OP Malhotra Circle Class-9 S.Chand ICSE Maths Ch-13. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Exe-13(a), Exe-13(b), with Chapter Test of S Chand OP Malhotra Maths . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-9.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | S. Chand |
| Subject | Maths |
| Class | 9th |
| Chapter-13 | Circle |
| Writer | OP Malhotra |
| Topics | Solution of Exe-13(a), Exe-13(b), with Chapter Test |
| Academic Session | 2021-2022 |
OP Malhotra Circle Class-9 S.Chand ICSE Maths Ch-13
-: Select Topics :-
Exercise-13
OP Malhotra Circle Class-9 S.Chand ICSE Maths Ch-13
Circle and line in a plane :
For a circle and a line on a plane, there can be three possibilities.
i) they can be non-intersecting
ii) they can have a single common point: in this case, the line touches the circle.
ii) they can have two common points: in this case, the line cuts the circle.
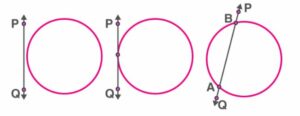
Tangent :
A tangent to a circle is a line which touches the circle at exactly one point. For every point on the circle, there is a unique tangent passing through it.
Secant :
A secant to a circle is a line which has two points in common with the circle. It cuts the circle at two points, forming a chord of the circle.
Circle:
A circle is a collection of all points in a plane which are at a constant distance from a fixed point.
Centre:
The fixed point is called the centre.
Radius:
The constant distance from the centre is called the radius.
Chord:
A line segment joining any two points on a circle is called a chord.
Diameter:
A chord passing through the centre of the circle is called diameter. It is the longest chord.
Tangent:
When a line meets the circle at one point or two coincidings The line is known as points, a tangent.
The tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
⇒ OP ⊥ AB

The lengths of the two tangents from an external point to a circle are equal.
⇒ AP = PB
Length of Tangent Segment
PB and PA are normally called the lengths of tangents from outside point P.
Properties of Tangent to Circle
Theorem 1: Prove that the tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
Given: XY is a tangent at point P to the circle with centre O.
To prove: OP ⊥ XY
Construction: Take a point Q on XY other than P and join OQ
Proof: If point Q lies inside the circle, then XY will become a secant and not a tangent to the circle
OQ > OP

This happens with every point on the line XY except the point P. OP is the shortest of all the distances of the point O to the points of XY
OP ⊥ XY …[Shortest side is the perpendicular]
Theorem 2: A line drawn through the end point of a radius and perpendicular to it, is the tangent to the circle.
Given: A circle C(O, r) and a line APB is perpendicular to OP, where OP is the radius.
To prove: AB is tangent at P.
Construction: Take a point Q on the line AB, different from P and join OQ.
Proof: Since OP ⊥ AB
OP < OQ ⇒ OQ > OP

The point Q lies outside the circle.
Therefore, every point on AB, other than P, lies outside the circle.
This shows that AB meets the circle at point P.
Hence, AP is a tangent to the circle at P.
Theorem 3: Prove that the lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal
Given: PT and PS are tangents from an external point P to the circle with centre O.
To prove: PT = PS
Construction: Join O to P, T and S.

Exercise-13 (a)
OP Malhotra Circle Class-9 S.Chand ICSE Maths Ch-13
Question 1:
Calculate the length of a chord which is at a distance of 12 cm from the circle of radius 13 cm.
Question 2:
In the figure, the radius of the given circle, ……….. calculate its length.
Question 3:
…………………..
……………………
……………………
Question 21:
In the figure, AB and CD are equal chords of a circle whose centre is …………….. angle ONM.
Exercise-13 (b)
OP Malhotra Circle Class-9 S.Chand ICSE Maths Ch-13
Question 1:
Find :
(i) ……………..
…………………..
Question 2:
Triangle ABC is inscribed in a circle and angle P = angle Q Prove that ………….
Question 3:
……………………..
………………………
…………………….
Question 9:
Each side of a regular hexagon, inscribed in a circle subtends an angle 60 degree at the centre and is equal to the radius of the circle prove it.
Chapter Test
OP Malhotra Circle Class-9 S.Chand ICSE Maths Ch-13
Question 1:
Which type of triangle can be constructed with a ……….. 8 cm sides ?
Question 2:
Give all name that apply to figure.
……………
Question 3:
……………………
……………………
……………………
Question 32:
In the figure, YZ is parallel to MN, XY is parallel to LM and XZ is parallel to Ln. Them MY is
…………………….
— : End of Circle OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions :–
Return to :– OP Malhotra S Chand Solutions for ICSE Class-9 Maths
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends