Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Solutions Chapter-12. We Provide Step by Step Answer of Intext Questions, Exe-12 A, Exe-12 B, Exe-12 C, Exe-12 D, Exe-12 E, Exe-12 F, Miscellaneous and Previous Year Questions of Exercise-12 Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 . Visit official Website CISCE for detail information about ICSE Board Class-10.
| Board | ICSE |
| Publications | Selina Publishers PVT LTD |
| Subject | Concise Chemistry |
| Class | 10th |
| writer | Dr SP Singh |
| Chapter-12 | Organic Chemistry |
| Topics | Solutions of Intext Questions, Exe-12 A, Exe-12 B, Exe-12 C, Exe-12 D, Exe-12 E, Exe-12 F, Miscellaneous and Previous Year Questions of Exercise-12 |
| Edition | 2021-2022 |
Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Concise Selina Solutions Chapter-12
-: Select Topics :-
How to Solve Organic Chemistry for ICSE Class-10
Focus on Nomenclature of Organic Compound. Chemical Properties with reaction of Alkane, Alkene Alkyne, and Alcohol. Conversion of Organic Compound. Lab preparation of organic Compound and its uses.
Before viewing Solution of Selina Concise Chapter-12 Organic Chemistry . Read the Chapter -12 Organic Chemistry Carefully to understand the concept in better way .
Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Chapter-12 Intext
Page-188
Question 1
(a) What are organic compounds?
(b) What is the Vital force theory? Why was it discarded?
Answer 1
(a) Organic chemistry may be defined as the chemistry of hydrocarbons and its derivatives.
(b) Vital Force Theory is a theory made by the Scientist Berzelius in 1809 which assumed that organic compounds are only formed in living cells and it is impossible to prepare them in laboratories.
It was discarded because Friedrich Wohler showed that it was possible to obtain an organic compound(urea) in the laboratory.
Question 2
(a) Name a few sources of organic compounds
(b) Give the various applications of organic chemistry
Answer 2
(a) Few sources of organic compounds are:
Plants
Animals
Coal
Petroleum
Wood
(b) The various applications of organic chemistry is:
It is used in the production of soaps, shampoos, powders and perfumes.
Various fuels like natural gas, petroleum are also organic compounds.
The fabrics that we use to make various dresses are also made from organic compounds.
Question 3
Organic chemistry plays a key role in all walks of life. Discuss
Answer 3
Organic compounds are present everywhere. They are present in:
It is present in the production of soaps, shampoos, powders and perfumes.
It is present in the food we eat like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins etc.
Fuel like natural gas, petroleum are also organic compounds.
Medicines, explosives, dyes, insecticides are all organic compounds.
Thus we can say that organic compounds play a key role in all walks of life.
Question 4
Carbon shows some unique properties, name them.
Answer 4
The unique properties shown by carbon are:
Tetravalency of carbon
Catenation
Isomerism
Question 5
Explain the following:
(a) Tetra valency
(b) Catenation
Answer 5
(a) Tetra valency: Carbon can neither lose nor gain electrons to attain octet. Thus it shares four electrons with other atoms. This characteristics of carbon by virtue of which it forms four covalent bonds, is called Tetra valency of carbon.
In structural form :
![]()
(b) Catenation: The property of self -linking of atoms of an element through covalent bonds in order to form straight chains, branched chains and cyclic chains of different sizes is known as catenation.
Carbon- carbon bond is strong so carbon can combine with other carbon atoms to form chains or rings and can involve single, double and triple bonds.
Question 6
Write any four properties of organic compounds that distinguish them from inorganic compounds.
Answer 6
Four properties of organic compound that distinguish them from inorganic compounds are:
(i) Presence of carbon.
(ii) Solubility in the organic solvents.
(iii) Forming of covalent bonds.
(iv) Having low melting and boiling points.
Question 7
Why are organic compounds studied as a separate branch of chemistry?
Answer 7
Due to the unique nature of carbon atom, it gives rise to formation of large number of compounds. Thus this demands a separate branch of chemistry.
Question 8
What are Hydrocarbons? Compare saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?
Answer 8
Hydrocarbons are compounds that are made up of only carbon and hydrogen.
Comparison of saturated and Unsaturated hydrocarbons:
| Saturated Hydrocarbon | Unsaturated Hydrocarbon |
| 1. Carbon atoms are joined only by single bonds. | Carbon atoms are joined by double or by triple bonds. |
| 2. They are less reactive due to the non-availability of electrons in the single covalent bond. | They are more reactive due to presence of electrons in the double or the triple bond. |
| 3. They undergo substitution reaction. | They undergo addition reaction. |
Question 9
Give reason for the existence of large numbers of organic compounds
Answer 9
Due to presence of unique properties of carbon like Tetravalency, catenation and Isomerism large number of organic compounds are formed.
Question 10
Give at least one example in each case to show structure of isomers of
(a) Single bond compound
(b) Double bond compound
(c) Triple bond Compound
Answer 10
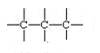
(a) Single Bond compound: For example: In pentane
![]()
(b) Double bond compound: For example:- In pentene
![]()
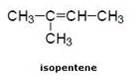
![]()
(c) Triple bond compound: In case of Hexyne:
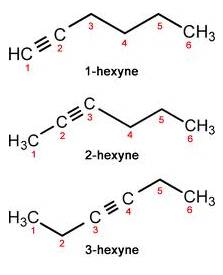
Question 11
Name a compound of each type and draw the figure.
(a) Cyclic compound with single bond
(b) Cyclic compound with triple bond
Answer 11
(a) Cyclic compound with single bond: cyclopentane
Structure:
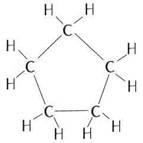
(b) Cyclic compound with triple bond: cyclopentyne
Structure:
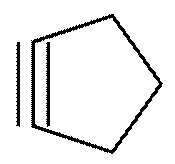
Question 12
Give the name of one member of each of the following:
(a) Saturated hydrocarbons
(b) Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Answer 12
The member of each of the following is:
(a) Saturated Hydrocarbon: Hexane (C6H14)
(b) Unsaturated Hydrocarbon: Hexene (C6H12)
Question 13
Define substitution and addition reaction .Give an example for each.
Answer 13
Substitution reaction: A reaction in which one atom of a molecule is replaced by another atom (or group of atoms) is called a substitution reaction.
Addition reaction: A reaction involving addition of atom(s) or molecules(s) to the double or the triple bond of an unsaturated compound so as to yield a saturated product is known as addition reaction.
Page-193
Question 1
Define a functional group and give the structural formula of the following functional group:
(a) Ketons
(b) Alcohols
(c) Aldehydes
Answer 1
A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that defines the structure (or the properties of a particular family) of organic compounds.
The structural formula of
(a) Halides :-R-X
Example:
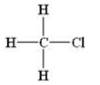
(b)Alcohols:- R-OH
Example:
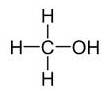
(c) Aldehydes:-R-CH=O
Example:
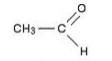
Question 2
Write the name and formula of the fourth member of the following homologous series:
(a) Alkyne
(b) Alcohol
Answer 2
(a) Butyne; its formula is C4H6.
(b) Butanol; its formula is C4H9OH.
Question 3
Which part of an organic compound determines
(i) Physical properties
(ii) Chemical properties
Answer 3
(i) Physical properties: The alkyl group determines the physical properties.
(ii) Chemical properties: The functional group is responsible for the chemical properties.
Question 4
Name the alkyl radical and the functional group of the following organic compounds:
(a) CH3OH
(b) C2H5OH
(c) C3H7CHO
(d) C4H9COOH
(e) CH3COOH
(f) HCHO
Answer 4
The alkyl radical and the functional group are:
| Sr.No | Formula | Name of alkyl radical | Name of Functional group |
| a | CH3OH | Methyl | Alcohol |
| b | C2H5OH | Ethyl | Alcohol |
| c | C3H7CHO | Propyl | Aldehyde |
| d | C4H9COOH | Butyl | Carboxyl |
| e | CH3COOH | CH3 | COOH |
| f | HCHO | H | CHO |
Question 5
(a) What is an alkyl group?
(b) Give the names of any three alkyl radicals. How are they formed?
Answer 5
(a) An alkyl group is obtained by removing one atom of hydrogen from an alkane molecule. Alkyl group is named by replacing the suffix ‘ane’ of the alkane with the suffix -yl.
(b) The name of three alkyl radicals are:
Methyl
Ethyl
Propyl
They are formed by removing 1 hydrogen from an alkane.
CH4 ![]() -CH3+H+
-CH3+H+
Methyl
CH3-CH3 ![]() CH3-CH2 -+ H+
CH3-CH2 -+ H+
Ethyl
CH3-CH2-CH3 ![]() CH3-CH2-CH2 -+ H+
CH3-CH2-CH2 -+ H+
Propyl
Question 6
Give the names and the structural formula of the first three members of the homologous series of alkanes
Answer 6
The names and the structural formula of first three members of the homologous series of alkane are:
(i)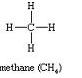
CH4Methane
(ii)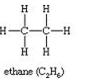
C2H6Ethane
(iii)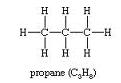
C3H8Propane
Question 7
(a) What is a Homologous series?
(b) What is the difference in the molecular formula of any two adjacent homologues:
(i) In terms of molecular mass
(ii) In terms of number and kind of atoms per molecule?
Answer 7
(a) A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having a similar structure and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by a CH2 group.
(b) The difference in molecular formula of any two adjacent homologues is
(i) It differs by 14 a.m.u in terms of molecular mass.
(ii) It differs by three atoms. The kind of atoms it differs is one carbon and two hydrogen.
Exercise-12 (A) Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Selina Solutions
Page-194
Question 1
(a)

Answer 1 (a)
2,2 dimethyl propane
Question 1 (b)
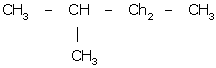
Answer 1(b)
2-methyl butane
Question 1(c)
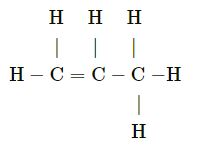
Answer 1(c)
Prop-1-ene
Question 1(d)
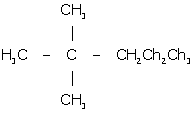
Answer 1 (d)
2,2-dimethyl pentane
Question 1(e)
CH3 – C = C – CH2CH2
Answer 1(e)
Pent-2-ene
Question 1(f)

Answer 1 (f)
3-methyl but-1-yne
Question 1(g)
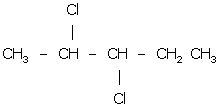
Answer 1(g)
2,3-dichloro pentane
Question 1(h)

Answer 1(h)
3-methyl heptane
Question 1(i)
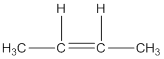
Answer 1 (i)
Bute-2-ene
Question 1(j)
![]()
Answer 1(j)
Hept-2-yne
Question 1(k)
Write the IUPAC name of the following:
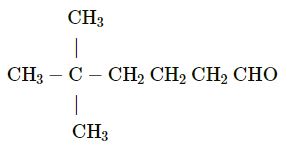
Answer 1(k)
structure of 2,2, di methyl hexanal
Question 1(l)
Write the IUPAC name of the following:
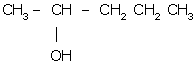
Answer 1(l)
Pent-2-ol
Question 1(m)

Answer 1(m)
2-methyl pent-1-oic acid
Question 1(n)
Write the IUPAC name of the following:

Answer 1(n)
2-bromo-2-methyl butane
Question 1(o)

Answer 1 (o)
1-bromo-3-methyl butane
Question 1(p)
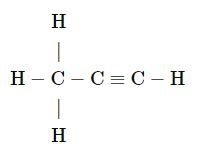
Answer 1 (p)
Prop-1-yne
Question 1(q)
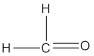
Answer 1 (q)
Methanal
Question 1(r)
Write the IUPAC name of the following:
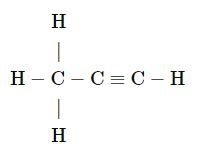 (2019)
(2019)
Answer 1(r)
Prop-1-yne
Question 1(t)
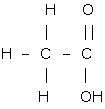
Answer 1(t)
Ethanoic acid
Question 1(u)
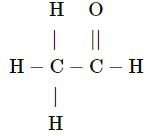
Answer-1(u)
ethenal
Question 1(v)
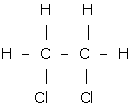
Answer 1(v)
1,2-dichloro ethane
Question 2
Write the structures of the following compounds:
(a) Prop-1-ene
(b) 2,3-dimethylbutane
(c) 2-methylpropane
(d) 3-hexene
(e) Prop-1-yne
(f) 2-methylprop-1-ene
(g) Alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O
Answer 2
The structure of the following compounds are:
(a) Prop-1-ene
CH3-CH=CH2
(b) 2,3-dimethylbutane
CH3-CH(CH3)-CH(CH3)-CH3
(c) 2-methylpropane
CH3-CH(CH3)-CH3
(d) 3-hexene
CH3-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-CH3
(e) Prop-1-yne
CH3-C?CH
(f) 2-methylprop-1-ene
CH3-C(CH3)=CH2
(g) Alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH
Question 3
Choose the correct answer:
(a) C5H11 is an
(i) Alkane (ii) Alkene (iii) Alkyne (iv) Alkyl group
(b) A hydrocarbon of the general CnH2n is
(i) C15H30 (ii) C12H26 (iii) C8H20 (iv) C6H14
(c) The total number of different carbon chains that four carbon atoms form in alkane is
(i) 5 (ii) 4 (iii) 3 (iv) 2
(d) CH3-CH2-OH and CH3-O-CH3 are
(i) Position isomers (ii) chain isomers (iii) homologous (iv) functional group isomers
(e) The IUPAC name of the compound is
![]()
(i) 3-trimethylhexane (ii) 3-methyl hexane (iii) 4-methyl hexane
Answer 3
(a)
Correct option (iv) CnH2n+1 is the formula for alkyl group. Hence it is C5H11.
(b)
Correct option (i) A hydrocarbon of general CnH2n is C15H30.
(c)
Correct option (iv) The total number of carbon chains that four carbon atoms form in alkane is 2.They are
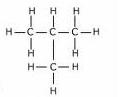
(d)
Correct option (iv) functional isomers as they have same molecular formula but different functional groups.
(e)
Correct option (ii) ![]()
The IUPAC name of this compound is: 3-methyl hexane.
Question 4
Fill in the blanks using the appropriate words given in the brackets :
(a) Propane and ethane are________. (Homologues, isomers)
(b) A saturated hydrocarbon does not participate in a/an _________ reaction.(substitution, addition)
(c) Succeeding members of a homologous series differ by______. (CH,CH2,CH3)
(d) As the molecular masses of hydrocarbons increase, their boiling points ______ and melting point ______. (increase, decrease)
(e) C25H52 and C50H102 belong to ______ homologous series.(the same, different)
(f) CO is an _______Compound.(organic, inorganic)
(g) The chemical properties of an organic compound are largely decided by the …….. and the physical properties of an organic compound are largely decided by the _______. (functional group, number of carbon atoms)
(h) CHO is the functional group of an______. (alcohol, aldehyde)
(i) The root in the IUPAC name of an organic compound depends upon the number of carbon atoms in______. (any chain, principal chain)
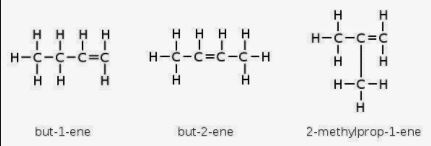
(j) But-1-ene and but-2-ene are examples of _____ isomerism. (Chain , position , functional)
Answer 4
(a) Propane and ethane are homologues.
(b) A saturated hydrocarbon does not participate in a/an addition reaction.
(c) Succeeding members of a homologous series differ by CH2.
(d) As the molecular masses of hydrocarbons increase, their boiling points Increase and melting point increase.
(e) C25H52 and C50H102 belong to the same homologous series.
(f) CO is an inorganic Compound.
(g) The chemical properties of an organic compound are largely decided by the functional group and the physical properties of an organic compound are largely decided by the number of carbon atoms.
(h) CHO is the functional group of an aldehyde.
(i) The root in the IUPAC name of an organic compound depends upon the number of carbon atoms in Principal Chain.
(j) But-1-ene and but-2-ene are examples of position isomerism.
Page-196
Question 5
Define or explain chain isomerism and position isomerism with examples in each case.
Answer-5
Chain isomerism :– Chain isomerism arises due to the difference in the arrangement of C atoms in the chain.
example:- there are two isomers of butane, C4H10. In one of them, the carbon atoms lie in a “straight-chain” whereas in the other the chain is branched.
Position isomerism:- It is due to the difference in the position of functional groups.
example:- there are two structural isomers with the molecular formula C3H7Br. In one of them, the bromine atom is at the end of the chain, whereas in the other it is attached in the middle.
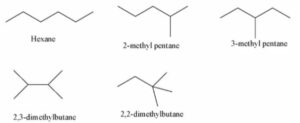
Question-6
(a) Define the term isomerism. State two main causes of isomerism.
(b) Draw the chain isomers of hexane (C6H14) .
(c) Draw position isomers of butane (C4H8) ?
Answer-6
(a) Isomerism: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formula are known as isomers and the phenomenon as isomerism.
Two main causes of isomerism :
Difference in mode of linking of atoms.
Difference in the arrangement of atoms or groups in space.
(b)
(c)
Question-7
Draw the structural formula for each of the following compounds:
(a) isomer of n-butane
(b) vinegar
(c) 2-propanol
(d) ethanol
(e) acetone
(f) diethyl ether
What is used to describe these compounds taken together?
Answer 7
(a) 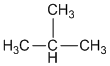
(b)
![]()
(c)
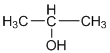
(d) ![]()
(e) 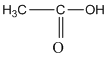
(f) ![]()
Question 8
(a) What is the special feature of the structure of
(i) ethene (C2H4 )
(ii) ethyne (C2H2 ) 2019
(b) What type of reaction is common to both these compounds? Why does methane not undergo this type of reaction?
(c) What is IUPAC name of dimethyl ether. (2018)
Answer 8
(a) ![]() (i) (Ethene)
(i) (Ethene)
In the above structure, both carbons are bonded
with double bonds.
(ii) ![]() (Ethyne)
(Ethyne)
In the above structure, both carbons are bonded
with triple bonds.
(b) Addition reactions are common to both these compounds. Methane does not undergo this type of reaction because it is bounded with four hydrogen atoms, while in ethane, double bonds break and provide a site for addition.
(c) Methoxymethane
Question 9
Which type of reaction will (i) ethane and (II) ethane undergo?
Answer 9
(i) Ethane undergoes substitution reactions.
(ii) Ethene undergoes addition reactions.
Question 10
Choosing only words from the following list, write down appropriate words to fill in the blanks from (a) to (e) given below. Addition, carbohydrates, CnH2n-2, CnH2n,CnH2n+2, electrochemical homologous, hydrocarbon, saturated, substitution, unsaturated.
The alkanes form an (a) ………… series with the general formula (b) ………….. The alkanes are (c) …………. (d) …………… which generally undergo (e) …………. reactions.
Answer 10
The alkanes form an (a) electrochemical homologous series with the general formula (b) CnH2n+2. The alkanes are (c) saturated (d) hydrocarbons which generally undergo (e) substitution reactions.
Question 11
Draw the structural formula of a compound with two carbon atoms in each of the following cases.
(a) An alkane with a carbon to carbon single bond
(b) An alcohol containing two carbon atoms
(c) An unsaturated hydrocarbon with a carbon to carbon triple bond
Answer 11
a.
![]()
b.![]()
c.![]()
Question 12
Ethane, Ethene, Ethanoic acid, Ethyne, Ethanol From the above, name
(a) The compound with -OH as the part of its structure.
(b) The compound with -COOH as the part of its structure.
(c) Homologue of the homologous series with the general formula CnH2n.
Answer 12
(a) Ethanol
(b) Ethanoic acid
(c) Ethene
Question 13
Give the correct IUPAC name and the functional group for each of the compounds whose structural formulae are given below:
(a)

(b) 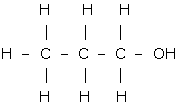
Answer 13
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanol
Question-14
Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologus series of hydrocarbons:
| General formula | CnH2n | CnH2n-2 | CnH2n+2 |
| IUPAC name of the homologus series | |||
| Characteristic bond type | Single bond | ||
| IUPAC name of the first member of the series | |||
| Type of reaction with chlorine | Addition |
Answer-14
The homologous series of hydrocarbons are:
| General formula | CnH2n | CnH2n-2 | CnH2n+2 |
| IUPAC name of the homologus series | Alkenes | Alkynes | Alkanes |
| Characteristic bond type | Double bond | Triple bond | Single bond |
| IUPAC name of the first member of the series | Ethene | Ethyne | Methane |
| Type of reaction with chlorine | Addition | Addition | Substitution |
Fill in the blanks with correct words from the brackets:
(a )Alkenes are the (i) _______ (analogous/homologous) series of (ii ) ______ (saturated /unsaturated) hydrocarbons. They differ from alkanes due to presence of (iii) _______ (double/ single) bonds. Alkenes mainly undergo (iv) ______ (addition/ substitution) reactions.
(b) Fill in the blank with the correct word
The organic compound which undergoes substitution reaction is (2018)
C2H2
C2H4
C10H18
C2H6
(c) Draw the structural formulae of the two isomers of Butane. Give the correct IUPAC name of each of the isomer.
Answer-15
(a )Alkenes are the (i) homologous series of (ii) unsaturated hydrocarbons. They differ from alkanes due to presence of (iii) single bonds. Alkenes mainly undergo (iv) addition reactions.
(b) The organic compound which undergoes substitution reaction is C2H6.
(c) structural formulae of the two isomers of Butane
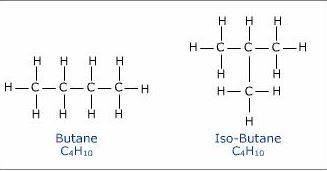
Selina Solution of Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Exercise-12 (B)
Page-202
Question 1
State the sources of alkanes.
Answer 1
Sources of alkane:
The principal sources of alkanes are Natural gas and petroleum.
Question 2
Methane is a green house gas. Comment.
Answer 2
Methane is a primary constituent of natural gas. It absorbs outgoing heat radiation from the earth, and thus contributes to the green house effect and so it is considered as a green house gas.
Question 3
Give the general formula of alkanes.
Answer 3
The general formula of alkane is :
CnH 2n+2
Question 4
Draw the structures of isomers of
(a) Butane (2018)(b) Pentane
Write the IUPAC and common names of these isomers
Answer 4
(a)The structures of isomers of butane are:
(i)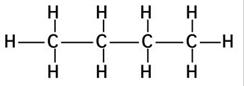
Common name:- n-Butane
IUPAC name:- Butane
(ii)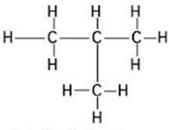
Common name:-iso butane
IUPAC name:- 2-methyl propane
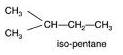
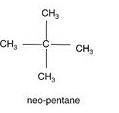
(b) The structures of isomers of Pentane are:
(i)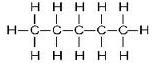
Common name: n-pentane
IUPAC name:- Pentane
(ii)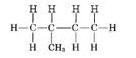
Common name:- iso pentane
IUPAC name:- 2-methyl butane
(iii)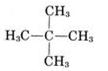
Common name- neo pentane
IUPAC name:- 2,2-dimethyl propane
Question 5
Write the
(a) Molecular formula
(b) Electron dot formula and
(c) Structural formula of methane and ethane
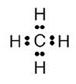
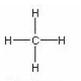
Answer 5
For methane:
(a) Molecular formula is CH4
(b) Electron dot formula
(c) Structural formula
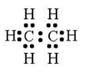
For ethane:
(a) Molecular formula is :- C2H6
(b) Electron dot formula:
(a) Structural Formula:
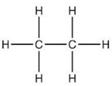
Question 6
How is
(a) Methane and
(b) Ethane prepared in the laboratory
Answer 6
(a) Laboratory preparation of methane:
When the mixture of sodium ethanoate and soda lime is taken in a hard glass test tube and heated, the gas evolved is methane. It is collected by downward displacement of water.
CH3COONa+NaOH ![]() Na2CO3+CH4
Na2CO3+CH4
(b) Laboratory preparation of ethane:
When the mixture of sodium propionate and soda lime is taken in the boiling tube and heated the ethane gas is evolved. It is also collected by downward displacement of water.
C2H5COONa+Na![]() OH Na2CO3+C2H6
OH Na2CO3+C2H6
Question 7
How are methane and ethane prepared from methyl iodide and ethyl bromide?
Answer 7
When methyl iodide is reduced by nascent hydrogen at ordinary room temperature then methane is formed.
CH3I+2[H] ![]() CH4+HI
CH4+HI
When bromoethane is reduced by nascent hydrogen at ordinary room temperature then ethane is produced.
C2H5Br+2[H] ![]() C2H6+HBr
C2H6+HBr
Question 8
What is substitution reaction? Give the reaction of chlorine with ethane and name the product formed?
Answer 8
A reaction in which one atom of a molecule is replaced by another atom (or group of atoms)is called a substitution reaction.
When ethane reacts with chlorine
C2H6 +Cl2 ![]() C2H5Cl + HCl
C2H5Cl + HCl
Chloroethane
C2H5Cl + Cl2 ![]() C2H4Cl2+HCl
C2H4Cl2+HCl
Dichloroethane
C2H4Cl2 +Cl2 ![]() C2H3Cl3+HCl
C2H3Cl3+HCl
Trichloroethane
C2H3Cl3 + Cl2 ![]() C2H2Cl4 + HCl
C2H2Cl4 + HCl
Tetrachloroethane
C2H2Cl4 +Cl2 ![]() C2HCl5 +HCl
C2HCl5 +HCl
Penta chloroethane
C2HCl5 +Cl2 ![]() C2Cl6 + HCl
C2Cl6 + HCl
Hexachloroethane
Question 9
Name the compounds formed when methane burns in
(a) Sufficient air(b) insufficient air
Give a balanced equation
Answer 9
(a) Sufficient air: When methane burns in sufficient air, then carbon dioxide and water vapors are formed.
CH4 + 2O2 ![]() CO2+2H2O
CO2+2H2O
(b) Insufficient air: When methane burns in insufficient air , then carbon monoxide and water is formed.
2CH4 + 3O2 ![]() 2CO + 4H2O
2CO + 4H2O
Question 10
Write the names and formula of the products formed when
(a) Methane and (b) ethane , reacts with :
(i) Chlorine (ii) bromine
Write the chemical equations.
Answer 10
(a)
(i) When methane reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight or UV light, it undergoes substitution reaction to form Tetrachloromethane.
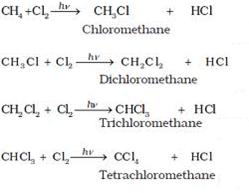
(ii) When it reacts with bromine it forms Tetra bromomethane
CH4 + Br2![]() CH3Br + HCl
CH3Br + HCl
CH3Br + Br2 ![]() CH2Br2 + HCl
CH2Br2 + HCl
Dibromo methane
CH2Br2 + Br2 ![]() CHBr3 + HCl
CHBr3 + HCl
Tribromo methane
CHBr3 + Br2 ![]() CBr4 + HCl
CBr4 + HCl
Tetra bromomethane
(b)
(i) When ethane reacts with chlorine it forms hexa choroethane.
C2H6 +Cl![]() 2 C2H5Cl + HCl
2 C2H5Cl + HCl
Chloroethane
C2H5Cl + Cl2 ![]() C2H4Cl2+HCl
C2H4Cl2+HCl
Dichloroethane
C2H4Cl2 +Cl2 ![]() C2H3Cl3+HCl
C2H3Cl3+HCl
Trichloroethane
C2H3Cl3 + Cl2 ![]() C2H2Cl4 + HCl
C2H2Cl4 + HCl
Tetrachloroethane
C2H2Cl4 +Cl2 ![]() C2HCl5 +HCl
C2HCl5 +HCl
Penta chloroethane
C2HCl5 +Cl2 ![]() C2Cl6 + HCl
C2Cl6 + HCl
Hexachloroethane
(ii) When ethane reacts with bromine it forms Hexa bromoethane
C2H6 +Br2 ![]() C2H5Br + HBr
C2H5Br + HBr
Bromoethane
C2H5Br + Br2 ![]() C2H4Br2+HBr
C2H4Br2+HBr
Dibromoethane
C2H4Br2 +Br2 ![]() C2H3Br3+HBr
C2H3Br3+HBr
Tri bromoethane
C2H3Br3 + Br2 ![]() C2H2Br4 + HBr
C2H2Br4 + HBr
Tetra bromoethane
C2H2Br4 +Br2 ![]() C2HBr5 +HBr
C2HBr5 +HBr
Penta bromoethane
C2HBr5 +Br2![]() C2Br6 + HBr
C2Br6 + HBr
Hexa Bromoethane
Question 11
Name the compound prepared from
(a) Sodium propionate
(b) Methyl iodide
(c) Ethyl bromide
Write the balanced equation for the same
Answer 11
(a) Ethane is prepared from sodium propionate.
C2H5COONa+NaOH ![]() Na2CO3+C2H6
Na2CO3+C2H6
(b) Methane is prepared from methyl iodide.
CH3I+2[H] ![]() CH4+HI
CH4+HI
(c) Ethane is prepared from ethyl bromide.
C2H5Br+2[H] ![]() C2H6+HBr
C2H6+HBr
Question 12
Write the equation for the complete combustion of
(i) methane (ii) ethane.
Answer 12
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
Question 13
Convert
(a) Methane into chloroform
(b) Sodium acetate into methane
(c) Methyl iodide into ethane
(d) methane to methyl alcohol
Answer 13
(a) Methane into chloroform
CH4+Cl2 CH3Cl+HCl
CH3Cl+Cl2 CH2Cl2+HCl
CH2Cl2+Cl2 CHCl3+HCl
(b) Sodium acetate into methane
CH3COONa+NaOHNa2CO3+CH4
(c) Methyl iodide into ethane
2CH3I +2NaCH3-CH3+2NaI
(d) Methane to methyl alcohol
CH4 -→CH3(OH)
Question 14
Give three uses of:
(a) Methane
(b) ethane
Answer 14
(a) Methane: Three uses of methane are:
(i) Methane is a source of carbon monoxide and hydrogen
(ii) It is used in the preparation of ethyne, methanal, chloromethane, carbon tetrachloride.
(iii) It is employed as a domestic fuel.
(b) Ethane:
Three uses of ethane are:
(i) It is used in the preparation of ethene, ethanol, and ethanol.
(ii) It forms ethyl chloride, which is used to make tetraethyllead.
(iii) It is also a good fuel.
Question 15
Under what conditions does ethane get converted to:
(a) Ethyl alcohol
(b) Acetaldehyde
(c) Acetic acid
Answer 15
(a) When a mixture of ethane and oxygen is compressed to about 120atm pressure and passed over copper tubes at 475K, ethyl alcohol is formed.
2C2H6 +O2![]() 2C2H5OH
2C2H5OH
(b) When mixture of ethane and oxygen is passed through heated molybdenum oxide, the mixture is oxidized to Acetaldehyde.
C2H6 +O2 ![]() CH3CHO+H2O
CH3CHO+H2O
(c) Ethanol formed from ethane gets oxidized to acetic acid.
2C2H6 +O2 2![]() C2H5OH
C2H5OH
C2H5OH + O2 ![]() CH3COOH+H2O
CH3COOH+H2O
Question 16
Using appropriate catalysts, ethane can be oxidized to an alcohol, an aldehyde and an acid. Name the alcohol, aldehyde and acid formed when ethane is oxidized.
Answer 16
Ethane can be oxidized as follows:
When a mixture of ethane and oxygen in the ratio 9:1 by volume is compressed to about 120 atm pressure and passed over copper tubes at 475K, ethyl alcohol is formed.
2C2H6 + O2 ![]() 2C2H5OH
2C2H5OH
When a mixture of ethane and oxygen is passed through heated MoO, the mixture is oxidized to ethanal.
C2H6+ O2 ![]() CH3CHO + H2O
CH3CHO + H2O
When a manganese based catalyst is used 100oC, ethane can be oxidized to ethanoic acid.
2C2H6 + 3O2 ![]() 2CH3COOH + 2H2O
2CH3COOH + 2H2O
Chapter-12 Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Exercise-12 (C)
Page-206
Question 1
Write : (a) molecular formula , (b) electron dot formula and (c) structural formula of ethene .(Ethylene)
Answer 1
(a) The molecular formula of ethene is C2H4
(b) Electron dot formula of ethene is:
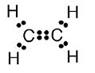
(c) Structural formula of ethene:
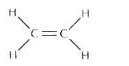
Question 2
The molecules of alkene family are represented by a general formula CnH2n.Answer The following :
(a) What do n and 2n signify?
(b) What is the name of alkene when n=4?
(c) What is the molecular formula of alkene when n=4?
(d) What is the molecular formula of the alkene if there are ten H atoms in it?
(e) What is the structural formula of the third member of the alkene family?
(f) Write the molecular formula of lower and higher homologus of an alkene which contains four carbon atoms.
Answer 2
(a) n signifies the number of carbon atoms and 2n signifies the number of hydrogen atoms.
(b) The name of alkene when n=4 is Butene.
(c) The molecular formula of alkene when n=4 is C4H8.
(d) The molecular formula of alkene when there are 10 H atom in it C5H10.
(e) The structural formula of the third member of alkene is
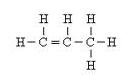
(f) Lower homologus of alkene which contain four carbons is C3H6.
Higher homologus of alkene which contain four carbons is C5H10.
Question 3
(a) Distinguish between the saturated hydrocarbon ethane and the unsaturated hydrocarbon ethene by drawing their structural formulae.
(b) Draw the structure of isomers of butane and write their IUPAC names.
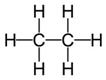
Answer 3
| Ethane | Ethene |
 |
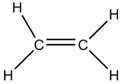 |
| It has carbon -carbon single bond. | It has carbon-carbon double bond |
| It is saturated. | It is unsaturated |
| Alkanes undergo substitution reaction. | Alkenes undergo addition reaction. |
(b) There are two isomers are possible for butane:
Question 4
Give a balanced equation for the lab Preparation of ethylene. How is the gas collected?
Answer 4
Balanced Equation of ethylene:
CH3-CH2OH + H2SO4 ![]() CH3-CH2HSO4+H2O
CH3-CH2HSO4+H2O
CH3-CH2HSO4![]() CH2=CH2
CH2=CH2
The gas is collected by downward displacement of water.
Question 5
How is ethene prepared by:
(a) De hydro halogenation reaction?
(b) Dehydration reaction?
Give equations and name the products formed.
Answer 5
(a) Dehydrohalogenation reaction:
C2H5Cl + KOH(alc.and hot) ![]() C2H4 + KCl + H2O
C2H4 + KCl + H2O
Ethene
(b) Dehydration reaction:
C2H5OH ![]() C2H4+H2O
C2H4+H2O
Ethene
Question 6
(a) Ethylene when reacts with halogens (chlorine and bromine) form saturated products. Name them and write balanced equations.
(b) Give the conditions and the main product formed by hydrogenation of ethylene.
Answer 6
(a) Chlorine and bromine are added to the double bond of ethene to form saturated ethylene chloride and ethylene bromide respectively.
CH2 = CH2 + Cl2 ![]() CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
1,2-dichloro ethane
CH2 = CH2 + Br2![]() CH2(Br)-CH2(Br)
CH2(Br)-CH2(Br)
1,2-dibromo ethane
(b) When ethene and hydrogen are passed over finely divided catalyst such as platinum or palladium at ordinary temperature or nickel at 200o C, the two atom of hydrogen molecule are added to the unsaturated molecule, which thus becomes a saturated one.
C2H4 +H2 ![]() C2H6
C2H6
Question 7
Convert ethanol into ethene using
(a) Solid dehydrating agent
(b) Hot conc. H2SO4
Give only balanced equations.
Answer 7
Conversion of ethanol to ethene by using
(a) Solid dehydrating agent:
![]()
(b) Hot conc. H2SO4:
![]()
Question 8
Write the following properties of ethene:
(a) Physical state
(b) Odour
(c) Density as compared to air
(d) Solubility
Answer 8
(a) Physical state: Ethene is a colourless and inflammable gas.
(b) Odour: It has faint sweetish odour.
(c) Density as compared to air: It has density less than one hence it is lighter than air.
(d) Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether and chloroform.
Question 9
How would you convert:
(a) ethyl bromide into ethene
(b) Ethene into 1,2-dibromoethane
(b) Ethene into ethane
Answer 9
(a)
Ethene into ethyl bromide: When ethene is treated with HBr bromoethane is formed.
CH2=CH2 + HBr → CH3-CH2Br
Ethyl bromide
(b) Ethene into 1, 2 -dibromoethane: Ethene reacts with bromine at room temperature to form saturated ethylene chloride.
CH2=CH2 + Br2 ![]() CH2(Br)-CH2(Br)
CH2(Br)-CH2(Br)
1,2-dibromo ethane
(c)
C2H4 + H2 ![]() C2H6
C2H6
Question 10
Give balanced equation when:
(a) Ethene is burnt in excess of oxygen
(b) Ethene reacts with chlorine (2019)
(c) Ethene combines with Hydrogen chloride
(d) A mixture of ethene and hydrogen is passed over nickel at 2000C.
Answer 10
(a) C2H4+3O2![]() 2CO2 +2H2O + heat
2CO2 +2H2O + heat
(b) CH2=CH2+Cl2 ![]() CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
(c) CH2=CH2 + HCl ![]() CH3-CH2-Cl
CH3-CH2-Cl
(d) C2H4 +H2 ![]() C2H6
C2H6
Question 11
Give the formula and names of A, B ,C and D in the following equations:
(a) CH4 ![]() A
A ![]() B
B ![]() C
C ![]() D
D
(b) C2H2 ![]() A
A ![]() B
B ![]() C
C ![]() D
D
(c) C2H4 +B ![]() C2H6
C2H6
Answer 11
(a) CH4 ![]() CH3Cl
CH3Cl ![]() CH2C
CH2C![]() l2 CHCl3
l2 CHCl3 ![]() CCl4
CCl4
A= mono chloromethane
B= di chloromethane
C=Tri chloromethane
D=Tetra chloromethane
(b) C2H2 ![]() C2H4
C2H4![]() C2H6
C2H6 ![]() C2H5Br
C2H5Br ![]() C2H4Br
C2H4Br
A= Ethene
B=ethane
C=bromoethane
D=dibromoethane
(c) C2H4 +H2![]() C2H6
C2H6
B= hydrogen
Question 12
Write the name and formula of the product formed in each case below:
(a) C2H4 +Cl2 ![]() ______
______
(b) C2H5Br +KOH (alc.) ![]() ______
______
(c) CH2=CH2 ![]() _______
_______
(d) CH2=CH2+HBr ![]() _______
_______
Answer 12
(a) C2H4 +Cl2 ![]() CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
1,2- dichloro ethane
(b) C2H5Br +KOH (alc.) ![]() C2H4 +KBr +H2O
C2H4 +KBr +H2O
Ethane
(c) CH2=CH2 ![]() CH2(OH)-CH2(OH)
CH2(OH)-CH2(OH)
1,2- Ethandiol
(d) CH2=CH2+HBr ![]() CH3-CH2Cl
CH3-CH2Cl
chloroethane
Question 13
What do you observe when ethylene is passed through alkaline KMnO4 solution?
Answer 13
When ethylene is passed through alkaline KMnO4 solution 1, 2-Ethanediol is formed. The Purple color of KMnO4 decolorizes.
CH2=CH2+H-O-H +[O] ![]() CH2(OH)-CH2(OH)
CH2(OH)-CH2(OH)
Cold alkaline
KMnO4 solution
Question 14
Name three compounds formed by ethylene and give the use of these compounds.
Answer 14
Three compounds formed by ethylene are:
Polythene
Ethanol
Epoxyethane
Uses of above compounds:
Polythene is used as carry bags.
Ethanol is used as a starting material for other products, mainly cosmetics and toiletry preparation.
Epoxyethane is used in the manufacture of detergents.
Organic Chemistry Exercise 12- (D) Selina Concise Solution
Page-210
Question 1
What are the sources for alkynes? Give the general formula of alkynes.
Answer 1
Natural gas and Petroleum are sources for alkynes.
The general formula of alkynes are:
CnH2n-2
Question 2
Give an example of isomers shown by triple bond hydrocarbon (alkynes) and write its IUPAC name.
Answer 2
Butyne is an example, its isomers are:
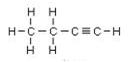
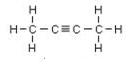
IUPAC name: But-2-yne But-1-yne
Question 3
How is ethyne prepared in the laboratory?
(a) Draw diagram
(b) Give equation
(c) How is pure dry gas collected?
Answer 3
(a) Diagram of acetylene preparation:
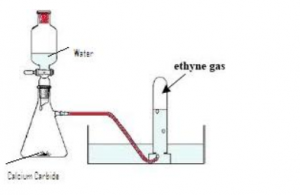
(b) CaC2 +2H2O ![]() Ca(OH)2 +C2H2
Ca(OH)2 +C2H2
(c) The pure dry gas is collected by downward displacement of water, since it is insoluble in water.
Question 4
Give the method of preparation of ethyne by 1,2-dibromoethene.
Answer 4
When 1,2 -dibromoethane is boiled with alcoholic potassium hydroxide ,ethyne is formed.
Question 5
Name the hydrocarbon which:
(a) Is a tetrahedral molecule
(b) Is a planar molecule
(c) Is a linear molecule
(d) Forms a red precipitate with ammoniacal solution of copper (I) chloride
(e) Is known as paraffin
(f) Is known as olefin
(g) A compound which will give acetylene (ethene) gas when treated with water.
Answer 5
(a) The hydrocarbon which is tetrahedral is Methane.
(b) The hydrocarbon which is planar molecule is ethene.
(c) The hydrocarbon which is a linear molecule is Ethyne.
(d) The hydrocarbon which forms a red precipitate with ammoniacal solution of copper chloride is acetylene.
(e) Alkanes are also called as paraffin.
(f) Alkenes are also called olefin.
(g) Calcium carbide
Question 6
Classify the following compounds as alkanes, alkenes and alkynes.
C3H4,C3H8, C5H8, C3H6
Answer 6
The following compounds can be classified as:
C3H4:- Alkynes
C3H8:- Alkanes
C5H8:- Alkynes
C3H6:- Alkenes
Question 7
Give a chemical test to distinguish between
(a) Saturated and unsaturated compounds.
(b) Ethane and ethene
(c) Ethene (ethylene) and ethyne (acetylene)
Answer 7
Chemical test to distinguish :
(b) Ethane and ethene:
| S.No. | Test | Ethane | Ethene |
| 1. | On adding a few drops of bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride to the hydrocarbon | No change is observed | The reddish brown colour gets decolorized |
| 2. | On adding a few drops of alkaline potassium permanganate (purple colour) to the hydrocarbon | No change is observed | The purple colour fades. |
(c) Ethene and ethyne:
| S.No. | Test | Ethene | Ethyne |
| 1. | On adding a few drops of ammonical cuprous chloride to the hydrocarbon | No change is observed | Red precipitate of copper acetylide is formed |
| 2. | On adding ammonical silver nitrate | No observation | White precipitate of silver acetylide is formed. |
Question 8
Compound X bubbled through bromine dissolved in CCl4

(a) Draw the structure of X.
(b) State your observation during the reaction.
Answer 8
(a) HC≡CH
(b) Brown colour of CCl4 disappeared due to formation of addition product, i.e. 1, 2-dibromo ethane.
Question 9
Give balanced equations for the following conversations.
(a) An alkene to an alkane
(b) An alkene to an alcohol
(c) An alkyne to a alkene
Answer 9
(a) An alkene to an alkane
![]()
(b) An alkene to an alcohol
![]()
(c) An alkyne to an alkene
![]()
Question 10
Name the products formed and write an equation when ethyne is added to the following in an inert solvent:
(a) Chlorine
(b) Bromine
(c) Iodine
(d) hydrogen
(e) excess of hydrochloric acid
Answer 10
(a) Ethyne in an inert solvent of carbon tetrachloride adds chlorine to change into 1,2-dichloro ethene with carbon-carbon double bond, and then to an 1,1,2,2-tetrachloro ethane with carbon-carbon single bond.
C2H2 ![]() C2H2 Cl2
C2H2 Cl2 ![]() C2H2Cl4
C2H2Cl4
1,2-dichloro ethene1,1,2,2 -tetrachloro ethane
(b) Ethyne in an inert solvent of carbon tetrachloride adds bromine to change into 1,2-dibromo ethene and then to 1,1,2,2 -tetrabromo ethane .
C2H2 ![]() C2H2 Br2
C2H2 Br2 ![]() C2H2Br4
C2H2Br4
(c) Iodine reacts slowly in the presence of alcohol to form di-iodo ethene
CH ![]() CH +I2
CH +I2 ![]() ICH=CHI
ICH=CHI
1,2-di-iodoethene
(d) In the presence of nickel, platinum or palladium ethyne change to ethene and then to ethane.
CH ![]() CH
CH ![]() CH2=CH2
CH2=CH2 ![]() CH3-CH3
CH3-CH3
(e) 
Question-11
Substitution reactions are characteristic reactions of ………( alkynes /alkenes/ alkanes )
Answer-11
Substitution reactions are characteristic reactions of Alkanes.
Question-12
(a) Write an equation for the laboratory preparation of
(i) An unsaturated hydrocarbon from calcium carbide.
(ii) Alcohol from ethyl bromide.
(b) What would you see, when ethyne is bubbled through a solution of bromine in carbon tetrachloride?
(c) Name the addition product formed between ethene and water
Answer-12
(a)
(i) and (ii)
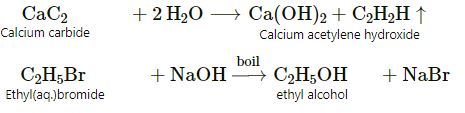
(b) When bromine in carbon tetrachloride is added to ethyne, the orange colour of the bromine disappears due to the formation of the colourless ethylene bromide.
(c) Water reacts with ethene to form ethanol.
![]()
Question-13
Give reason
(a ) ethyne is more reactive than ethene ?
(b) Ethene is more reactive then ethane.
(c) Hydrocarbons are excellent fuels.
Answer-13
(a ) Ethyne is a highly reactive compound than ethene because of the presence of a triple bond between its two carbon atoms.
(b) Ethene is a highly reactive compound than ethane because of the presence of a double bond between its two carbon atoms.
(c) Hydrocarbons such as alkanes undergo combustion reactions with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water vapour. Alkanes are flammable which makes them excellent fuels.
Methane, for example, is the principal component of natural gas.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Question-14
(a)
Write a balanced equation:
(i) When butane is burnt in oxygen.
(ii) Preparation of ethylene from ethyl alcohol.
(i) Convert ethane to acetic acid
(ii) Convert ethyne to ethane
Answer-14
(a)
(i) 2C4H10 + 13O2 → 8CO2 + 10H2O
(ii) 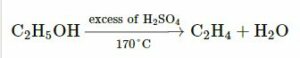
(b)
(i) Convert ethane to acetic acid
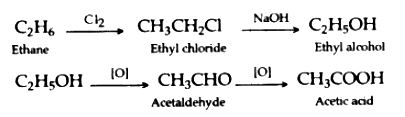
(ii) Convert ethyne to ethane
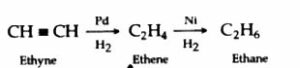
Question-15
(a ) Write the equation for the preparation of carbon tetrachloride from methane.
(b) Draw the structure formula of ethyne
(c) How is the structure of alkynes different from that of alkenes?
Answer-15
(a )
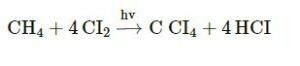
(b) H – C ≡ C – H
(c) Alkynes contain a triple bond whereas alkenes contain a double bond.
Solution of Concise Selina Publication Organic Chemistry Exercise 12-(E)
Page-214
Question 1
(a) What are alcohols? State their sources.
(b) Give general formulae of monohydric alcohol.
Answer 1
(a) Alcohols are the hydroxyl derivatives of alkanes and are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of the alkane with OH group.
Methanol is obtained from destructive distillation of wood while ethanol is obtained from fermentation of sugar.
(b) General formula of monohydric alcohol:
CnH2n+ 1OH
Question 2
Give the
(a) Dot diagram of first member of alcohol,
(b) Abbreviated formula of third member of alcohol
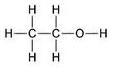
(c) Structure of second member of the alcohol group
(d) Structure of alcohol with 4 carbon atoms
Answer 2
(a) Dot diagram

(b) Abbreviated formula
C2H5OH
(c) Structure:
Question 3
State the method of preparation of ethanol:
(a) By hydrolysis of ethene
(b) By hydrolysis of ethyl bromide
Answer 3
(a) By hydrolysis of ethene: When concentrated sulphuric acid is added to ethene at a temperature of 80oC and pressure of 30 atm. ethyl hydrogen sulphate is produced. Ethyl hydrogen sulphate on hydrolysis with boiling water gives ethanol.
C2H4 +H2SO4 ![]() C2H5HSO4
C2H5HSO4
C2H5HSO4 + H2O ![]() C2H5OH +H2SO4
C2H5OH +H2SO4
(b) By hydrolysis of alkyl halide: Alcohols can be prepared by the hydrolysis of alkyl halide with a hot dilute alkali.
C2H5Cl + KOH ![]() C2H5OH +KCl
C2H5OH +KCl
Question 4
Halo alkanes react with alkalies to produce alcohol. Give the equation for the preparation of the second member of the homologous series of alcohol. State under what condition the reaction occurs.
Answer 4
When an aqueous solution of a strong alkali like NaOH is treated with chloroethane, it gives ethyl alcohol.
![]()
Question 5
(a)How do the boiling point and melting point change in the homologous series of alcohols?
(b) Name the product formed when ethanol reacts with acetic acid. Give an equation
(c) What is the name given to this type of reaction?
Answer 5
(a)The melting and boiling point of the successive members of the homologous series of alcohols increase with the increase in molecular mass.
(b)When ethanol reacts with acetic acid ethyl acetate is formed.
C2H5OH + CH3COOH ![]() CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
(c) This reaction is known as esterification reaction.
Question 6
Complete and balance the following equations. State the conditions wherever necessary.
(a) CH![]() CH + H2
CH + H2 ![]() _________+ H2
_________+ H2 ![]() ________
________
(b) C2H4 + Cl2 ![]() __________
__________
(c) C2H4 + HCl ![]() _________
_________
(d) CaC2 + H2O ![]() _________
_________
(e) C2H2 + Br2 ![]() __________
__________
(f) C2H5OH ![]() ________
________
Answer 6
(a) CH ![]() CH +H2
CH +H2 ![]() CH2=CH2 +H2
CH2=CH2 +H2 ![]() CH3-CH3
CH3-CH3
(b) C2H4 + Cl2 ![]() CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
CH2(Cl)-CH2(Cl)
(c) C2H4 + HCl ![]() CH3-CH2Cl
CH3-CH2Cl
(d) CaC2 + 2H2O![]() C2H2+Ca(OH)2
C2H2+Ca(OH)2
(e) C2H2 + Br2 ![]() H(Br)C=C(Br)H
H(Br)C=C(Br)H
(f) C2H5OH ![]() CH3CHO
CH3CHO
Question 7
What is the effect of ethanol on human body?
Answer 7
Ethanol affects that part of the brain which controls our muscular movements and then gives temporary relief from tiredness. But it damages the liver and kidney too.
Question 8
How are the following obtained
(a) Absolute alcohol
(b) Spurious alcohol
(c) Methylated spirit?
Answer 8
(a) Absolute alcohol: Absolute alcohol may be obtained by distilling moist alcohol with benzene. The mixture of water and benzene distills off and anhydrous alcohol is left behind.
(b) Spurious alcohol: It is made by improper distillation. It contains large portions of methanol in a mixture of alcohols.
(c) Methylated spirit: Methylated spirit or denatured alcohol is ethyl alcohol with 5%methyl alcohol, a coloured dye and some pyridine.
Question 9
Name the products formed and give appropriate chemical equations for the following:
(a) Sodium reacting with ethyl alcohol
(b) Ethanol oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate
Answer 9
(a) Sodium reacting with ethyl alcohol:
2C2H5OH + 2Na ![]() 2C2H5ONa + H2
2C2H5ONa + H2
When sodium reacts with ethyl alcohol hydrogen is evolved with formation of sodium ethoxide.
(b) Ethanol oxidized by K2Cr2O7:
C2H5OH ![]() CH3CHO+H2O
CH3CHO+H2O ![]() CH3COOH
CH3COOH
Alcohols gets oxidized and get converted into ethanal and then into acetic acid.
Question 10
Give the trivial (common) names and IUPAC names of the following:
(a) C3H6
(b) C2H4
(c) C2H2
(d) CH3OH
(e) C2H5OH
Answer 10
| S No | Formula | Common Name | IUPAC |
| 1 | C3H6 | Propylene | Propene |
| 2 | C2H4 | Ethylene | Ethene |
| 3 | C2H2 | Acetylene | Ethyne |
| 4 | CH3OH | Methyl alcohol | Methanol |
| 5 | C2H5OH | Ethyl alcohol | Ethanol |
Question 11
Ethanol can be oxidized to Ethanoic acid. Write the equation and name the oxidizing agent.
Answer 11
C2H5OH![]() CH3CHO+H2O
CH3CHO+H2O ![]() CH3COOH
CH3COOH
The oxidizing agents that can be used are potassium dichromate and potassium permanganate.
Question 12
Name an Organic compound which is:
(a) Used for illuminating country houses
(b) Used for making a household plastic material
(c) Called ‘wood spirit’
(d) Poisonous and contain OH group
(e) Consumed as a drink
(f) Made from water gas
(g) solvent for ethanol.
(h) Dehydrated to produce ethene
Answer 12
(a) Used for illuminating country houses : Ethyne
(b) Used for making a household plastic material: ethyne
(c) Called ‘wood spirit’ : Methanol
(d) Poisonous: Methanol
(e) Consumed as a drink: Ethanol
(f) Made from water gas: Methanol
(g) Methanol
(h) Ethanol or ethyl alcohol can be dehydrated to produce ethene
Question-13
Ethanol can be converted into ethene which can be changed into ethane. Choose the correct
word or phrase from the brackets to complete the following sentences.
(a) The conversion of ethanol into ethene is an example of ___________
(b) Converting ethanol into ethene requires the use of ___________
(c) The conversion of ethene into ethane is an example of ___________
(d) The catalyst used in the conversion of ethene into ethane is commonly ___________
Answer-13
(a) The conversion of ethanol into ethene is an example of Dehydration.
(b) Converting ethanol into ethene requires the use of Conc. H2SO4.
(c) The conversion of ethene into ethane is an example of hydrogenation.
(d) The catalyst used in the conversion of ethene into ethane is commonly nickel.
Question-14
Write the equation of the following laboratory preparations
(a) Ethane from sodium propionate
(b) Ethene from iodoethane
(d) Methanol from Iodomethane.
Answer-14
(a) Ethane from sodium propionate
![]()
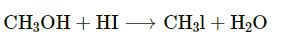
(b) Ethene from iodoethane
![]()
CaC2 +2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
(d) Methanol from Iodomethane.
CH3 I+ H2O → CH3 OH + HI
Question-16
Write the equation for the following reaction:
(a) Calcium carbide and water
(b) Ethene and water (steam)
(a) Calcium carbide and water
CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
(b) Ethene and water (steam)
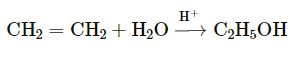
Exercise 12 – (F) Organic Chemistry Solution of Concise Chemistry Selina Publication
Page-217
Question 1
What are carboxylic acids? Give their general formula?
Answer 1
An organic compound containing the carboxyl group(COOH) is known as carboxylic acid.
The general formula: CnH2n+1COOH
Question 2
Write the names of:
(a)Give the structural formulae of acetic acid
(a) First three members of carboxylic acid series IUPAC name of acetic acid
(b) Three compounds which can be oxidized directly, or in stages to produce acetic acid
Answer 2
(a) First three members of carboxylic acids are:
Methanoic acid
Ethanoic acid
Propanoic acid
(b) Three compounds that can be oxidized directly or in stages to produce acetic acid are:
Ethanol
Acetylene
Ethanal
Question 3
(a)Give the structural formula (2019)
(b) IUPAC name of acetic acid.
(c)What is glacial acetic acid?
Answer 3
(a)Structural formula of acetic acid:
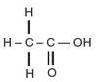
(b)IUPAC name of acetic acid is: Ethanoic acid
(c) Glacial acetic acid is the pure form of acetic acid. It does not contain water.
Question 4
Vinegar is greyish in colour with particular taste. Explain.
Answer 4
Vinegar commonly called Sirka is a dilute solution of acetic acid. The presence of colouring matter gives it a greyish colour while the presence of some other organic acids and organic compounds impart it the usual taste and flavour.
Question 5
Complete:
(a) Vinegar is prepared by the bacterial oxidation of ______.
(b) The organic acid present in vinegar is __________.
(c) The next higher homologue of Ethanoic acid is ______.
Answer 5
(a) Ethanol
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Propanoic acid
Question 6
How is acetic acid prepared from
(a) ethanol
(b) acetylene?
Answer 6
(a)It is prepared in the lab by the oxidation of ethanol with acidified potassium dichromate.
C2H5OH ![]() CH3CHO
CH3CHO ![]() CH3COOH
CH3COOH
(b)Acetylene is first converted to acetaldehyde by passing through 40% H2SO4 at 60°C in the presence of 1% HgSO4.
The acetaldehyde is then oxidised to acetic acid in the presence of catalyst manganous acetate at 70°C.
C2H2 + H2O  CH3CHO
CH3CHO
CH3CHO + O2  2CH3COOH
2CH3COOH
Question 7
What do you notice when acetic acid reacts with
(a) Litmus
(b) Metals
(c) Alkalies
(d) alcohol
Answer 7
(a) When acetic acid reacts with litmus it turns blue litmus red.
(b) When acetic acid reacts with metals hydrogen is evolved.
2CH3COOH + Zn ![]() (CH3COO)2Zn + H2
(CH3COO)2Zn + H2
(c) When acetic acid reacts with alkalies it forms salt
CH3COOH + NaOH ![]() CH3COONa + H2O
CH3COONa + H2O
(d) Acetic acid reacts with alcohols forming esters
CH3COOH + C2H5OH ![]() CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
Question 8
Acetic acid is a typical acid. Write the equation in each case for its reaction with
(a) Metal
(b) A base/alkali
(c) A carbonate
(d) A bicarbonate
Answer 8
(a) 2CH3COOH + Zn ![]() (CH3COO)2Zn + H2
(CH3COO)2Zn + H2
(b) CH3COOH + NaOH ![]() CH3COONa + H2O
CH3COONa + H2O
(c) 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 ![]() 2CH3COONa +H2O+ CO2
2CH3COONa +H2O+ CO2
(d) CH3COOH + NaHCO3 ![]() CH3COONa + H2O +CO2
CH3COONa + H2O +CO2
Question 9
What do you observe when acetic acid is added to:
(a) Sodium bicarbonate
(b) Ethyl alcohol in the presence of sulphuric acid
(c) Neutral FeCl3 solution
Answer 9
(a) When acetic acid is added to sodium bicarbonate, carbondioxide is liberated.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3![]() CH3COONa + H2O +CO2
CH3COONa + H2O +CO2
(b) When acetic acid is added to ethyl alcohol in presence of sulphuric acid ester (ethyl acetate) is formed.
CH3COOH + C2H5OH CH![]() 3COOC2H5 + H2O
3COOC2H5 + H2O
(c) When acetic acid is added to neutral FeCl3, wine red color is produced.
Question 10
Name :
(a) Compound formed when acetic acid and ethanol react together
(b) Reducing agent used to convert acetic acid into ethanol
(c) Substance used to change acetic acid to acetic anhydride
Answer 10
(a) When acetic acid and ethanol react it results in the formation of ethyl acetate.
(b) Lithum aluminium hydride(LiAlH4) is used to convert acetic acid to ethanol.
(c) Phosphorous pentoxide(P2O5) is heated along with acetic acid to form acetic anhydride.
Exercise- Miscellaneous, Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Chapter-12 Selina Solution
Page-217
Question 1
(a)Which of the following statements is wrong about alkanes?
(i) They are all saturated hydrocarbons.
(ii)They can undergo addition as well as substitution reactions.
(iii) They are almost non-polar in nature.
(iv) On complete combustion, they give out carbon dioxide and water.
(b) The organic compound obtained as the end product of the fermentation of sugar solution is
(i) Methanol
(ii)Ethanol
(iii) Ethane
(iv) Methanoic acid
(c) Find the odd one out and explain :
(i) C3H8
(ii) C5H10
(iii) C2H6
(iv) CH4
Answer 1
(a)
option (ii) is wrong that They can undergo addition as well as substitution reactions.
(b)
The organic compound obtained as the end product of the fermentation of sugar solution is(ii) Ethanol .
(c)
option (ii)C5H10 is an alkene, while the rest are alkanes.
Question 2
Give the chemical equation for :
(i) The laboratory preparation of methane from sodium acetate.
Answer 2
(i) The laboratory preparation of methane from sodium acetate.
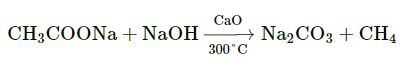
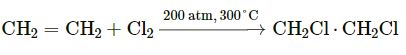
Question 3
State how the following conversion can be carried out:
(a) Ethyl chloride to ethyl alcohol
(b) Ethyl chloride to ethene
(c) Ethene to ethyl alcohol
(d) Ethyl alcohol to ethene
Answer 3
(a) Ethyl chloride to ethyl alcohol
By treating ethyl chloride with aqueous KOH
(b) Ethyl chloride to ethene
By heating ethyl chloride with alcoholic KOH
(c) Ethene to ethyl alcohol
By passing ethene into conc. H2SO4 at 80°C and high pressure
(d) Ethyl alcohol to ethene
By heating ethyl alcohol with conc. H2SO4 at 170°C
Question 4
(a) Define isomerism.
(b) Give the IUPAC name of the isomer C4H10 which has a branched-chain.
Answer-4
(a) Isomerism: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are known as isomers, and the phenomenon is known as isomerism.
(b) The IUPAC name of the branched isomer of butane is 2-methyl propane
Question 5
A compound X when treated with an organic acid Y (having vinegar like smell) in the presence of the acid Z, forms a compound P which has fruity smell.
(a) Identify X, Y and Z
(b) Write structural formula of X and Y.
(c) What type of compound P is?
(d)Name the above reaction.
(e) If compound X and Y both have 2 carbon atoms. Write the reaction.
Answer 5
(a) X = Ethanol, C2H5OH
Y = Acetic acid, CH3COOH
Z = Conc. H2SO4
(b)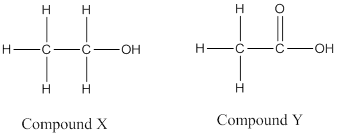
(c) Compound P is an ester named ethyl acetate.
(d) Esterification
(e)![]()
Previous Years Question of Chapter 12 ,Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10
( Page-217)
Question 2010
(a) An organic compound undergoes addition reactions and gives a red precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride. Therefore, the organic compound could be
(i) Ethane (ii) Ethene, (iii). Ethyne, (iv) Ethanol
(b) An organic weak acid is
(i) Formic acid ,(ii) Sulphuric acid,(iii). Nitric acid,(iv) Hydrochloric acid
(c) The organic compound mixed with ethanol to make it spurious is
(i) Methanol,(ii) Methanoic acid,(iii). Methanal,(iv) Ethanoic acid
(d) Draw the structural formula for each of the following:
(i) Ethanoic acid,(ii) But-2-yne,
(e) Compound A is bubbled through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride and the product is CH2Br – CH2Br.
(i) Draw the structural formula of A.
(ii) What type of reaction has A undergone?
(iii) What is your observation?
(iv) Name (not formula) the compound formed when steam reacts with A in the presence of phosphoric acid.
(v) What is the procedure for converting the product of (e) (iv) back to A?
Answer 2010
(i) iii.Ethyne
(b) i. Formic acid
(c) i. Methanol
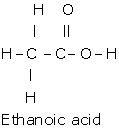
(d) i. 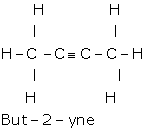
(e)
(i) ![]()
(ii) Addition reaction
(iii) Bromine solution gets decolourised
(iv) Ethanol
(v) By heating it (ethanol) with concentrated sulphuric acid at 170°C
Page-218
Question 2011
(a) The functional group present in acetic acid is
(i) Ketonic – =C=O,(ii) Hydroxyl – OH,(iii). Aldehydic – CHO, (iv) Carboxyl – COOH
(b) The unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo
(i) a substitution reaction,(ii) an oxidation reaction,(iii). an addition reaction,(iv) none of the above
(c) The number of C-H bonds in ethane molecule is
(i) Four,(ii) Six,(iii) Eight,(iv) Ten
(d) Choose the correct word/phrase from within the brackets to complete the following sentences:
(i) The catalyst used for conversion of ethene to ethane is commonly (nickel /iron/cobalt)
(ii) When acetaldehyde is oxidised with acidified potassium dichromate, it forms (ester/ethanol/ acetic acid)
(iii). Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 so as to form a compound and water. The chemical reaction which takes place is called (dehydration/hydrogenation/ esterification)
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction taking place between 1, 2-dibromoethane and alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
(v) The product formed when ethene gas reacts with water in the presence of sulphuric acid ………… (ethanol/ethanal/ethanoic acid)
(e) Write balanced chemical equations for the following:
(i) Monochloroethane is hydrolysed with aqueous KOH.
(ii) A mixture of sodalime and sodium acetate is heated.
(iii). Ethanol under high pressure and low temperature is treated with acidified potassium dichromate.
(iv) Water is added to calcium carbide.
(v) Ethanol reacts with sodium at room temperature.
Answer 2011
(a) iv. Carboxyl – COOH
(b) iii. An addition reaction
(c) iiiSix
(d) (i) Nickel
(ii) Acetic acid
(iii). Esterification
(iv) ![]()
(v) Ethanol
(e)
(i) ![]()
(ii) ![]()
(iii)![]()
(iv) CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
(v) 2C2H5OH+ 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question 2012
(a) Give the structural formula for the following:
(i) Methanoic acid,(ii) Ethanol,(iii). Ethyne,(iv) Acetone
(v) 2-methyl propane
(b) From the following organic compounds given below, choose one compound in each case which relates to the description [i] to [iv]:
[Ethyne, ethanol, acetic acid, ethene, methane]
(i) An unsaturated hydrocarbon used for welding purposes.
(ii) An organic compound whose functional group is carboxyl.
(iii)A hydrocarbon which on catalytic hydrogenation gives a saturated hydrocarbon.
(iv) An organic compound used as a thermometric liquid.
(c)
(i) Why is pure acetic acid known as glacial acetic acid?
(ii) Give a chemical equation for the reaction between ethyl alcohol and acetic acid.
Answer 2012
(a)
i.
![]()
ii.
![]()
iii.
![]()
iv
.![]()
v
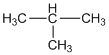
(b)
(i) Ethyne
(ii) Acetic acid
(iii). Ethene
(iv) Ethanol
(c)
(i). Pure acetic acid is called glacial acid because it forms an ice-like solid when cooled.
(ii) ![]()
Question 2013
(a)
(i) Give a chemical test to distinguish ethene gas and ethane gas.
(ii) Identify the statement that is incorrect about alkanes:
(A). They are hydrocarbons.
(B) There is a single covalent bond between carbon and hydrogen.
(C) They can undergo both substitution as well as addition reactions.
(D) On complete combustion, they produce carbon dioxide and water.
(b) Give the structural formulae for the following:
(i) An isomer of n-butane
(ii) 2-propanol
Answer 2013
(a)
(i) Ethene gas de colourises the purple colour of KMnO4, whereas ethane does not decolourise KMnO4 solution.
(ii) They can undergo both substitution as well as addition reactions.
(b)
(i) Isomer of n-butane: Isobutane
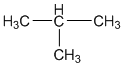
(ii) 2-propanol
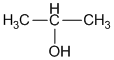
Page-219
Question 2014
(a) The IUPAC name of acetylene is
(i) propane,(ii) propyne,(iii) ethane,(iv) ethyne
(b) Name the hydrocarbons containing the  functional group.
functional group.
(c) Give preparation of ethane from sodium propionate.
(d) Distinguish ethane andethene (using alkaline potassium permanganate solution).
(e) Give the structural formula of the following:
(i) ethanol
(ii) 1-propanal
(iii) ethanoic acid
(iv) 1, 2, di chloroethane
(f) Give preparation of ethanol from mono chloroethane and aq. sodium hydroxide.
Answer 2014
(a)
(iv)ethyne
(b) Ketones
(c) ![]()
(d) Ethenegas decolourises the purple colour of KMnO4, whereas ethane does not decolourise KMnO4 solution.
(e) (i)Ethanol:
![]()
(ii) 1-propanal:
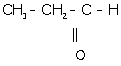
(iii). Ethanoic acid:
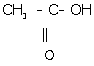
(iv) 1, 2-dichloroethane:
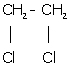
(f)
The balanced chemical equation for the preparation
of ethanol from mono chloroethane and aqueous
sodium hydroxide:
C2H5-Cl + NaOH (aq.) ![]() C2H5OH + NaCl
C2H5OH + NaCl
Question 2015
(a) Give balanced chemical equations for the following conversions:
(i) Ethanoic acid to ethyl ethanoate
(ii) Calcium carbide to ethylene
(iii) Sodium ethanoate to methane
(b) Using their structural formula, identify the functional group by circling them:
(i) Dimethyl ether
(ii) Propanone
(c) Name the following:
(i) Process by which ethane is obtained from ethane
(ii) A hydrocarbon which contributes towards the greenhouse effect
(iii) Distinctive reaction that takes place when ethanol is treated with acetic acid
(iv) The property of elements by virtue of which atoms of the element can link to each other in the form of a long chain or ring structure
(v) Reaction when an alkyl halide is treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide
Answer 2015
(a)
(i) Ethanoic acid to ethyl ethanoate
CH3COOH + C2H5OH ![]() CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
(ii) Calcium carbide to ethylene
CaC2 + 2 H2O → Ca(OH)2 + CH º CH
(iii) Sodium ethanoate to methane
CH3COONa + NaOH ![]() Na2CO3 + CH4
Na2CO3 + CH4
(b)
(i) Dimethyl ether
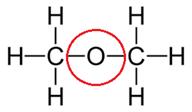
(ii) Propanone
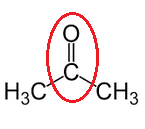
(c) Name the following:
(i) Hydrogenation
(ii) Methane
(iii) Esterification
(iv) Catenation
(v) Dehydrohalogenation
–: End of Organic Chemistry ICSE Class-10 Selina Concise Solutions :–
Return to: – Concise Selina Solutions for ICSE Chemistry Class-10
Thanks
Please Share with Your Friends


Q4. Fill in the blanks:
f. CO is an -inorganic- compound.
Please make the required changes
Which Exercise ?
In ex-12A
Q.4. Fill in the balnks:
f. CO is an –inorganic– compound.
Please make the required changes.