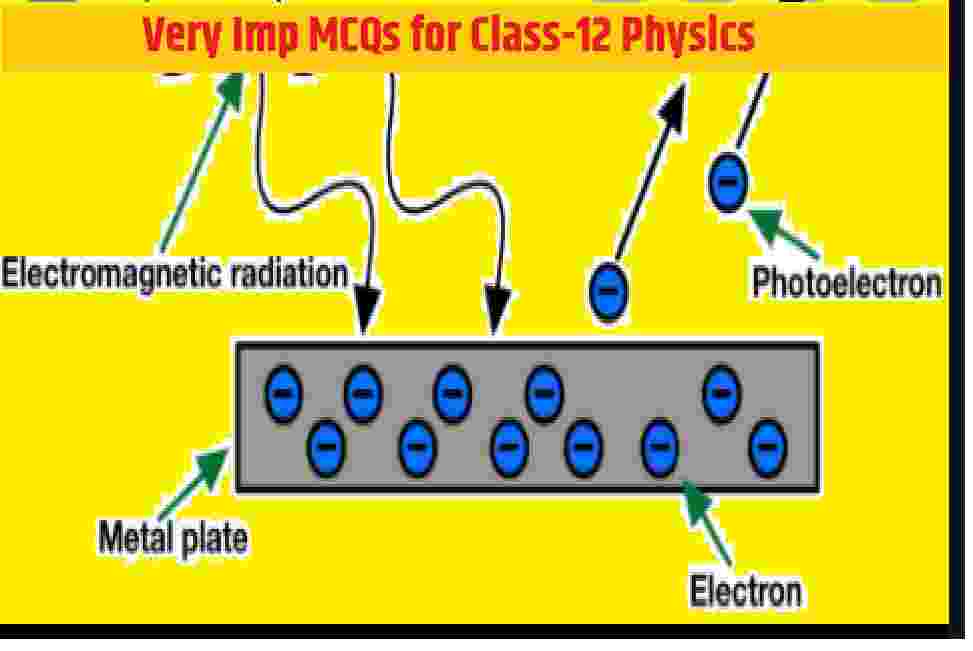
Photoelectric Effect MCQs Type Question for ISC Class 12 Physics . These MCQs / Objective Type Questions is based on latest reduced syllabus according 2021-22 session on bifurcated pattern. Main motto of MCQ Type Question is cracking the next upcoming Sem-2 exam of council. Visit official website CISCE for detail information about ISC Class-12 Physics.
ISC Class 12 Physics Photoelectric Effect MCQs Type Question
| Board | ISC |
| Class | 12th (XII) |
| Subject | Physics |
| Chapter | Photoelectric Effect |
| Syllabus | on bifurcated syllabus (after reduction) |
| Session | 2021-22 |
| Bifurcated | Sem-2 |
| Topic | MCQs / Objective Type Question |
Important MCQs Photoelectric Effect for ISC Class 12
Question 1. Choose the correct option among the following, regarding work function ϕ of material in a photoelectric effect
(a) Is different for different materials
(b) Is same for all metals
(c) Depends upon frequency of the incident light
(d) Depends upon intensity of the incident light
Answer: (a) Is different for different materials
Question 2. Which photon is more energetic: A red one or a violet one?
(a) Both
(b) Red
(c) Violet
(d) Neither
Answer: (c) Violet
Question 3. Maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted In photoelectric effect increases when :
(a) intensity of light is increased
(b) light source is brought nearer the metal
(c) frequency of light is decreased
(d) wavelength of light is decreased
Answer: (d) wavelength of light is decreased
Question 4. Why are alkali metals most suited as photo-sensitive metals?
(a) High frequency
(b) Zero rest mass
(c) High work function
(d) Low work function
Answer: (d) Low work function
Question 5. The Kinetic energy of a photoelectron emitted on shining a light of wavelength 6.2 X 10-6 m on a metal surface of work function 0.1 eV is _____
(a) 0.01 eV
(b) 0.02 eV
(c) 0.1 eV
(d) 1 eV
Answer: (c) 0.1 eV
Question 6. During Einstein’s Photoelectric Experiment, what changes are observed when the frequency of the incident radiation is increased?
(a) The value of saturation current increases
(b) No effect
(c) The value of stopping potential increases
(d) The value of stopping potential decreases
Answer: (c) The value of stopping potential increases
Question 7. Photoelectric emission is possible at all frequencies.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (b) False
Question 8. The work function of lithium is 2.5 eV. The maximum wavelength of light that can cause the photoelectric effect in lithium is _____
(a) 3980 Å
(b) 4980 Å
(c) 5980 Å
(d) 6980 Å
Answer: (b) 4980 Å
Question 9. What is the frequency of a photon whose energy is 66.3 eV?
(a) 196 × 1016 Hz
(b) 1336 × 1016 Hz
(c) 1.6 × 1016 Hz
(d) 16 × 1016 Hz
Answer: (c) 1.6 × 1016 Hz
Question 10. Light of wavelength 4000 Å is incident on a sodium surface for which the threshold wavelength of photo-electrons is 5420 Å. The work function of sodium is
(a) 5 eV
(b) 3 eV
(c) 2.29 eV
(d) 0.57 eV
Answer: (c) 2.29 eV
Question 11. Calculate the energy of a photon of wavelength 6600 angstroms.
(a) 30 × 10-19 J
(b) 3 × 10-19 J
(c) 300 × 10-19 J
(d) 3000 × 10-19 J
Answer: (b) 3 × 10-19 J
Question 12. Which radiations will be most effective for the emission of electrons from a metallic surface?
(a) Microwaves
(b) X rays
(c) Ultraviolet
(d) Infrared
Answer: (c) Ultraviolet
Question 13. In a photoelectric experiment for 4000 Å incident radiation, the potential difference to stop the ejection is 2 V. If the incident light is changed to 3000 Å, then the potential required to stop the ejection of electrons will be
(a) 2 V
(b) Less than 2 V
(c) Zero
(d) Greater than 2 V
Answer: (d) Greater than 2 V
Question 14. What is the relation between the interaction parameter, ‘b’, and atomic radius, R, for the Photoelectric effect?
(a) b > R
(b) b ≈ R
(c) b < R
(d) no relation between b and R
Answer: (a) b > R
Question 15. Two metals A and B have work functions 4 eV and 10 eV respectively. Which metal has a higher threshold wavelength?
(a) Metal A
(b) Metal B
(c) Both
(d) Neither
Answer: (a) Metal A
Question 16. How does the intensity affect the photoelectric current?
(a) As intensity increases, the photoelectric effect increases
(b) As the intensity increases, the photoelectric effect decreases
(c) As the intensity decreases, the photoelectric effect becomes twice
(d) No effect
Answer: (a) As intensity increases, the photoelectric effect increases
Question 17. If the work function for a certain metal is 3.2 x 10-19 joule and it is illuminated with light of frequency 8 x 1014 Hz. The maximum kinetic energy of the photo-electrons would be (h= 6.63 x 10-34 Js).
(a) 2.1 x 10-19 J
(b) 8.5 x 10-19 J
(c) 5.3 x 10-19 J
(d) 3.2 x 10-19 J
Answer: (a) 2.1 x 10-19 J
Question 18. The photoelectric emission could be explained by the ___
(a) Wave nature of light
(b) Particle nature of light
(c) Dual nature of light
(d) Quantum nature
Answer: (b) Particle nature of light
Question 19. Give the unit of work function.
(a) Electron volt
(b) Joule
(c) Hertz
(d) Watt
Answer: (a) Electron volt
Question 20. Light of wavelength 3500 Å is incident on two metals A and B. Which metal will yield more photoelectrons if their work functions are 5 eV and 2 eV respectively?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) A & B
(d) C
Answer: (b) B
Question 21. The stopping potential value is 0.6 V when the light source is kept at a distance of 20 cm. When the source is kept at 40 cm away, the stopping potential will be
(a) 0.6 V
(b) 0.3 V
(c) 1.2 V
(d) 2.4 V
Answer: (a) 0.6 V
Question 22. If the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is doubled, what will happen to the energy of photons?
(a) Remains the same
(b) Doubled
(c) Halved
(d) Infinite
Answer: (c) Halved
Question 23. Which of the following metals will exhibit a photoelectric effect most easily?
(a) Sodium
(b) Lithium
(c) Magnesium
(d) Caesium
Answer: (d) Caesium
Question 24. What is the effect of intensity on the stopping potential?
(a) As intensity increases, stopping potential increases linearly
(b) As intensity increases, stopping potential decreases linearly
(c) As intensity decreases, stopping potential increases exponentially
(d) No effect
Answer: (d) No effect
Question 25. On which part of the photoelectric cell does the radiation strikes?
(a) Cathode
(b) Anode
(c) Ammeter
(d) Radiation does not strike on the photoelectric cell
Answer: (a) Cathode
Question 26. Photoelectrons stopping potential depends on
(a) Frequency of incident light and nature of the cathode material
(b) The intensity of the incident light
(c) The frequency of the incident light
(d) Nature of cathode material
Answer: (a) Frequency of incident light and nature of the cathode material
Question 27. Which device works on the principle of photoelectric effect ?
(a) Photo emission cell
(b) Photo junction diode
(c) Photo voltaic cell
(d) All are correct
Answer: (d) All are correct
Question 28. A photocell is receiving light from a source placed at a distance of 1m. If the same source is to be placed at a distance of 2 m, then the ejected electron
(a) Moves in one-fourth energy as that of the initial energy
(b) Moves with one-fourth momentum as that of the initial momentum
(c) Will be half in number
(d) Will be one-fourth in number
Answer: (d) Will be one-fourth in number
Question 29. The most suitable metal for photoelectric emission have ________ work function.
(a) low
(b) high
(c) medium
(d) all are correct
Answer: (a) low
Question 30. How many laws of Photoelectric emission ?
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 1
Answer: (b) 2
Question 31. What happens to the wavelength of a photon after it collides with an electron?
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same
(d) Infinite
Answer: (a) Increases
Question 32. Photoelectric effect was explained by
(a) Einstein
(b) Faraday
(c) Plank
(d) Hertz
Answer: (a) Einstein
Question 33. Which of the following gases are filled inside the Photoelectric cells?
(a) Carbon Dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Neon
(d) Oxygen
Answer: (c) Neon
Question 34. Photocell is a device to
(a) Store photons
(b) Measure light intensity
(c) Convert photon energy into mechanical energy
(d) Store electrical energy for replacing storage batteries
Answer: (b) Measure light intensity
Question 35. What is the time lag between the incidence of photons and the ejection of photoelectrons?
(a) Greater than 10-5 s
(b) Between 10-5 s and 10-9 s
(c) Less than 10-9 s
(d) 1 second
Answer: (c) Less than 10-9 s
Question 36. What is the value of the maximum kinetic energy acquired by electron due to radiation of wavelength 100 nm?
(a) 12 eV
(b) 6.2 eV
(c) 100 eV
(d) 300 eV
Answer: (b) 6.2 eV
Question 37. The minimum energy required to remove an electron is called
(a) Stopping potential
(b) Work function
(c) Kinetic energy
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Work function
Question 38. The maximum ________ energy of emitted electrons is linear to the frequency of light flux.
(a) potential
(b) kinetic
(c) elastic
(d) radiant
Answer: (b) kinetic
Question 39. For a photosensitive surface, the work function is 3.3 × 10-19 J. Find threshold frequency. (Take h = 6.6 × 10-34 Js)
(a) 5 × 1014 Hz
(b) 0.5 × 1014 Hz
(c) 25 × 1014 Hz
(d) 2.5 × 1014 Hz
Answer: (a) 5 × 1014 Hz
Question 40. The number of photo electrons emitted for light of a frequency v (higher than the threshold frequency v0) is proportional to:
(a) Threshold frequency (v0)
(b) Intensity of light
(c) Frequency of light (v)
(d) v – v0
Answer: (b) Intensity of light
–: End of Photoelectric Effect MCQs :–
-: also visit :-
- ISC Sem-2 Question Bank Class-12
- Sem-2 ISC Specimen Paper for Class-12
- ISC Class-12 Textbook Solutions ,Syllabus, Solved Paper
- Previous Year Question Paper for ISC Class-12
Please share with your ISC friends if it is helpful
Thanks