
(i) Law of Dominance Out of a pair of contrasting characters present together, only one is able to express itself while the other remains suppressed. The one that expresses is the dominant character and the one that is unexpressed is the recessive one.
(ii) Law of Segregation : The two members of a pair of factors separate during the formation of gametes. The gametes combine together by random fusion at the time of zygote formation. This law is also known as ‘law of purity of gametes’.
(iii) Law of Independent Assortment: When there are two pairs of contrasting characters, the distribution of the members of one pair into the gametes is independent of the distribution of the other pair.
Question 3 :
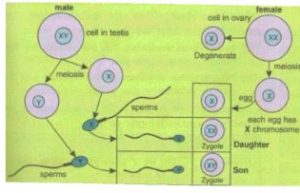
Does the sex of the child depend on the father or is it just a matter of chance? Discuss.
Answer :
The sex of the child depends on the father. The egg contains only one X chromosome, but half of the sperms contain X-chromosome whereas the other half contains Y-chromosome. It is simply a matter of chance as to which category of sperm fuses with the ovum and this determines whether the child will be male or female.
If the egg fuses with X-bearing sperm, the resulting combination is XX and the resulting child is female.
If the egg fuses with Y-bearing sperm, the resulting combination is XY and the resulting child is male.
E. Structured / Application and Skill Type
(Page 35)
Question 1 :
In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring, when both parents are ‘Bb’ or have heterozygous black fur.
Answer :
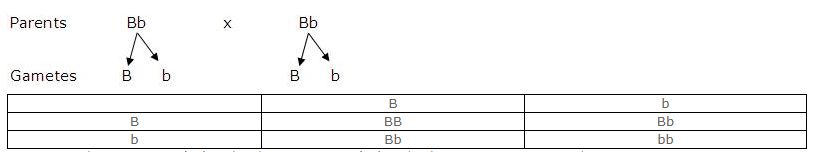
Genotype – 1(Homozygous Black Fur) :2 (Heterozygous Black Fur):1 (Homozygous Brown Fur)
Phenotype – 3 (Black Fur) :1(Brown Fur)
Question 2 :
Two pairs (A & B) of rabbits were crossed as given below:

(a) Can you tell which coat colour (black or white) is dominant?
(b) Is the coat colour sex-linked?
Answer :
(a) Black
(b) No
Question 3 :
Make a Punnett square for finding out the proportion of different genotypes in the progeny of a genetic cross between
(a) A pure tall (TT) pea plant with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant.
(b) Red flower variety of pea (RR) with white flower variety of pea (rr).
Answer :
(a)

Genotype – 1(Homozygous red) :2 (Heterozygous red):1 (Homozygous white)
Phenotype – 3 (Red) :1(White)
Question 4 :
A family consists of two parents and their five children and the pedigree chart shown below shows the inheritance of the trait colour blindness in them.
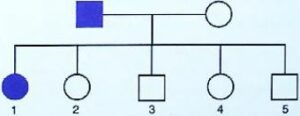
(a) Who is colour blind in the parents – the Father or the Mother?
(b) How many daughters and how many sons have been born in the family?
(c) What does the child 1 indicate about this trait?
(d) On which chromosome is the gene of this trait located?
(e) Name one other trait in humans which follows a similar pattern of inheritance.
Answer
(a) Father
(b) Two sons and three daughters
(c) The child 1 (daughter) is colour blind
(d) X chromosome
(e) Haemophilia
Return to Concise Selina ICSE Biology Solutions Class-10
Thanks