Linear Symmetry Class-6 RS Aggarwal ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-21 Solutions. We provide step by step Solutions of Exercise / lesson-21 Linear Symmetry for ICSE Class-6 RS Aggarwal Mathematics.
Our Solutions contain all type Questions with Exe-21 with Notes on Linear Symmetry to develop skill and confidence. Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-6 Mathematics.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Goyal brothers Prakshan |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 6th |
| Chapter-21 | Linear Symmetry |
| Writer | RS Aggrawal |
| Book Name | Foundation |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-21 |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
Linear Symmetry Class-6 RS Aggarwal ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-21 Solutions
Symmetry is when one shape becomes exactly like another if one flips, slide or turn it.
Axis of symmetry.
If a line divides a given figure into two identical halves, then the given figure is symmetrical about that line and the line is called the axis of symmetry.
Line of symmetry
When a figure is folded along a line such a way that the two parts exactly fit on top of each other, then the figure is said to have a line symmetry.
If a line divides a given figure into two identical halves, then the given figure is symmetrical about that line and the figure is said to have a line symmetry.
A figure has one line of symmetry, if there is a line about which the figure may be folded so that the two parts of the figure coincide each other completely.
Line of symmetry is the line which divides figure into two identical parts and these are mirror image of each others.
A figure may have no line of symmetry, only one line of symmetry, two lines of symmetry or multiple lines of symmetry.
Symmetry And Line Of Symmetry Definition
The symmetry of an object is defined as one half of the object is a mirror image of the other half. When an object is split into half, both the sides are exactly the same. The line which divides them is called the line of symmetry. One simple example is reflection symmetry. The object can be divided into one or more than one lines of symmetry
| S.NO | Type | Example |
| 1 | No line of symmetry | Scalene triangle |
| 2 | 1 line of symmetry | Isosceles triangle |
| 3 | 2 lines of symmetry | Rectangle |
| 4 | 3 lines of symmetry | Equilateral triangle |
Bilateral symmetry
If a figure is divided into two halves by only one line and these halves overlap each other completely, then the figure is said to have bilateral symmetry.
Example: A butterfly shows bilateral symmetry
Line symmetry
A figure has line symmetry if a line can be drawn dividing the figure into two symmetrical parts. The line is called a line of symmetry.
Point Symmetry
Point symmetry exists when a figure is drawn around a single central point.
It is for figures having a point through which the symmetry can be established. This point is called the centre of symmetry.
Linear Symmetry Class-6 RS Aggarwal ICSE Maths Goyal Brothers Prakashan Chapter-21 Solutions
Exe-21
Page 251-252
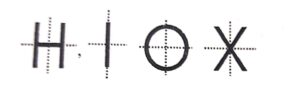
Question 1:
Which letters of English alphabet have two lines of symmetry ?
Answer :
These English Alphabet have two lines of symmetry :
Question 2:
Which letters of English alphabet have no line of symmetry ?
Answer :
In English Alphabet have no line of symmetry is :
F, G, J, L, N, P, Q, R, S, Z.
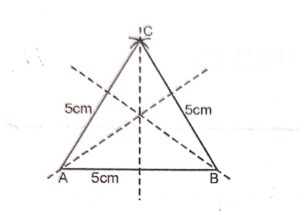
Question 3:
Construct a triangle ABC in which AB = BC= CA. Draw all the lines of symmetry of the triangle. How many lines of symmetry does the triangle have ?
Answer :
Constructions :
(i) Draw line segment AB = 5 cm.
(ii) With centre A and B and radius of 5 cm Draw arcs intersecting each other at C.
(iii) Join the CA and CB.
(iv) triangle CAB is the require triangle.
(v) Draw angle bisector of angle A, angle B and angle C.
These are three line symmetry of triangle CAB.
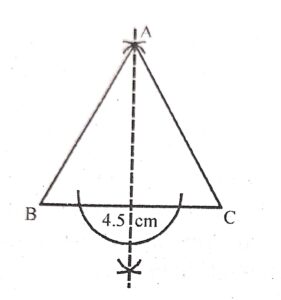
Question 4:
Construct a triangle ABC in which AB = AC= 5 cm and BC = 4.5 cm. Draw all its lines of symmetry. How many such lines are there ?
Answer :
Constructions :
(i) Draw line segment BC = 4.5 cm.
(ii) From B and C cut of arcs equal to 5 cm; which intersect each other at A
(iii) Join the AB and AC.
(iv) With A as centre, Draw a perpendicular bisector of line BC which is the only line of symmetry of the triangle ABC.
Question 5:
Draw a square of side 4 cm each. Draw all lines of its symmetry.
Answer :
Constructions :
(i) Make a square ABCD of sides 4 cm each.
(ii) Draw angle bisector of angle A, angle B, angle C, and angle D.
(iii) Draw perpendicular bisector of any two opposite lines.
(iv) These are the four line of symmetry of square ABCD.
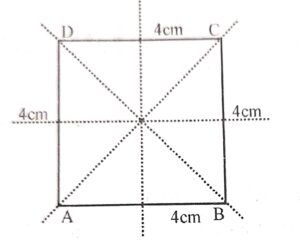
Question 6:
Which of the following are true statements :
(i) A scalene triangle has no line of symmetry.
(ii) An equilateral triangle has three line of symmetry .
(iii) An isosceles triangle has two lines of symmetry.
(iv) A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry.
(v) None of these letter J, F, N, G has a line of symmetry.
Answer :
(i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) True
(v) True
Question 7:
Draw a line of symmetry for each of the following :
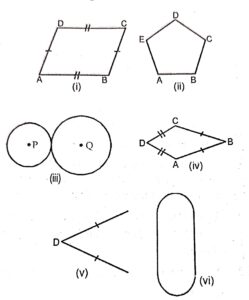
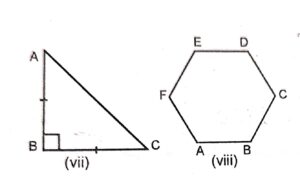
Answer :
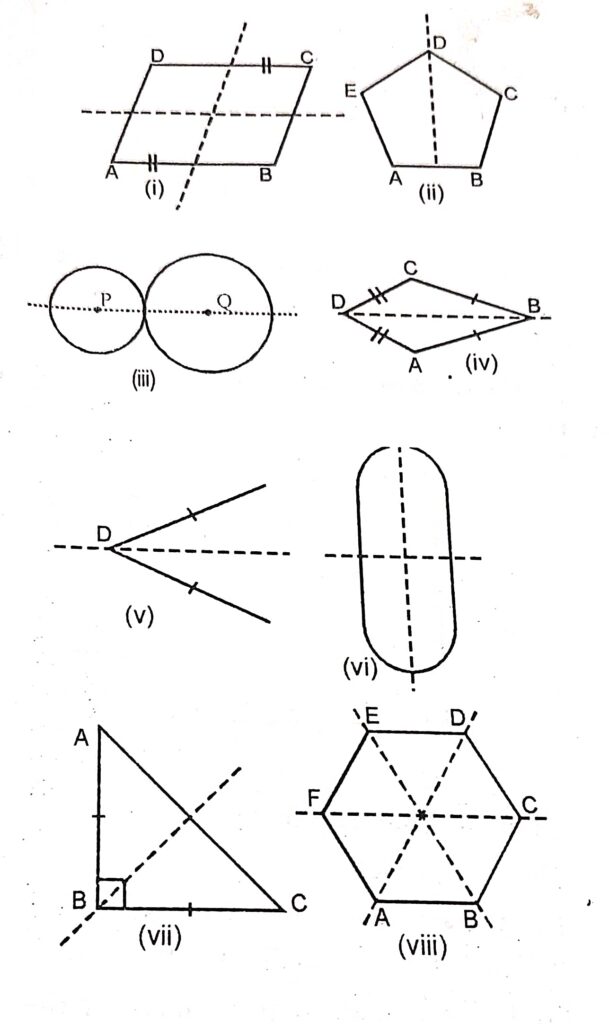
Question 8:
Find the line of symmetry of :
(i) The segment of a circle.
(ii) The sector of a circle
(iii) The arcs of a circle
Answer :
(i) Segment of a circle : It has one line of symmetry.
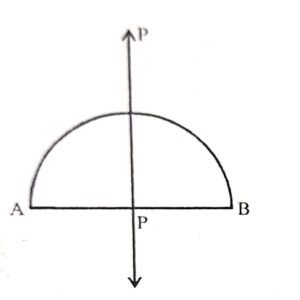
(ii) Sector of a circle : It has one line of symmetry.
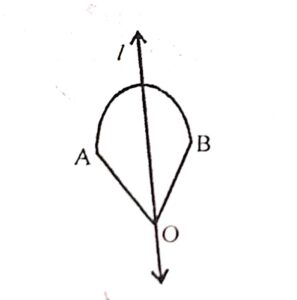
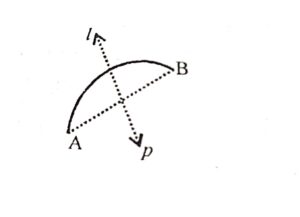
(iii) Arc of a circle : It has one line of symmetry .
–: End of Linear Symmetry Class-6 RS Aggarwal Solutions :–
Return to- RS Aggarwal Solutions for ICSE Class-6 Goyal Brothers Prakashan
Thanks